AI agents are intelligent systems that observe their surroundings, analyze data and take action to achieve goals such as task automation, error reduction and faster decision making. AI agents operate with autonomy, make decisions, learn from experience and adapt to new situations without constant human input. This capability makes them important in modern automation, where speed, precision and adaptability matter.
AI agents are built with components like perception, reasoning, learning, action and communication. AI agents allow them to collect data through sensors or interfaces, process and interpret that data, choose actions and communicate or execute decisions. 5 types of AI agents are simple reflex agents, model based agents, goal based agents, utility based agents and learning agents. They perform different roles from rule following to strategic decision making in complex environments such as autonomous driving, financial forecasting and real time robotics.
Artificial intelligence agents are used in applications including chatbots and virtual assistants, to self driving cars, healthcare tools and smart homes. Their applications improve customer service, streamline operations and optimize workflows. They offer benefits like efficiency, cost savings and 24/7 performance but also present risks such as bias, data breaches and ethical violations.
What are artificial intelligence (AI) agents?
Artificial intelligence (AI) agents are intelligent systems that interact with their environment through perception and action to achieve specific goals such as maximizing efficiency, improving decision accuracy and automating repetitive tasks. They operate without human input and make decisions based on environmental data. They are goal oriented and meet defined objectives such as fraud detection, supply chain optimization, user experience enhancement and accurate medical diagnosis. They learn and adapt over time and analyze past actions and outcomes to improve.
AI agents interact with users, systems or other agents to gather or exchange information. Autonomy, decision making, learning, interaction and goal focused characteristics make them capable of completing difficult tasks in any situation.
What are the examples of AI agents?
AI agents are used across many industries to automate tasks, improve efficiency and personalize experiences. They manage leads, deliver customer support, optimize marketing and power autonomous vehicles and smart home devices like smart lighting, smart security cameras and speakers.
The examples of AI agents are given below.
- Lead management AI agents: Lead management AI agents handle incoming customer inquiries, organize leads, send automated replies and set reminders that help businesses engage clients while optimizing sales processes like automated lead capture, CRM integration and sales pipeline management.
- Marketing AI agents: Marketing AI agents automate content creation, schedule campaigns, personalize messages and analyze results to reduce workload and provide effective marketing efforts.
- E commerce AI agents: E commerce AI agents improve online shopping by tracking orders, recommending products, sending cart reminders and optimizing searches such as personalized search results, voice activated search and search result ranking optimization for better customer experiences.
- Customer support chatbots: Customer support chatbots provide instant, 24/7 responses to queries, resolve issues and guide users, which allows human staff for complex tasks like financial risk assessment, medical diagnosis and treatment planning.
- Autonomous vehicles: Autonomous vehicles use multiple agent types to process sensor data, navigate safely, make real time driving decisions and adapt to changing conditions such as traffic patterns, weather fluctuations and road closures.
- Smart home devices: Smart home devices monitor and adjust home environments, respond to voice commands and learn user preferences such as temperature settings, lighting levels and music genres to increase comfort and security.
- Fraud detection AI agents: Fraud detection AI agents monitor transactions, analyze behaviors and flag suspicious activity in finance or e-commerce to prevent fraud.
What are the components of AI agents?
The components of AI agents are perception, reasoning, action, learning and communication. AI agents use perception to collect input from sensors, apply reasoning to analyze data and conditions, execute actions through actuators, apply machine learning to improve performance and use communication protocols to exchange information.
5 components of AI agents are outlined below.
- Perception: AI agents use sensors, cameras, microphones or digital interfaces to collect data from their surroundings. This helps them detect and understand changes in the environment.
- Reasoning: AI agents use logic to process information, understand the context and make decisions. They plan, solve problems and choose the best actions based on available data.
- Action: AI agents, after making decisions, use robotic parts like motors or software tools to affect the environment or help users.
- Learning: AI agents improve by using past data, results or feedback. AI agents apply methods like machine learning or reinforcement learning to make better decisions next time.
- Communication: AI agents share information with users, other systems or agents using text, voice or APIs to collaborate, answer questions and complete tasks.
What are the types of AI agents?
The types of AI (artificial intelligence) agents are simple reflex agents, model based reflex agents, utility based agents, goal based agents and learning agents. These agents differ in complexity and decision making capabilities. Simple reflex agents act on current input, advanced types like utility and goal based agents analyze outcomes or plan toward objectives. Learning agents improve over time using data by making them responsive and intelligent in powerful environments.
5 types of AI agents are given below.
1. Simple reflex agents
Simple reflex agents are intelligent systems that act based on current perception using predefined rules without consulting any memory or internal state. These include devices such as thermostats, robotic vacuum cleaners or traffic light systems, which respond to immediate input.
Simple reflex agents operate with no memory, predefined condition action rules, function in observable environments and have no capability for learning. They work by using sensors to perceive their surroundings, matching observations to pre programmed responses and executing actions via control elements.
Simple reflex agents have high speed, simplicity and cost efficiency but they have disadvantages like inflexibility, lack of responsiveness in changing environments and inability to learn or improve over time.
2. Model based reflex agents
Model based reflex agents are intelligent systems that use an internal model of the environment to make decisions, which allows them to track the current state and predict the outcome of actions. AI agents of this type include autonomous vehicles, robotic vacuum cleaners, modern irrigation systems and home automation systems such as smart lighting systems, smart security cameras and voice activated assistants.
Model based reflex agents feature state tracking, condition action rules, adaptability, improved performance, contextual understanding and predictive capability. They work by updating their internal state based on environmental changes and applying rules to select actions suited for the situation. Their strengths include adaptability and context aware responses but they become complex and require computation than simple agents.
Model based reflex agents handle changing environments by maintaining a history of past states and actions, which allows them to make context aware decisions. Simple reflex agents instead respond to the current sensory input without tracking or utilizing information from previous states.
3. Utility based agents
Utility based agents are intelligent systems that choose actions based on a utility function to maximize expected outcomes. They are used in self driving cars, stock trading bots, customized pricing systems, smart home thermostats and personalized content recommenders.
Utility based agents function by perceiving their environment, representing the current state, analyzing possible actions through a utility function, which executes the action that produces the highest utility and continuously learning from outcomes. Their features include a utility function for quantifying preferences, a systematic decision making process, the ability to adjust to fluctuations and versatility across fields like finance, logistics, robotics and e commerce.
Utility based agents' advantages are optimal decision making under uncertainty, adaptability and the ability to consider multiple factors. Their disadvantages include increased complexity, dependence on accurate models and challenges involving moral or ethical considerations like bias, lack of transparency and privacy violations.
4. Goal based agents
Goal based agents are intelligent systems designed to track defined objectives through reasoning and planning. They are used in self driving cars, robots navigating buildings, virtual assistants and chess playing AI.
Goal based agents detect the environment, reason about possible actions, execute the chosen steps, analyze progress and work toward goal completion. They are goal oriented, capable of strategic decision making, adaptable and use logical planning.
Goal based agents' advantages include effectiveness in complex tasks, adaptability and user friendly design. Their disadvantages involve the need for detailed environment knowledge, slower decision making and limited focus on set goals.
5. Learning agents
Learning agents are intelligent systems that autonomously improve their performance over time by learning from interactions with their environment and using feedback to adapt and optimize actions. These include self driving cars, robotics platforms, virtual assistants, game playing AI and personalized recommendation systems like Netflix, Amazon and Spotify.
Learning agents consist of four main components such as the learning element (improves knowledge and strategies), the performance element (executes actions), the critic (provides feedback) and the problem generator (suggests new experiences to facilitate ongoing learning). They learn using techniques like reinforcement learning, supervised learning, imitation learning and transfer learning, which allows them to recognize patterns, make predictions or optimize behaviors.
Learning agents are used in autonomous driving, robotics, customer support, game play and content or product recommendations, where adaptability and self improvement are important advantages.
The five types of AI agents are visualized below.
What are the applications of AI agents?
AI agents are used across industries such as and finance, healthcare and manufacturing to automate supply chains, optimize business operations, improve financial services, power customer support, improve healthcare, maintain manufacturing systems and allow autonomous technologies like drones and self driving vehicles
The use cases of AI agents are listed below.
- Supply chain management: AI agents automate supply chain operations, optimize delivery routes, track shipments and detect potential disruptions to maintain efficient and resilient logistics.
- Business optimization: AI agents analyze large datasets in business optimization, identify inefficiencies, suggest improvements, automate repetitive tasks and boost operational performance.
- Financial services: AI agents support financial services, detect fraud, execute algorithmic trades like statistical arbitrage, market making and mean reversion, assess risks and provide personalized financial advice to improve decision making and security.
- Customer service: AI agents power customer service platforms, run chatbots and virtual assistants like Alexa or Siri to deliver instant responses, resolve customer issues and personalize user experiences.
- Manufacturing and predictive maintenance: AI agents maintain manufacturing operations like production planning or assembly, monitor equipment, detect failures, schedule maintenance and maximize production efficiency.
- Healthcare: AI agents strengthen healthcare systems, support diagnostics, build personalized treatment plans, maintain patient records and improve hospital workflows and care quality.
- Autonomous systems: AI agents provide autonomous systems, control self driving vehicles, operate drones and robots, navigate surroundings, make decisions and perform independent tasks like navigating routes, avoiding obstacles and controlling vehicles.
The applications of AI agents across industries are visualized below.
How to use AI agents?
To use AI agents, understand their capabilities, define objectives, select suitable tools, configure workflows and test and refine performance for optimal results.
The steps to use AI agents are given below.
- Understand AI agents: AI agents demonstrate how they function, reveal their internal components and show their ability to automate tasks and make decisions in real world situations.
- Defining goals and tasks: AI agents follow clearly defined goals and tasks that align with business requirements or user expectations to ensure effective performance.
- Choosing the right agent and tools: AI agents match the selected type and technology stack with the project's goals, available data and required system integrations.
- Set up the workflow: AI agents operate within a configured workflow that includes input sources, decision rules, output actions and feedback loops to manage full automation.
- Testing and refinement: AI agents undergo deployment, face real time evaluation, receive feedback and improve their accuracy, speed and adaptability through continuous refinement.
What are the benefits of AI agents?
AI agents improve efficiency, offer 24/7 support, reduce costs and improve decision making. They boost customer and employee experiences, scale with business needs and handle customized tasks to specific operational and industry requirements like business goals, user needs and functional requirements.
The benefits of AI agents are listed below.
- Improved efficiency and productivity: AI agents automate repetitive and complex tasks that allow employees to focus on high value responsibilities, which boosts productivity and helps businesses operate efficiently.
- 24/7 availability: AI agents provide continuous support throughout the day and night, manage requests and ensure smooth operation across different time zones without depending on human availability.
- Cost savings: AI agents reduce the need for manual labor, lower the chances of errors and simplify workflows, which allows organizations to cut operational costs and improve overall profitability.
- Improved decision making: AI agents process large volumes of data, uncover patterns and trends and offer actionable insights that help companies to make well informed, accurate and strategic decisions.
- Enhanced customer experiences: AI agents deliver fast, personalized responses across digital platforms, improve customer satisfaction by resolving queries instantly and increase user loyalty through consistent engagement.
- Scalability and flexibility: AI agents respond quickly to shifting business needs, handle growing workloads effectively and scale operations without requiring additional employees or infrastructure.
- Improved employee experience: AI agents manage routine tasks, answer employee questions and reduce operational stress, which creates a more supportive environment where staff focus on strategic priorities.
- Specialized applications: AI agents execute specialized tasks customized to specific business requirements and integrate into company workflows to improve performance in niche areas.
What are the risks of AI agents?
Risks of AI agents are the potential negative consequences and challenges, which include technical, ethical, security and societal impacts that arise from deploying autonomous or semi autonomous AI systems.
The risks of AI agents are listed below.
- Lack of transparency and explainability: AI agents reduce transparency and make it difficult for users to understand or justify decisions because they function like black boxes, which weakens trust, challenges accountability and raises concerns in regulated or sensitive industries.
- Ethical and moral dilemmas: AI agents make autonomous decisions that introduce bias, discrimination or unfair outcomes, which forces society to confront complex ethical and moral dilemmas that question fairness and human values.
- Security and vulnerability to exploitation: AI agents expose systems to serious vulnerabilities because attackers exploit them through cyber threats, prompt injection, data poisoning or unauthorized access, which undermines data integrity and puts entire infrastructures at risk.
- Lack of accountability: AI driven actions are complex when agents operate autonomously or within interconnected systems.
- Unforeseen interactions and systemic risks: AI agents produce unexpected results or trigger harmful chain reactions when multiple agents interact in unpredictable ways, which introduces systemic risks and makes outcomes difficult to forecast or control.
- Over reliance on AI systems: AI agents weaken human oversight when organizations become dependent on automation, which leads to skill loss, diminished critical thinking and dangerous levels of disempowerment in sensitive decision making roles.
- Job displacement and socioeconomic inequality: AI agents displace workers by automating jobs across industries, which increases unemployment and widens socioeconomic inequality by concentrating opportunities and wealth among those who control the technology.
How to create an AI agent?
Creating an AI agent requires a clear plan, quality data, appropriate models and architecture, thorough training, integrations, testing and continuous monitoring for improvement.
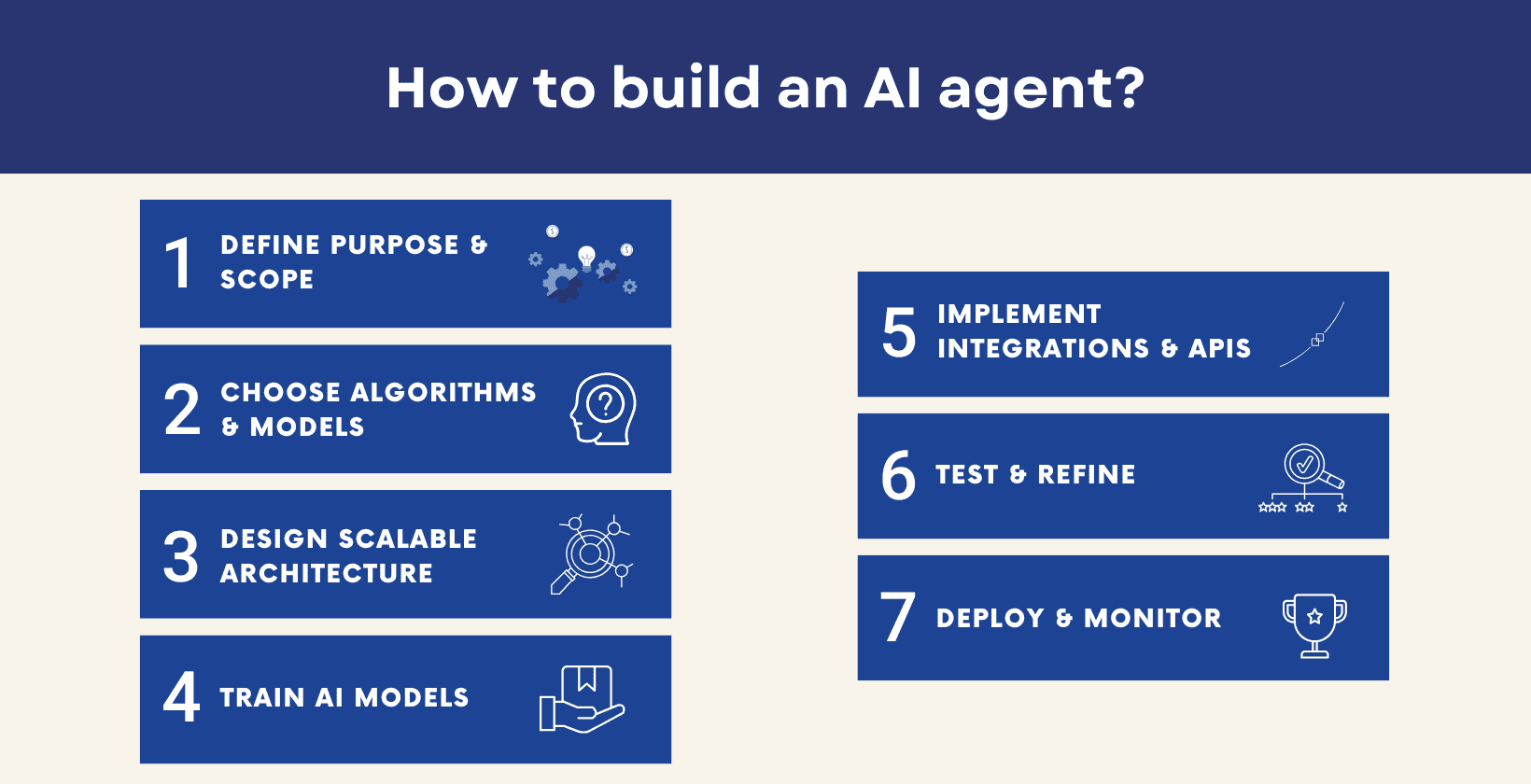
The 8 steps to create AI agents are given below.
- Define the purpose and scope: Define the purpose and scope by stating what tasks they must handle, what limitations they must respect and how those boundaries help the team maintain focus and prevent the project from exceeding its original objectives.
- Gather and prepare high quality data: Gather and prepare data by collecting accurate, relevant and usable datasets, then clean and structure the data to maintain the models that reflect real world conditions and deliver consistent and reliable performance.
- Choose algorithms and models: Choose algorithms and models by selecting the most appropriate AI techniques such as machine learning, deep learning or language models, which align with the agent’s goals.
- Design a modular and scalable architecture: Design a modular and scalable architecture by building the system in separate functional parts, which allows for easier updates, greater reusability and future expansion as the volume of data or user demand grows.
- Select and train AI models: Select and train models by applying the prepared data to shape the model’s behavior, then fine tune the model to improve accuracy, increase processing speed and ensure stable output across different conditions.
- Implement integrations and APIs: AI agents implement integrations and APIs by linking themselves with third party systems, tools or platforms through defined interfaces so they can access real time data and complete assigned tasks effectively in connected environments.
- Test and refine: Test and refine their functions by running through multiple inputs, scenarios and user cases, then evaluate the feedback to adjust outputs and enhance the overall user experience and system reliability.
- Deploy and monitor: Deploy and monitor their operations by going live for end users, tracking performance metrics and applying necessary updates to resolve errors.
The step-by-step process to create an AI agent is visualized below.
How much does it cost to create an AI agent?
The cost to create an AI agent ranges from $5,000 to over $200,000, depending on complexity. Basic AI agents cost $5,000–$20,000, mid level solutions range from $20,000–$100,000 and advanced, custom AI agents like autonomous AI agents or retrieval augmented generation (RAG) agents exceed $100,000. Total expenses depend on project requirements, data needs and integration complexity.
Can you create your own AI agent?
Yes, you can create your own AI agent because many tools, frameworks and no code platforms in 2025 allow individuals and businesses to build AI agents for various tasks without advanced programming skills.
Are AI agents considered sentient?
No, AI agents are not considered sentient because they lack consciousness and self awareness and they operate based on programmed algorithms without genuine understanding or emotions.
Sentience is defined as the capacity to experience feelings and sensations such as pain or pleasure and some form of conscious awareness and subjective experience. AI agents do not possess independent thought, consciousness or the ability to feel emotions or sensations, they merely process information and simulate aspects of human behavior without true awareness or sentience.
Are GPTs considered AI agents?
Yes, GPTs are considered AI agents because they process inputs, generate context aware responses and perform tasks autonomously based on user prompts.
GPTs or generative pre trained transformers are advanced neural network models, trained on large datasets to generate humanlike text, answer questions and perform various language tasks. They autonomously perceive user input, process it and generate contextually relevant responses when integrated into systems or applications, fulfilling the core functions of an AI agent like perception, resonance and action.
How are AI agents used in business today?
AI agents are used in businesses today to automate customer service, personalize shopping and recommendations, optimize sales and marketing, manage IT operations and optimize finance, accounting and human resources. AI agents also improve meeting management, boost content creation and optimize inventory management, which increases efficiency, decision making and customer experiences for companies of all sizes.
How will AI agents reshape the future of business?
AI agents will reshape business by automating tasks, optimizing processes and providing data driven insights, which increases productivity and efficiency across various operations. AI agents will allow new business models and revenue streams such as AI as a service and outcome based pricing, while improving the customer experience through hyper personalization and real time support. AI agents will transform the nature of work and employees will shift their focus from routine and complex workflows to creative, strategic tasks, fostering a collaborative environment between AI and human intelligence.
What is the difference between LLMs and AI agents?
LLMs (large language models) specialize in language understanding and text generation, responding to prompts without autonomy, while AI agents are autonomous systems that use models like LLMs to perform complex tasks, make decisions and interact with real world environments. LLMs such as chatgpt and gemini excel at conversation, AI agents like auto gpt or virtual assistants plan, act, adapt and execute workflows independently.
What is the difference between AI agents and AI chatbots?
AI agents and AI chatbots differ in their capabilities and intended use. AI chatbots are designed for simple, rule based conversations, while AI agents are built for autonomous, complex task execution and decision making across multiple systems.
AI chatbots focus on handling straightforward, scripted interactions such as answering FAQs, guiding users through basic processes or managing simple transactions. AI chatbots are reactive, limited in adaptability and focus on scripted interactions. AI agents are proactive, context aware, make independent decisions, learn from data and integrate with multiple systems for scalable automation like website support bots (chatbots) and virtual assistants that automate workflows (AI agents).
What is the difference between agentic and non agentic AI chatbots?
Agentic AI chatbots think and act on their own, learning and adapting as they go, while non agentic chatbots stick to scripts and handle only basic, repetitive tasks.
Agentic AI chatbots offer autonomy, learn from interactions, adapt to new contexts and handle complex tasks. Non agentic chatbots follow predefined scripts, do not learn and manage only simple, repetitive tasks. Businesses use agentic bots in dynamic fields like healthcare or finance, while non agentic bots suit basic customer service.
What is a multi AI agent system?
A multi AI agent system is a network of autonomous AI agents that work together to complete tasks, communicate and make decisions collaboratively. A multi AI agent system uses multiple autonomous AI agents with specific roles to solve complex problems or reach shared goals. Each agent handles part of the task, communicates with others and makes decisions. These systems allow greater flexibility, scale easily and support advanced uses like traffic control, logistics, robotics and smart homes.


