Generative artificial intelligence (Gen AI) refers to systems that create original content such as text, images, audio and more by learning patterns from large datasets. These AI models simulate human creativity and are designed to generate outputs that are novel yet contextually relevant. The history of generative AI includes GANs, which create realistic data through competing networks, VAEs, which generate new content by encoding and decoding data and transformer models like GPT, which produce human like text.
The primary goal of generative AI is to produce high quality, original content that supports creative, operational and strategic purposes across industries. It learns underlying data structures to generate new content that reflects, but doesn’t duplicate, those patterns. Generative AI applications are used in chatbots and translation for natural language processing. Other uses of generative AI include financial fraud detection, real estate analysis, and legal research. It also helps optimize manufacturing and supports game development.
Building a generative AI model involves clear objectives, preparing diverse data, choosing the right architecture, optimizing the model, validating performance, fine tuning for specific needs, deploying the system and maintaining it to assure continued accuracy and scalability.
Benefits of generative AI include improved efficiency, cost savings, automation of repetitive tasks, better decision making and support for digital transformation. It faces challenges such as bias, ethical concerns, property issues, regulatory compliance, data privacy, technical debt, high computational costs and risks of over reliance that managed carefully.
What is Generative AI?
Generative Artificial Intelligence (Gen AI) is a subfield of Artificial Intelligence that uses generative deep learning models to produce new content such as high quality text, images, videos, music, 3D models, code and stories in response to a prompt or request of a user.
Generative AI encodes the structures and relationships found in training data into mathematical representations, then decodes those representations to generate new content that resembles, but does not duplicate the original data. The generative AI relies on foundation models, large neural networks trained on massive datasets. It uses encoder-decoder architectures to transform input prompts into new outputs. Key model types include transformers, diffusion models, GANs and VAEs**.** Generative AI creates lifelike and relevant outputs across text, images, video, and 3D models. This makes it useful for applications like chatbots, media creation, scientific research and business automation.
Its outputs are indistinguishable from human generated content, though they also reflect the biases and limitations of the underlying data.
What are the generative AI examples?
The examples of generative AI include ChatGPT, DALL-E 2, Midjourney, Stable Diffusion and Vosu.ai.
Popular generative AI examples are given below.
- ChatGPT: ChatGPT is an advanced conversational generative AI developed by OpenAI. It generates human-like responses, answers questions, and helps with various tasks.
- DALL-E 2: A generative AI system by OpenAI that creates highly detailed and imaginative images from textual descriptions, which allows creative visual content generation.
- Midjourney: Midjourney is a generative AI tool developed by an independent research lab. It creates artistic and stylized images from user prompts and is widely used for creative design and concept art.
- Stable diffusion: An open source generative AI model that produces realistic images from text prompts, widely used for art, design and content creation.
- Vosu.ai: Vosu.ai offers multi modal generative AI capabilities for creating images, voice, avatars and video content based on user inputs.
What is the history of generative AI?
The history of generative AI spans from early symbolic algorithms to today’s advanced neural networks. Key milestones include the invention of backpropagation and the development of models like GANs and VAEs. The foundations of generative AI began in the 1950s. In 1952, Arthur Samuel pioneered machine learning. In 1958, Frank Rosenblatt invented the perceptron, the first trainable neural network. In the 1960s, Joseph Weizenbaum created one of the first chatbots ELIZA(1964 to 1967). It used simple pattern matching to mimic human conversation and became an important early step in natural language processing and generative AI. The 1980s saw the development of recurrent neural networks (RNNs) and in 1997, long short term memory (LSTM) networks allowed better handling of sequential data.
A major leap occurred in 2014 with the introduction of Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) by Ian Goodfellow, use two neural networks in competition to generate highly realistic images and other data types, which revolutionize content creation and deepfake technology. Diffusion models emerged around 2015, which advance image generation by learning to reverse the process of adding noise to data. The transformer architecture, proposed in 2017, lays the foundation for the development of large language models (LLMs), which understand and generate coherent text. OpenAI’s Generative Pre-trained Transformer (GPT) series began in 2018. It culminated in GPT-3 in 2020, which has 175 billion parameters and set new standards in language generation. ChatGPT launched in November 2022 and made generative AI mainstream. It let millions interact with AI and sparked global adoption. Recent years have seen the rise of diffusion based models like DALL·E 2, Stable Diffusion, and Midjourney, which generate high-quality images from text prompts. These advancements greatly expand the creative potential of generative AI.
What are the types of generative AI?
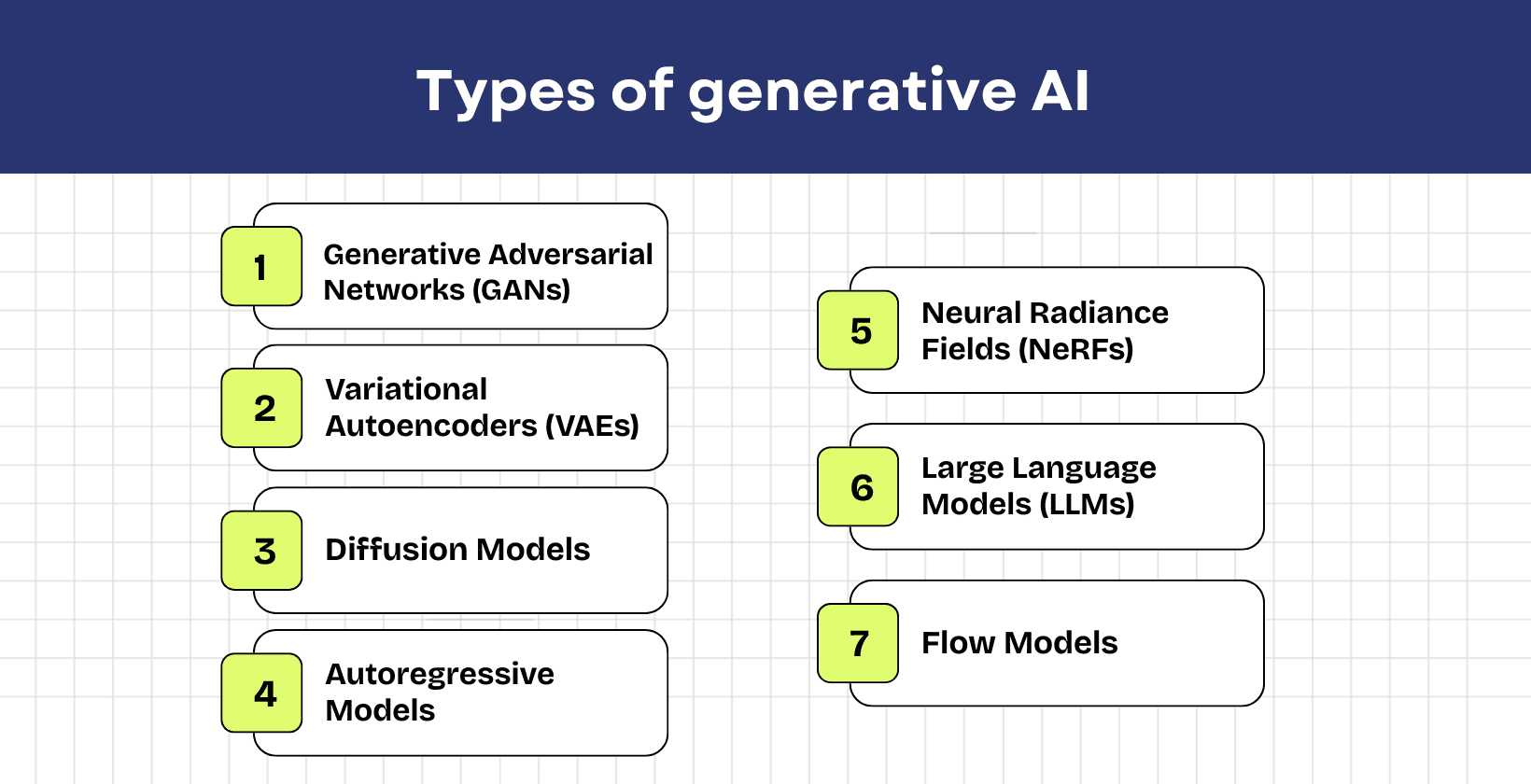
The 7 types of generative AI are Generative Adversarial Networks(GANs), Variational Autoencoders, Diffusion Models, Autoregressive Models and Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs).
The 7 types of generative AI are listed below.
- Generative adversarial networks (GANs): GANs use two neural networks such as the generator and the discriminator, that compete with each other. The generator creates new data, while the discriminator evaluates it, which results in highly realistic synthetic outputs.
- Variational autoencoders (VAEs): VAEs encode input data into a latent space and decode it back. They generate new samples by sampling from this learned distribution, used for images, audio and text.
- Diffusion models: Diffusion models generate data by transforming random noise into structured outputs through a learned denoising process. They are effective in creating high quality images from text or other prompts.
- Autoregressive models: Autoregressive models generate content one element at a time, which depends on previous outputs. They predict the next word or token in language generation based on the prior sequence, which allows coherent text creation.
- Neural radiance fields (NeRFs): NeRFs are neural networks that turn 2D images into realistic 3D views by the way light radiates. This makes it possible to create lifelike 3D reconstructions and visualizations.
- Large language models (LLMs): LLMs, such as GPT, are transformer based models trained on massive text datasets. They generate human-like text, answer questions, summarize, translate and perform various natural language tasks at scale.
- Flow models: Flow models use invertible neural networks to learn complex data distributions. They allow both data generation and calculation of how likely a given example is under the model, which makes them useful for creating images, audio, and other structured data.
What is the main goal of generative AI?
Generative AI aims to create new and original content. This AI produces a huge media, including text, images, audio, video and other digital formats. It writes articles, generates artwork, composes music, produces video clips and creates code. It learns from large datasets by finding patterns in how words and ideas are used, so it can create text that makes sense and fits the context. Generative AI supports rapid, scalable and diverse content creation for multiple platforms and industries. It streamlines workflows and opens new possibilities for creativity and automation.
Generative AI learns from existing data and generates outputs that are not direct copies. It creates content that is original in structure and form. Generative AI uses models such as GANs and large language models, which analyze complex data structures and synthesize content. This reflects human creativity while maintaining coherence and novelty. Generative AI improves content production by increasing consistency, which allows dynamic personalization. It supports businesses, creators and users who seek new solutions and ideas.
How does generative AI work?
Generative AI works through advanced machine learning techniques, neural networks and deep learning architectures. It learns from vast datasets and generates new, original content such as text, images, audio, or code. Generative AI begins with a learning process, the model trains on large data collections relevant to the content it aims to produce, neural networks, deep learning models, analyze and encode complex structures (like language, images or 3D shapes), relationships and features within the data, which allows the system to capture patterns and contextual detail.
Generative AI refines learning patterns as the model processes more data and it adjusts internal parameters to better represent statistical properties and context. The key architectures help transformers and large language models (LLM) understand and generate language by modeling long range dependencies. Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) use a generator and a discriminator network to create realistic synthetic data**. Variational Autoencoders (VAEs)** compress input into a latent space and decode it to form new samples by learning a probabilistic representation.
Generative AI performs content generation after training completion and it responds to prompts or specific conditions. A generative prompt is a sentence for a language model or a text description for an image generator. The model takes what it has learned patterns and features from data, and decodes it, meaning it turns this understanding into new outputs that are original, contextually accurate, and realistic. realistic.
Generative AI relies on core technologies like neural networks and deep learning, along with models such as GANs (Generative Adversarial Networks), VAEs (Variational Autoencoders), transformers, and LLMs (Large Language Models). These tools work together to create high-quality content in areas like text, images, and video with little to no human input.
How do generative AI models work?
Generative AI models work through deep learning and neural networks to create new and original content, such as text, images, audio, or code, without manual intervention. Generative AI begins with data processing, which collects, cleans and transforms diverse datasets into formats suitable for neural network input. This assures consistency and quality for accurate learning across content types.
Generative AI continues with the training phase, uses deep learning architectures such as transformers, generative adversarial networks (GANs), or variational autoencoders (VAEs) to analyze processed data. These neural networks contain multiple interconnected layers that extract features and learn complex patterns by adjusting internal parameters through iterative optimization. They encode statistical properties, relationships and context within the data.
Generative AI proceeds to content generation once trained, responds to prompts or conditions by decoding learned representations to produce outputs that are novel yet aligned with training data patterns. This response mechanism supports relevance and realism in generated content.
Generative AI follows an integrated workflow that includes data processing, model training and content generation. This structure allows the system to produce high quality, creative and contextually aligned content across domains, with output indistinguishable from human made work.
What are the use cases of Generative AI?
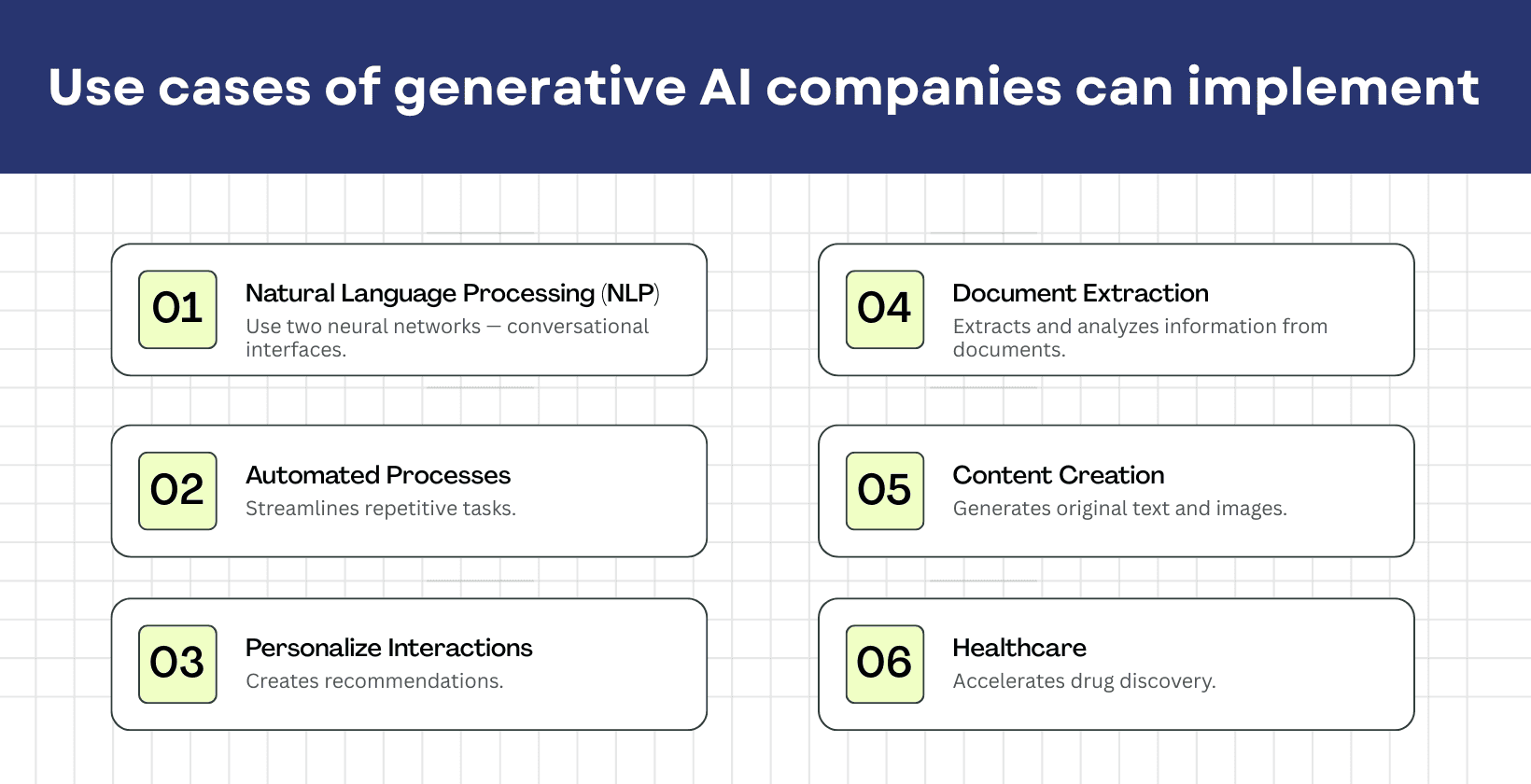
Generative AI transforms industries through organizations to create new content, automate processes and improve user experiences through intelligent automation.
The use cases of generative AI are listed below.
- Natural language processing (NLP): Generative AI powers advanced conversational interfaces like chatbots and virtual assistants, which allow natural language understanding, automated translation and intelligent document processing for improved human computer interactions.
- Automated processes: Generative AI streamlines repetitive tasks such as data entry, report generation and workflow automation, which reduces manual workload and increases operational efficiency while employees are allowed to focus on strategic activities.
- Personalized experiences: Generative AI creates recommendations, customized content and individualized user interfaces by analyzing user behavior and preferences, which leads to improved customer engagement and satisfaction across digital platforms.
- Document extraction: Generative AI extracts and analyzes information from unstructured documents, including contracts, invoices and reports, using advanced natural language processing, which improves accuracy and reduces processing time.
- Content creation: Generative AI generates original text, images, audio, video and multimedia content for marketing, education and entertainment purposes, which allows rapid content production at scale while maintaining quality and consistency.
- Healthcare: Generative AI accelerates drug discovery, improves medical imaging analysis, allows personalized treatment plans, automates clinical documentation and supports diagnostic decision making while improving patient outcomes and operational efficiency.
How to build a generative AI model?
To build a generative AI model, the steps include defining objectives, data collection and preparation, selecting an appropriate architecture and many more.
The 8 steps to build a generative AI model are given below.
1. Define the problem and objectives: Identify the specific problem that your generative AI model must solve and establish measurable objectives for success. Understand what type of content the model must generate and define the target outcomes.
2. Data collection and preparation: Data collection and preparation: Gather high-quality, diverse datasets such as images, text or audio that match your goals. Then clean and format the data by removing errors and inconsistencies to secure the best training for your generative AI model.
3. Model architecture selection: Choose the generative AI architecture that fits the use case, such as GANs, VAEs, or Transformers. Consider the architecture that meets model complexity, computational needs and performance characteristics.
4. Model training and optimization: Train the generative AI model through iterative cycles that use the prepared dataset. Feed the data that is preprocessed, adjust hyperparameters and monitor key metrics that help reduce prediction errors.
5. Evaluation and validation: Assess generative AI model performance using metrics and methods that provide quantitative and qualitative evaluation. Use validation datasets that test overfitting and evaluate the model's generalization capacity.
6. Fine tuning and customization: Refine generative AI model performance through instruction fine tuning, domain adaptation, or reinforcement learning from human feedback. This delivers the model to specific tasks and requirements.
7. Deployment and integration: Deploy the trained generative AI model into a production environment that includes infrastructure, APIs and scaling mechanisms. Set up monitoring systems that assure integration with existing systems.
8. Monitoring and maintenance: Monitor model performance continuously, detect drift and implement updates to maintain accuracy over time. Regular retraining with new data guarantees optimal performance in changing environments.
What are the benefits of generative AI?
Generative AI delivers operational, financial, creative and strategic advantages across industries through increased efficiency, reduced costs, automated repetitive tasks, improved productivity, allowed content generation, improved decision making and supported digital transformation.
The benefits of generative AI are listed below.
- Increase efficiency: Generative AI automates complex tasks and streamlines workflows, which reduces time spent on routine activities and allows teams to focus on strategic work that requires human creativity and judgment.
- Optimize costs: Generative AI helps organizations achieve significant cost savings through decreased labor requirements and improved resource allocation.
- Automate repetitive tasks: Generative AI technology handles routine functions like data entry, document processing and customer inquiries, freeing up employees to engage in higher value work and strategic initiatives.
- Improve productivity: Research shows generative AI boosts worker productivity by up to 66% by accelerating content generation, decision making processes and allowing for faster completion of professional tasks.
- Drive digital transformation: Generative AI catalyzes modernizing business operations, which allows organizations to adopt new business models and leverage AI-driven insights for competitive advantage.
- Improve creativity and innovation: The technology facilitates rapid ideation, design and prototyping, which supports teams to explore new possibilities and push creative boundaries in art, product development and problem solving.
- Allow content creation: Generative AI produces high quality text, images, audio, video and code on demand, which supports scalable content production for marketing, media, education and entertainment industries.
- Improve learning: Generative AI creates adaptive materials, personalized feedback and interactive simulations in educational settings that make learning more engaging and effective for students across different skill levels.
- Improve customer service: Generative AI powered chatbots and virtual assistants provide instant, accurate and context aware support, which improves customer satisfaction while reducing response times and operational costs.
What are the challenges of generative AI?
Generative AI presents transformative opportunities but also brings significant challenges, such as bias and fairness, ethical concerns, intellectual property, regulatory compliance, data privacy and security, technical debt and scalability.
The challenges of generative AI are listed below.
- Bias and fairness: Generative AI models inherit biases that exist in training data, which result in outputs that reinforce harmful stereotypes and cause unfair treatment toward specific demographic groups.
- Ethical concerns: Generative AI introduces ethical issues such as deepfake generation, misinformation and malicious use of automated content, which require strict oversight and responsible governance.
- Intellectual property: Generative AI produces content that closely mirrors copyrighted material, raising legal and ethical questions about originality, ownership, infringement and unauthorized use, high computational cost and over reliance and lack of originality.
- Regulatory compliance: Generative AI systems must comply with evolving legal frameworks and industry standards such as the EU AI Act, in regulated sectors including healthcare and finance.
- Data privacy and security: Generative AI handles large datasets that contain sensitive information, which makes strong data protection essential to prevent breaches, misuse and unintended exposure of private data.
- Technical debt and scalability: Generative AI system development introduces technical debt as models increase in size and complexity, which complicates scalability, maintenance and system integration.
- High computational costs: Generative AI training and deployment require substantial computing resources, which results in high energy consumption, operational costs and environmental impact that limit accessibility for many organizations.
- Over reliance and lack of originality: Generative AI dependence reduces human creativity and critical thinking and models produce content that is repetitive, derivative and lacking contextual depth or originality.
What are the biases of generative AI?
The biases of generative AI are data bias, machine bias, selection bias, confirmation bias, contextual bias, linguistic bias and automation bias.
The biases of generative AI are listed below.
- Data bias: Generative AI exhibits data bias when its training data is incomplete, unrepresentative, or reflects historical inequalities, which causes Generative AI to produce skewed outputs that mirror those data flaws.
- Machine bias: Generative AI reflects machine bias through systematic errors in its algorithm or model design, where internal logic or assumptions reinforce biases embedded in its training data or coding structure.
- Selection bias: Generative AI displays selection bias when its training dataset lacks representation of real world populations or tasks, which results in outputs that favor certain groups or perspectives.
- Confirmation bias: Generative AI demonstrates confirmation bias when it reproduces patterns or assumptions found in the data, which causes generative AI to perpetuate existing prejudices or align with prior stereotypes.`
- Contextual bias: Arises when generative AI misinterprets or oversimplifies context, which leads to outputs that lack nuance or fail to accurately reflect the intended meaning or situation.
- Linguistic bias: Generative AI contains linguistic bias when it generates language that reinforces gender, racial, or cultural stereotypes, which results from imbalanced datasets or embedded societal prejudices.
- Automation bias: Generative AI causes automation bias when users overly trust its outputs without sufficient scrutiny, which allows generative AI to perpetuate and amplify existing biases in automated decision making processes.
Is gen AI unethical?
No, gen AI is not inherently unethical, but it raises important ethical concerns that require attention. Generative AI presents key issues, including bias, misinformation, copyright infringement, data privacy and lack of transparency. Generative AI requires clear ethical guidelines, human oversight and ongoing evaluation to minimize harm, secure fairness and maintain accountability according to evolving legal and regulatory standards.
What is the argument against generative AI?
The argument against generative AI centers on its risks of spreading misinformation and manipulation, which expose sensitive data and raise ethical and societal concerns such as bias, job displacement and copyright infringement. Critics also highlight practical limitations, which include a lack of transparency, unreliable outputs and high computational costs, all of which challenge trust, accountability and responsible use in sensitive or creative domains.
How does generative AI impact creative industries?
Generative AI impacts creative industries by transforming content creation. This allows rapid production of art, music, writing and design with unprecedented speed and personalization. It supports creators to experiment, collaborate and scale ideas, driving innovation and efficiency. Generative AI also creates challenges, including concerns over originality, copyright, job displacement, environmental impact from high computational demands and the risk of diminishing critical thinking and creative skills.
Does generative AI create original content?
Yes, generative AI creates original content because generative AI models are designed to produce new, unique outputs such as text, images, audio, or code by learning patterns from datasets and generating content that is not a direct copy of any single example. They are novel combinations and indistinguishable from human created work, while these outputs are influenced by the training data.
What is a prompt in generative AI?
A prompt in generative AI is a clear instruction, such as a question, instruction or description given to an AI model to guide it in generating a specific response or creative output. The examples include “Write a poem about the ocean,” “Create a recipe using tomatoes and chicken,” or “Generate an image of a futuristic city.” The purpose of the prompt is to communicate the user’s intent, which assures the AI produces relevant, accurate and high quality results. Gen AI prompt engineering is the practice of crafting and refining these prompts to optimize the AI’s output through precise language, context and structure for the best results.
Is GPT a generative AI?
Yes, GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) is a type of generative AI. It creates original, human-like text by learning patterns from large datasets and responding to user prompts. As a transformer based language model, GPT is a type of generative AI category, which specializes in producing coherent, contextually relevant outputs across a wide range of natural language tasks.
What type of generative AI is ChatGPT?
ChatGPT is a large language model (LLM) based on the transformer architecture, designed as a text based generative AI. It generates human-like text by learning patterns from vast datasets that produce coherent, contextually relevant responses to user prompts. ChatGPT is optimized for dialogue and instruction following, which makes it a conversational generative AI model within the broader LLM category.