AI stands for artificial intelligence and it is the technology behind systems that learn from experience, adapt to new information and perform tasks that require human intelligence such as recognizing speech, making decisions or understanding language without explicit instructions for each task. AI systems such as digital assistants and chatbots like Alexa, Siri, ChatGPT or Gemini handle conversations and provide answers on websites without human involvement.
AI’s history began in the 1950s, with foundational work from figures like Alan Turing and the Dartmouth Conference in 1956. AI has evolved since then with advancements like machine learning and robotics.
AI is powered by technologies such as machine learning, deep learning and natural language processing. These technologies allow AI systems to analyze large datasets, select appropriate algorithms, train models and test them for accuracy. AI continuously learns from data and improves over time. AI is classified by its capabilities and functions such as narrow AI, general AI, artificial superintelligence (ASI), reactive machine and theory of mind.
AI is used in industries like healthcare, finance, transportation and retail by solving problems, automating tasks and improving overall processes. Its ability to improve decision-making and personalize services leads to increased productivity, faster decision-making, and more accurate outcomes. AI also has challenges such as ethical concerns, job displacement and privacy risks that have been addressed for responsible use and development.
What is AI?
AI (artificial intelligence) refers to computer systems or machines designed to perform tasks that require human intelligence. Artificial intelligence focuses on functions such as reasoning, problem-solving, language processing and perception. These systems rely on computational power and advanced AI technology to analyze data, recognize patterns, make decisions and learn from experience to improve over time.
Artificial intelligence performs repetitive tasks, understands and responds to human language and operates independently in complex environments. Its capabilities such as identifying objects, generating creative content and providing solutions across industries like healthcare, business and transportation, make artificial intelligence a powerful tool for innovation.
What are the examples of AI?
The examples of artificial intelligence are given below.
- Digital assistants: Digital assistants manage schedules, answer questions and control smart home devices like Alexa and smart speakers using voice commands and natural language processing.
- Chatbots: Chatbots provide instant customer support by understanding and responding to user queries on websites and mobile apps.
- Social media: Social media analyzes user activity to personalize timelines, suggest new friends and highlight trending topics relevant to individual preferences such as browsing history, liked posts and followed accounts.
- Facial recognition: Facial recognition identifies individuals by analyzing facial features like eyes and jawline to unlock devices and improve security systems.
- Fraud detection: Facial detection monitors transactions, analyzes patterns and flag suspicious activities such as unusual transactions and unauthorized access to prevent financial losses in banking.
- Autonomous vehicles: Autonomous vehicles use sensors and AI to navigate roads, avoid obstacles and transport passengers without human drivers.
- Medical imaging: Medical imaging assists doctors by detecting tumors, fractures, and abnormalities in X-rays and MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) scans with high accuracy.
What is the history of AI?
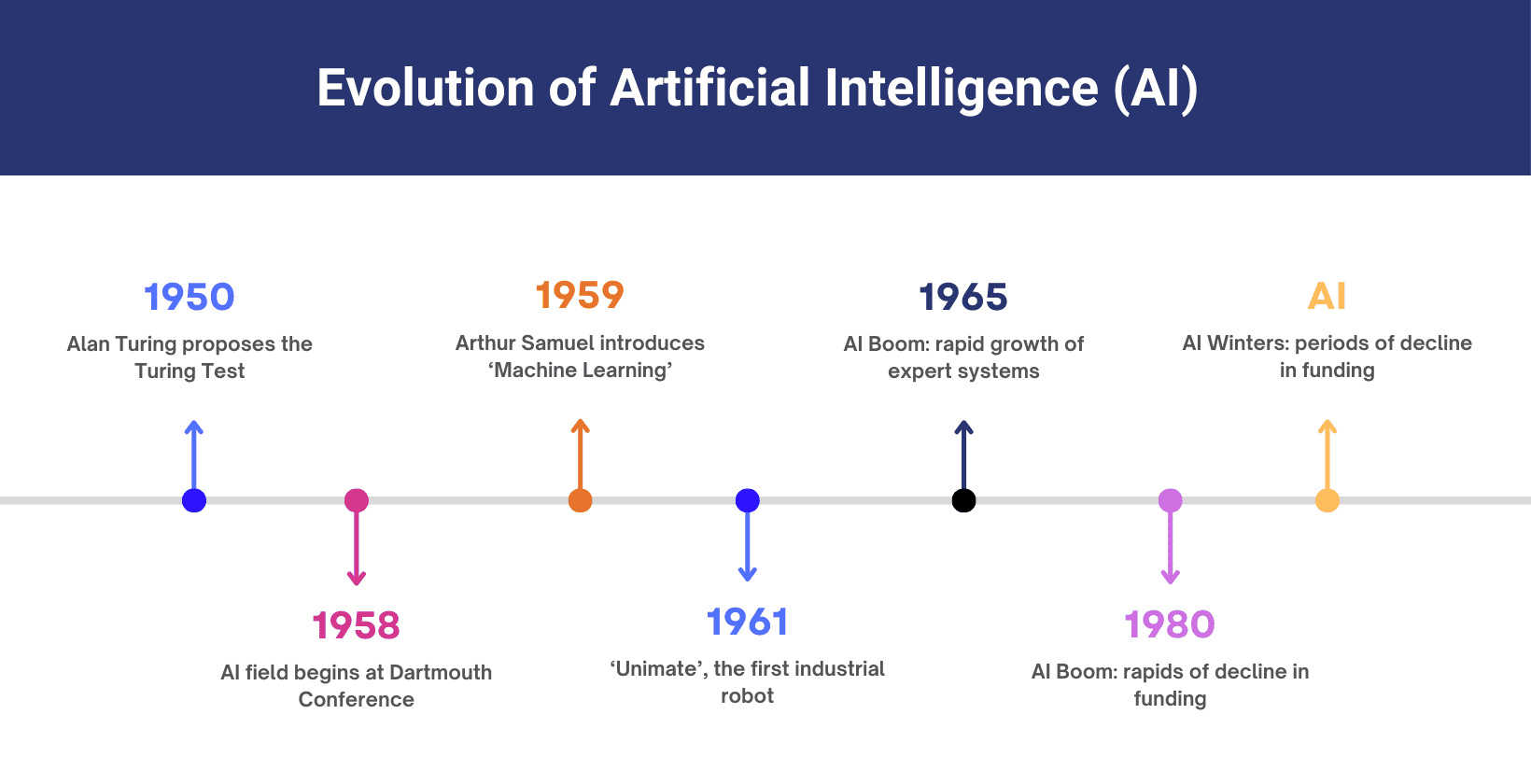
The history of artificial intelligence began in the mid-20th century with foundational ideas from mathematicians and logicians. In 1950, Alan Turing proposed the Turing Test to measure machine intelligence. The field formally began in 1956 at the Dartmouth Conference, organized by John McCarthy, Marvin Minsky, Nathan Rochester and Claude Shannon. McCarthy named the term "artificial intelligence" and developed the Lisp programming language in 1958, which became important for AI research. Researchers aimed to create machines that perform tasks requiring human intelligence such as reasoning, learning and problem-solving.
Artificial intelligence models human cognitive functions using methods such as machine learning, expert systems, natural language processing and neural networks. Arthur Samuel introduced the term "machine learning" in 1959. Unimate, the first industrial robot, was introduced in 1961. The first expert system appeared in 1965. The field has gone through cycles of rapid progress and decline such as the AI booms of the 1980s and the periods of reduced funding and interest known as AI winters. These milestones highlight how artificial intelligence has advanced over time and influenced various fields such as robotics, gaming and data analysis.
The evolution of artificial intelligence is visualised below.
What are the key technologies behind AI?
The key technologies behind AI are foundational components that allow machines to process information, learn from data and perform complex tasks. Artificial intelligence technology relies on a combination of software, hardware and algorithms to give intelligent solutions across industries like healthcare, finance and marketing.
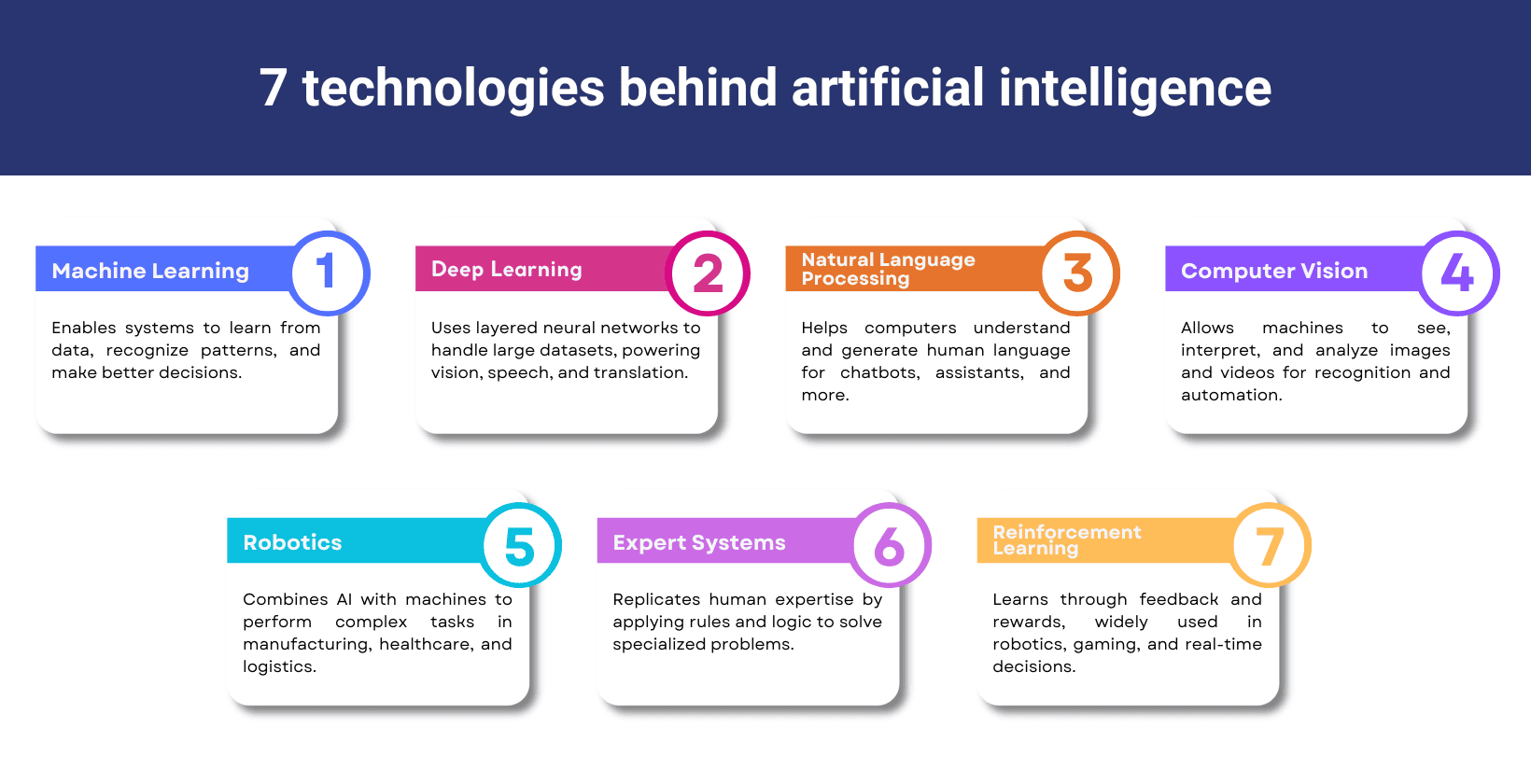
7 key technologies behind artificial intelligence are outlined below.
- Machine learning (ML): Machine learning (ML) is an artificial intelligence technology that helps systems to learn from data, recognize patterns and make decisions without direct programming for each specific task.
- Deep learning (DL): Deep learning uses layered neural networks to process large data sets and powers applications like image recognition, language translation and autonomous vehicles.
- Natural language processing (NLP): NLP allows computers to understand and generate human language. It supports chatbots, voice assistants and language-based user interfaces.
- Computer vision: Computer vision helps machines to interpret and analyze visual information. It is important for facial recognition, medical imaging and automated inspection systems such as AI software, machine vision and data analytics tools.
- Robotics: Robotics combines artificial intelligence technology with mechanical systems to perform tasks autonomously. AI technologies in robotics improve automation in manufacturing, healthcare and logistics.
- Expert systems: Expert systems use AI technologies to replicate human expertise in specialized fields and these systems apply rules and logic to solve complex problems in areas like climate change, global financial crises and education.
- Reinforcement learning: Reinforcement learning is an artificial intelligence technology where systems learn by receiving feedback from their actions. This approach is used in robotics, gaming and real-time decision-making.
The core technologies that power artificial intelligence are visualised below.
Why is artificial intelligence important?
Artificial intelligence is important because it solves problems, automates tasks, makes better decisions and improves the way things work in many areas of life. Artificial intelligence learns from data, adapts to new information and provides insights that help organizations and individuals operate more efficiently.
Artificial intelligence processes large volumes of information quickly, works without tiredness and reduces the risk of human error. This difference allows artificial intelligence to handle repetitive tasks, analyze complex patterns and provide consistent results.
Artificial intelligence impacts industries like healthcare, finance, manufacturing, retail and education. It allows accurate diagnoses, automates finances, boosts production, personalizes shopping and improves learning.
How does AI work?
Artificial intelligence works by using algorithms to analyze data, identify data patterns, and learn through machine learning. This process allows artificial intelligence development to improve performance and make better decisions over time.
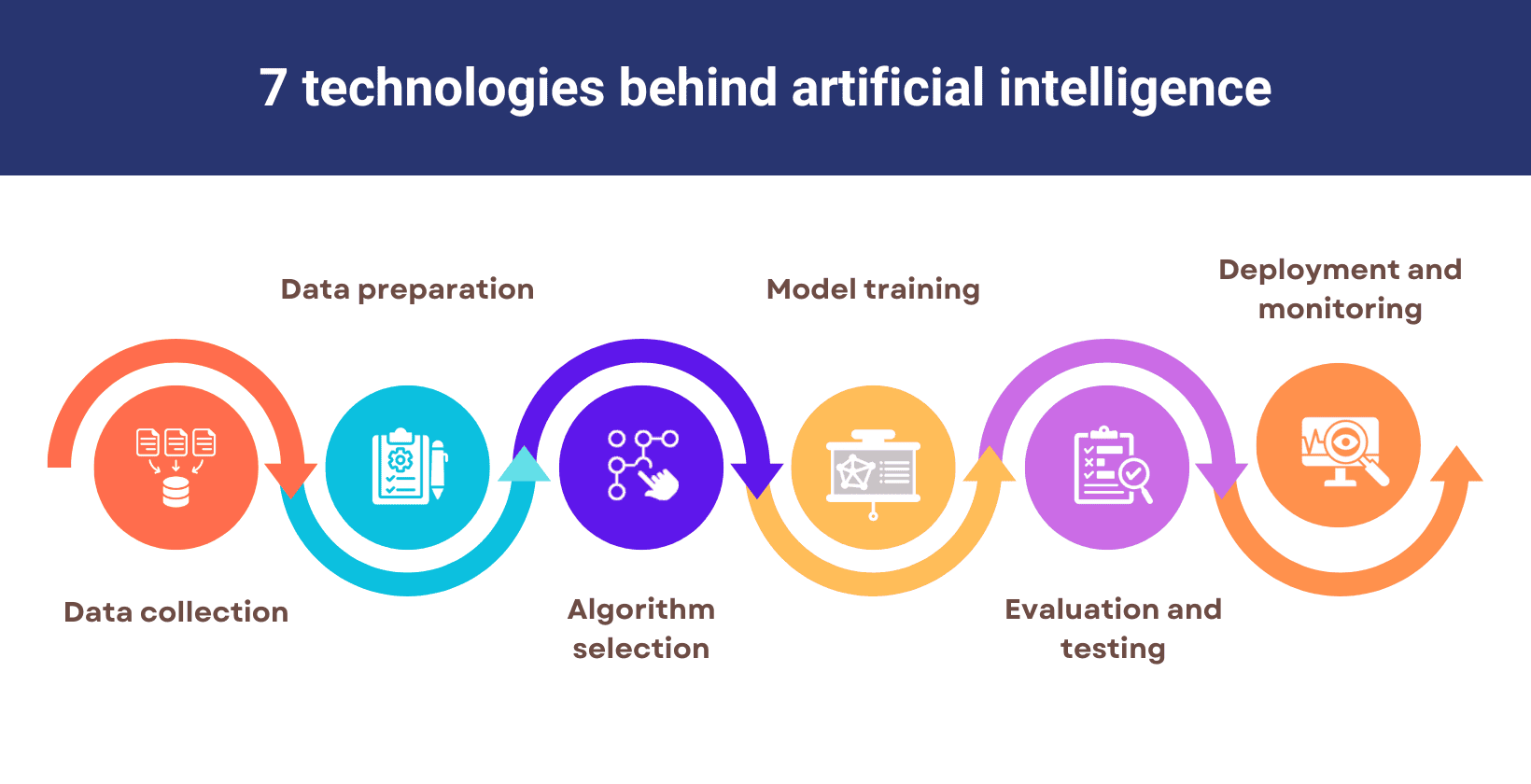
The process of how AI works is given below.
- Data collection: Artificial intelligence development begins with gathering large datasets, which allows the system to recognize patterns that support learning and decision-making like customer behavior and market trends.
- Data preparation: Data preparation involves cleaning and organizing raw data. This step makes the data accurate and ready for machine learning and allows algorithms to work effectively.
- Algorithm selection: Algorithm selection is important in artificial intelligence for achieving high accuracy and efficient data processing. Developers select algorithms based on the problem type, data quality and computational resources that influence how AI systems detect patterns, learn from examples and adapt to new information.
- Model training: Machine learning allows AI to learn from data to process input data, identify data patterns and adjust its parameters to improve accuracy and performance.
- Evaluation and testing: Evaluation and testing measure how well the AI model performs on new data. This step allows artificial intelligence development to achieve reliable and accurate outcomes such as correct prediction and error-free decisions.
- Deployment and monitoring: AI systems are deployed and monitored in real-world settings after training. Monitoring helps the system learn from new data and maintain strong performance.
The process of how artificial intelligence works is shown below.
What are the types of artificial intelligence?
The types of artificial intelligence are categorized by capabilities and functionalities. Capability-based AI types include narrow AI, general AI and artificial superintelligence, which span from specialized systems to hypothetical superintelligent entities. Reactive machines, limited memory, theory of mind, and self-aware AI are categorized by functionalities that describe how AI processes information and interacts with its environment.
3 types of artificial intelligence categorized by capabilities are given below.
- Narrow AI (weak AI): Narrow AI, also known as artificial narrow intelligence, is the most common type of AI currently in use. It performs a single task within a specific domain such as digital voice assistants or image recognition tools.
- General AI (strong AI): General AI, also known as artificial general intelligence (AGI), matches human cognitive abilities and helps it learn, reason and solve problems across any area like a human.
- Artificial superintelligence (ASI): Artificial superintelligence exceeds human intelligence in every field like creativity and emotional understanding. This type of AI remains theoretical and does not exist yet.
4 types of artificial intelligence categorized by functionalities are given below.
- Reactive machines: Reactive machines respond only to current inputs without memory or learning. They include basic game-playing programs and simple spam filters.
- Limited memory: Limited memory systems use historical data to improve decisions and accuracy. Most modern AI systems like self-driving cars and chatbots, operate in this category
- Theory of mind: Theory of mind AI aims to interpret human emotions, beliefs and intentions for more natural interactions but this type is still experimental due to its complexity.
- Self-aware AI: Self-aware AI possesses consciousness and self-understanding that recognizes its own existence and emotions. This type of AI remains hypothetical and unrealized.
What are the uses of artificial intelligence?
The uses of artificial intelligence are transforming industries by improving efficiency, accuracy and personalization in healthcare, finance, transportation and retail. AI applications automate processes, improve decision-making and provide customized services for businesses and individuals like Amazon, Apple and students.
5 applications of artificial intelligence are listed below.
- Healthcare: Artificial intelligence supports medical imaging, diagnostic processes and personalized treatment plans to help doctors provide faster and more accurate care**.**
- Finance: Artificial intelligence helps detect fraud, automate trading and provide personalized financial advice to make financial transactions safer and more efficient for users and institutions.
- Transportation: Artificial intelligence powers self-driving vehicles, optimizes traffic management and improves logistics, which leads to safer roads and more reliable delivery of goods and services.
- Retail and e-commerce: Artificial intelligence gives personalized recommendations, automates inventory management and allows real-time customer support to improve shopping experiences for consumers and retailers.
- Smart home and daily life: Artificial intelligence manages voice assistants like Alexa, Google Assistant, and Siri, as well as smart security systems and energy usage to improve home safety and energy efficiency in daily life.
These uses of AI show how technology is providing practical, impactful solutions across both industries and daily routines.
What are the benefits of artificial intelligence?
The benefits of artificial intelligence are seen in improved efficiency, smarter decision-making, reduced error, and increased productivity across many fields. AI helps organizations and individuals achieve better outcomes and adapt to change.
The benefits of AI are given below.
- Improved efficiency: Artificial intelligence automates repetitive tasks, streamlines workflows and manages large datasets that allow organizations to achieve more in less time.
- Improved decision-making: Artificial intelligence analyzes complex data, identifies patterns and delivers actionable insights that support faster and more informed decisions like predicting customer purchasing behavior or optimizing inventory management.
- Improved accuracy: Artificial intelligence reduces human error in data processing, diagnostics and operations that leads to higher accuracy and more reliable results across various applications such as financial forecasting or weather prediction.
- Increased productivity: Artificial intelligence handles routine work, optimizes resource use and allows teams to focus on creative and strategic projects like drawing, animation creating and marketing strategy planning.
- Strengthened security: Artificial intelligence detects threats, monitors systems and helps prevent cyberattacks that increase safety in digital and physical environments.
- Improved personalization: Artificial intelligence customizes product recommendations, content suggestions, marketing messages and user interfaces based on preferences to boost customer satisfaction.
- Improved customer service: Artificial intelligence powers chatbots and virtual assistants, providing quick, accurate and 24/7 support for customer inquiries and problem resolution.
- Driven innovation: Artificial intelligence supports new discoveries and solutions in healthcare, energy and logistics, which helps industries grow and adapt to future challenges.
These benefits of artificial intelligence show how AI is transforming industries by improving efficiency, accuracy and personalization, which makes daily life and business operations smarter.
What are the drawbacks of artificial intelligence?
The drawbacks of artificial intelligence are ethical concerns, job displacement, privacy issues, security risks and high development costs like advanced medical image analysis systems or fraud detection systems. These challenges of AI impact individuals, organizations and society as artificial intelligence becomes more integrated into daily life.
The drawbacks of AI are listed below.
- Ethical concerns: Artificial intelligence raises ethical concerns about decision-making, transparency and accountability. Unchecked systems make unfair or harmful choices in sensitive sectors like healthcare and criminal justice.
- Potential for biased algorithms: Artificial intelligence reflects biases present in training data, leading to discriminatory outcomes in hiring, lending, law enforcement and other areas that affect social and economic equality.
- Job displacement: Artificial intelligence automates tasks that cause job displacement and unemployment in industries with repetitive or routine work.
- Privacy concerns: Artificial intelligence systems depend on large datasets that raise privacy concerns about data collection, surveillance and the misuse or exposure of sensitive personal information.
- Security Risks: Artificial intelligence has security risks such as vulnerability to hacking, misuse for cyberattacks and the creation of deepfakes or other malicious content that threaten digital and physical safety.
- High Development Costs: Artificial intelligence requires investment in research, development and maintenance. High costs limit access and create barriers for smaller organizations like local retail shops or consulting firms.
What is the biggest problem with AI?
The biggest problem with AI is the potential bias in AI systems that leads to unfairness and discriminatory decisions. This issue arises because AI learns from biased data or lacks transparency in its decision-making processes like predictive analytics, risk assessment and fraud detection. Bias in AI causes harmful outcomes such as unjust hiring, lending or law enforcement actions, which reduces trust and equality in society.
Why can AI not be trusted?
AI can not be trusted because it lacks the qualities of transparency and explainability that make its decisions difficult to predict or fully understand. The controversies of AI include poor data quality that introduces bias, autonomous decision-making without human oversight and the inability to address ethical concerns like fairness. These issues make it harder for people to trust AI and its outcomes such as inaccurate predictions or unfair loan approvals.
Can AI cause cybersecurity issues?
Yes, AI can cause cybersecurity issues because its systems are vulnerable to attacks, failures and misuse. AI systems like chatbots or autonomous vehicles expose sensitive data and risk unauthorized access. AI in cybersecurit introduces attackers to new attack vectors that bypass security measures and create deepfakes. It allows user deception, bypassing security protocols and the spread of misinformation.
Can AI tools threaten user privacy?
Yes, AI tools can threaten user privacy because many AI systems collect sensitive data from users, which increases the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access. AI collects information for training without consent that leads to the exposure of personal details. Algorithmic bias in AI tools causes unfair profiling or misuse of private information, which makes strong privacy safeguards necessary when deploying these technologies.
What is an AI model?
An AI model is a computer program based on algorithms that learns from data to perform specific tasks such as AI assistants, image recognition and video editing. An AI model works by analyzing patterns in the data, making predictions or decisions and continuously improving its accuracy as it processes more information.
What is AI model training?
AI model training is the process of providing data to an AI algorithm to allow it to learn and make accurate predictions. AI model training involves exposing the computer program to large datasets, adjusting its internal parameters and refining its performance so it recognizes patterns and performs specific tasks effectively.
What is an AI agent?
An AI agent is a system that acts autonomously in its environment to achieve specific goals. It makes decisions based on the information it receives and adapts its behavior over time to improve its performance and outcomes. The characteristics of an AI agent include autonomy, goal-oriented actions, adaptability and decision-making capabilities like credit risk assessment or early disease detection.
What is an AI prompt?
An AI prompt is a user's input or instruction provided to an artificial intelligence system. The prompt guides the AI to generate a specific response based on the information or context given. AI prompts include questions, commands or creative tasks that allow the AI system to answer queries, produce content or make customized recommendations such as product suggestions and skincare routines.
What is prompt engineering in AI?
AI prompt engineering is the process of designing instructions for generative AI models to guide them toward producing desired outputs.
What is predictive AI?
Predictive AI is a type of artificial intelligence that uses machine learning algorithms to analyze historical data and predict future outcomes. It helps organizations anticipate behaviors, forecast risks and make informed decisions like financial investment or policy making by identifying patterns and trends in past events. The core concepts of predictive AI include data analysis, pattern recognition, forecasting and continuous model improvement using new data.
What is AI augmentation?
AI augmentation refers to the use of artificial intelligence to improve human capabilities in decision-making processes. AI augmentation supports better outcomes in collaboration rather than replacement in various tasks and industries by combining human and AI systems. This synergy of human and artificial intelligence boosts overall performance and innovation.
What is the future of AI?
The future of AI is ongoing technology advancements and increased automation that make artificial intelligence an important part of modern life. As AI becomes more integrated into daily routines and business processes, it will drive innovation, streamline tasks and improve decision-making across industries. The future of AI promises smarter solutions, higher efficiency and new opportunities for individuals and organizations as these technologies evolve and expand their reach.
What is generative AI?
Generative AI, also known as GenAI, is a type of artificial intelligence that analyzes existing data to autonomously generate new content such as text, images and videos based on prompts. The primary role of generative AI is to create diverse content for multiple platforms, which increases efficiency and scalability in content production.
What is generative AI vs AI?
Generative AI is a subset of AI focused on creating new content like text or images and traditional AI focuses on analysis and decision-making based on existing data. Generative AI and AI both play important roles in technology.
Can AI create images?
Yes, AI **can create images through AI image generators that use advanced algorithms such as generative adversarial networks (GANs) and diffusion models to generate images based on user input. These systems generate visuals like portraits, landscapes and concept art by processing text prompts. This makes AI a powerful tool for creative tasks in areas like digital marketing, game design and education.
What is an AI image?
An AI image refers to a visual artwork produced by artificial intelligence programs, generated from text descriptions or data that showcases the creative capabilities of modern AI technology.
What is AI art?
AI-generated art refers to creative works produced with the help of AI, which uses text prompts to guide the creation of unique digital pieces
What is the best AI art generator?
The best AI art generator is Vosu.ai, which offers multiple art generation models, diverse artistic styles, customization options and a user friendly interface for creative projects.
What is AI video?
AI video is content created or improved using artificial intelligence technologies like Runway (ML) or Vosu.ai. AI video generation involves transforming text descriptions or other inputs into videos that automate tasks like editing, adding effects and generating realistic avatars or scenes.
What is an AI voice?
AI voice refers to synthetic speech generated by artificial intelligence to replicate human-like speaking. It converts text into audio using advanced algorithms and produces natural-sounding output in different languages and tones.
What is Character AI?
Character AI refers to digital personas generated by advanced AI technology. Its features include customizable characters with strong conversational abilities that allow users to interact naturally. Character AI supports multi-character interaction and allows responsive and engaging conversations.
What is stable diffusion AI?
Stable diffusion AI is a generative AI model that uses a deep learning technique called latent diffusion to generate images from text descriptions. It transforms text prompts into detailed visuals by iteratively refining random noise that helps users to create or edit high-quality and realistic images.
What is AI upscaling?
AI upscaling is a process that uses artificial intelligence to increase resolution in images or videos. AI upscaling generates details and reduces noise by training with data. This process results in clearer, sharper visuals even when improving low-quality or pixelated sources.
What is the EU AI Act?
The EU AI Act is a comprehensive regulation by the European Union that introduces a risk-based framework for artificial intelligence. The AI Act sets specific rules like transparency requirements and human oversight obligations for AI systems based on potential harm to ensure safety, transparency and ethical use of artificial intelligence.