Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to technologies that allow machines to mimic human like capabilities such as learning, problem solving and decision making. AI is evident in applications without being defined which range from automation and data analysis to personalized customer service and predictive algorithms.
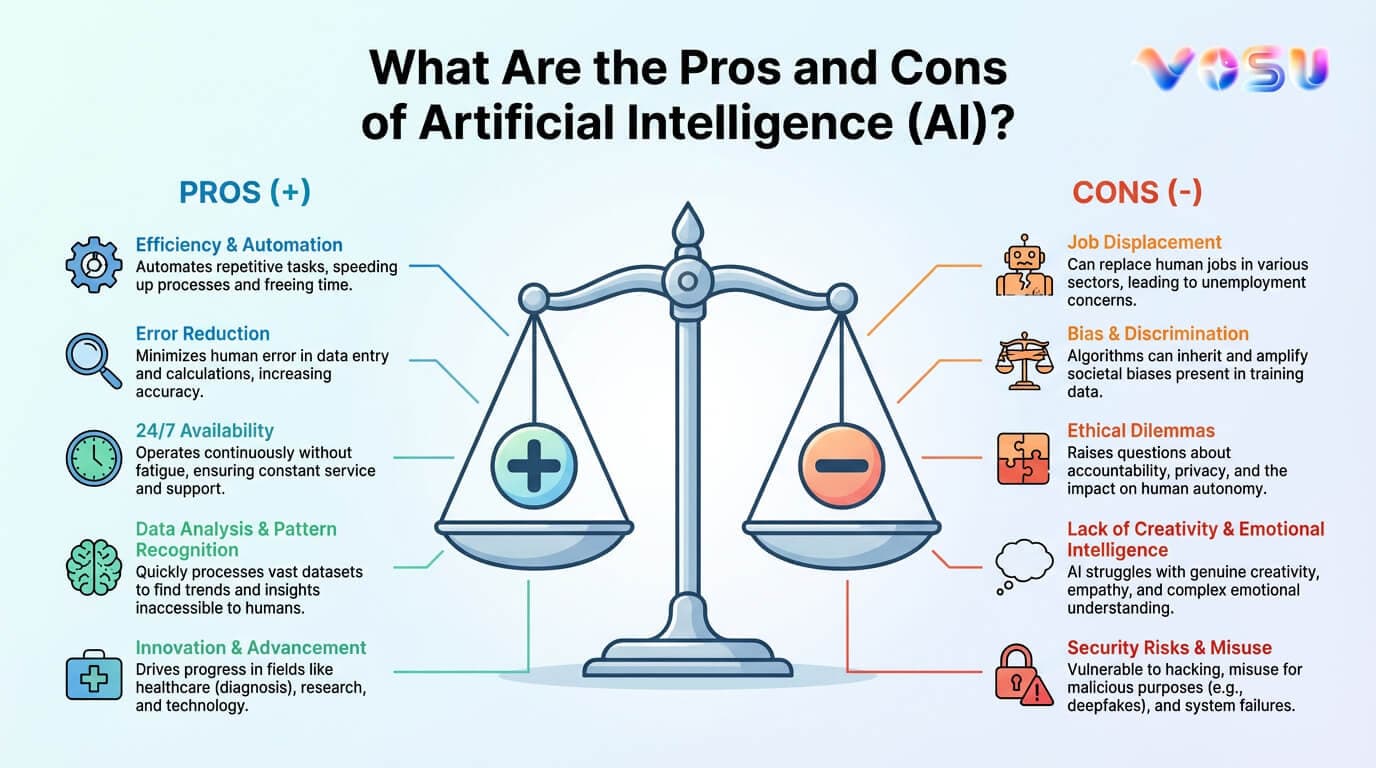
The advantages and disadvantages of AI reflect its growing impact across industries and daily life. AI improves accuracy by reducing human error, improves efficiency through automation and allows continuous 24/7 operations without fatigue. It contributes to better decision making by analyzing huge datasets in real time, supports innovation in creative industries and personalizes learning and customer experiences. AI minimizes human risk by operating in hazardous environments and secures unbiased decisions when responsibly developed.
AI is not a monolith. Traditional automation follows explicit rules, but machine learning systems adapt by finding patterns in data. Generative AI, which surged after 2022, produces new text, images, and video rather than just analyzing inputs. This taxonomy helps clarify where benefits and risks apply. The pros and cons of artificial intelligence are considered carefully because of their implications for ethics, employment and privacy. AI compromises data privacy due to its reliance on large scale personal data collection. It presents ethical challenges due to algorithmic bias and the lack of transparency in how decisions are made. AI-generated content increases the risk of misinformation, including deepfakes and fake news. Automation displaces human workers, particularly in routine jobs and overreliance on AI suppresses creativity and critical thinking. High development and maintenance costs restrict access for small organizations.
What are the advantages of Artificial Intelligence?
The advantages of artificial intelligence are eliminating human error, minimizing human risk, easing the learning process, improving the decision making process and cost savings.
The top 11 advantages of artificial intelligence are outlined below.
1. Eliminate human error
Artificial intelligence eliminates human error by automating complex procedures with consistent precision and increased accuracy. Human error rates range from 1% to 5% and worsen under stress, fatigue or time pressure.
According to KodexoLabs (2025), AI systems demonstrate consistent performance across varying conditions and can achieve accuracy rates of up to 99.9% in specialized applications. In medical imaging, research led by PMC (2024) reports that AI models detect cancer with an accuracy rate of up to 94.5%, outperforming the 88% average for human radiologists (PMC, 2024). AI can reduce certain types of human error in well-specified tasks and at scale. It also introduces new failure modes, so safeguards, monitoring, and fallback procedures are critical to avoid propagating mistakes at scale.
2. Minimize human risk
AI-powered robots and automation reduce human exposure to dangerous environments such as mines, nuclear zones, or disaster areas. These machines can neutralize explosives, inspect unstable structures, or detect gas leaks in real time while humans remain safely at a distance. The ability to continuously monitor conditions with precision adds another layer of protection against injury or fatal accidents. This makes AI indispensable in industries where human involvement would otherwise carry unacceptable risks.
3. Ensure constant availability
AI systems function 24/7 without interruption, unlike human workers who need rest and breaks. This allows customer support chatbots, healthcare monitors, and fraud detection systems to remain active across all time zones. The result is fewer missed inquiries, faster problem resolution, and stronger reliability for both organizations and clients.
24/7 operation of AI depends on reliable infrastructure, robust data pipelines, and clear SLAs. Organizations must also plan for model drift, outages, and the costs of maintaining redundancy.
4. Automate repetitive tasks
AI relieves humans from tedious, repetitive tasks such as data entry, report generation, or invoice verification. These processes are completed more quickly and with greater accuracy and reduce the frustration and errors often associated with manual work. By managing routine operations around the clock, AI allows businesses to save time and resources. Human employees can then focus on strategic or creative projects that demand judgment and innovation.
5. Deliver unbiased decisions
AI offers the potential to reduce bias by focusing decisions on data-driven variables rather than subjective human judgment. Applications like recruitment or loan approvals can be made more equitable when algorithms are trained on representative datasets and regularly audited. AI can improve outcomes in sensitive areas by anonymizing inputs and embedding fairness constraints. Still, without safeguards, these same systems risk encoding or amplifying the very biases they aim to avoid.
6. Ease learning processes
AI-powered education platforms adapt lessons to individual students’ strengths, weaknesses, and learning styles. Virtual tutors, real-time feedback, and automated grading allow for highly personalized and accessible learning experiences. This approach promotes deeper understanding and keeps learners engaged at their own pace. At the same time, over-reliance on AI raises concerns about data privacy, explainability, and ensuring equal access across different demographics.
7. Boost operational efficiency
AI drives efficiency by optimizing supply chains, logistics, and production lines across industries. Predictive analytics helps prevent equipment breakdowns, while automated systems streamline warehouse operations and reduce inventory costs. Retailers, manufacturers, and service providers alike use AI to cut downtime and accelerate workflows. These improvements reduce expenses, enhance speed, and support consistent quality.
8. Improve customer experience
AI enhances customer journeys by providing instant responses, personalized recommendations, and proactive solutions. Chatbots and virtual assistants reduce wait times and deliver consistent service at any hour. By analyzing customer data in real time, AI can anticipate needs and flag potential problems before they occur. This creates smoother, more engaging experiences that strengthen loyalty.
9. Enhance the decision making process
AI improves decision making by rapidly analyzing massive datasets and identifying patterns invisible to human observers. Businesses use it for demand forecasting, risk assessment, and resource allocation, while healthcare professionals rely on it for advanced diagnostics. These insights allow organizations to make faster, more evidence-based choices with reduced error. In volatile environments, AI provides the agility needed to respond quickly and effectively.
10. Achieve cost savings
Automation and workflow optimization powered by AI reduce labor costs and operational inefficiencies. Predictive maintenance avoids expensive equipment failures, while energy-use monitoring cuts unnecessary expenses. Real-time analysis enables businesses to allocate resources more effectively and reduce waste. Over time, these savings translate into higher profitability and competitive advantage.
11. Enable creative innovation
AI augments human creativity by generating art, music, writing, and design ideas at scale and speed. Generative AI tools like ChatGPT, Vidu AI and DALL-E allow creators to experiment with new concepts, iterate faster, and push beyond traditional boundaries. In industries such as film, literature, or visual arts, AI enhances production workflows while opening up new styles of expression. This collaboration between human imagination and machine intelligence fuels innovation across creative fields.
Multi-model platforms like VosuAI combine video generation, avatars, voice, and images in one place to help teams prototype campaigns faster and keep brand consistency.
What are the disadvantages of Artificial Intelligence?
The main disadvantages of Artificial Intelligence are compromising data privacy, ethical challenges, critical information, human unemployment, suppressing creative thinking and requiring high development costs.
The main 6 disadvantages of artificial intelligence are outlined below.
1. Compromise data privacy
AI systems pose major privacy risks because they collect and process vast amounts of personal data, increasing the likelihood of breaches and misuse. Weak safeguards or cyberattacks can expose sensitive information, leading to identity theft and fraud. AI-powered tracking also enables detailed behavioral monitoring without clear consent, which erodes user trust and autonomy. To mitigate these risks, organizations must apply strong protections such as differential privacy, role-based access controls, and compliance with frameworks like GDPR and the EU AI Act.
2. Trigger ethical challenges
AI raises serious ethical concerns through algorithmic bias, surveillance, and unintentional discrimination. Biased training data can produce unfair outcomes in hiring, lending, and law enforcement, while large-scale data collection often happens without transparent consent. Automation threatens job security, widening inequality, and accountability becomes difficult when decisions lack explainability. These issues highlight the need for clear ethical standards, oversight mechanisms, and responsible AI development practices.
3. Falsify critical information
AI enables the creation of convincing fake content such as deepfakes, fabricated audio, or AI-written propaganda. These tools have been exploited in politics to spread false endorsements and in media to circulate fake news, undermining public trust and copyright protections. The risk of large-scale misinformation grows, as generative models become widely available. The ability to falsify information at speed threatens the integrity of public discourse in the AI era.
4. Decrease human employment
AI automation displaces workers in industries dependent on routine tasks such as logistics, retail, and manufacturing. Low and middle-skill employees are especially vulnerable, while economic gains concentrate among AI developers and executives. Examples include self-checkout systems replacing cashiers, autonomous vehicles reducing demand for drivers, and robotics cutting factory labor.
However, AI reshapes rather than simply eliminates jobs. Routine tasks are automated, while new roles emerge in oversight, data stewardship, and prompt engineering. The transition is uneven across sectors, and reskilling programs are critical to mitigate inequality.
5. Suppress creative thinking
Overreliance on AI tools for writing, idea generation, or decision making can weaken critical thinking and imagination. Humans risk losing independent judgment, empathy, and context-based creativity as they delegate more tasks to algorithms. Skills atrophy over time, a “use it or lose it” effect which leaves innovation and adaptability diminished. However, when used as a co-pilot, AI can expand ideation, accelerate iteration, and inspire new directions, while humans retain authorship and judgment.
6. Require high development cost
Implementing AI solutions is expensive and requires investments ranging from $50,000 to $500,000 depending on complexity and support needs. Costs stem from collecting and labeling datasets, upgrading infrastructure, hiring skilled talent, and maintaining ongoing updates. These expenses make AI adoption difficult for small businesses and forces many to rely on generic off-the-shelf tools or avoid AI altogether. This creates a competitive gap where larger firms gain significant advantages in efficiency and innovation.
What are the uses of AI?
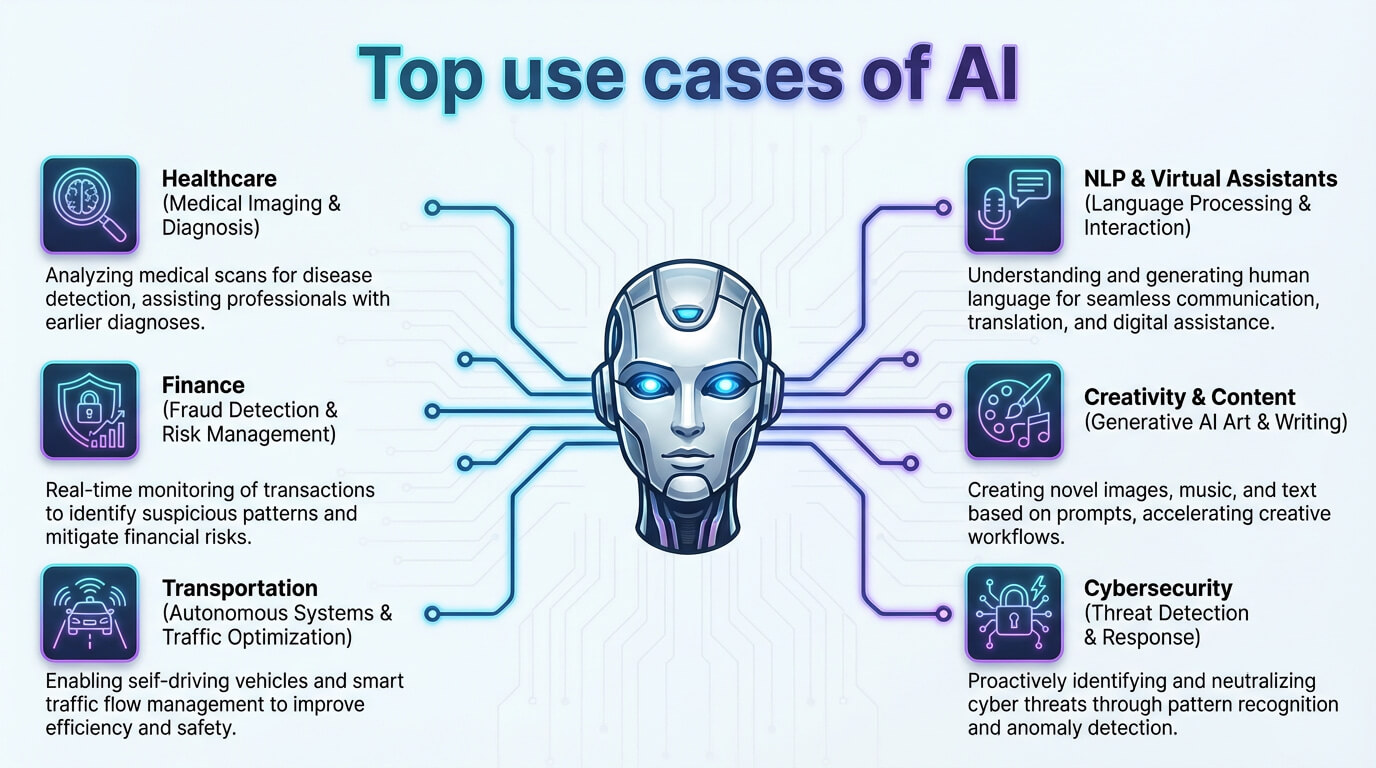
The uses of artificial intelligence include fraud prevention, agriculture, business, education, media, robotics and surveillance, as well as healthcare, transportation, customer service, finance, supply chain management, creative industries, and scientific research.
10 applications of artificial intelligence in 2025 are outlined below.
- Generative media for marketing: AI creates unique visuals, short videos, and ad variations tailored to audience preferences. For example, a retail brand produces multiple ad formats for a single product launch using generative AI. The measurable outcome is faster campaign rollout with consistent branding.
- Synthetic avatars and voice: AI-driven avatars and voice models engage customers through apps, banking portals, and e‑commerce platforms. For example, a telecom company offers a virtual AI agent that explains billing in local languages. The measurable outcome is more engaging and scalable customer interaction.
- Call center summarization: AI listens to customer calls and generates concise summaries for service agents and CRM systems. For example, a support center uses AI to automatically log action items after each call. The measurable outcome is reduced manual data entry and quicker follow‑up.
- Software development copilots: AI supports programmers by suggesting code structures, debugging, and generating documentation. For example, a development team uses an AI copilot to draft secure login modules. The measurable outcome is faster release cycles with fewer coding errors.
- Research assistants: AI processes vast academic and business datasets, surfacing key insights for decision‑makers. For example, scientists use AI to summarize the latest medical studies into quick reference notes. The measurable outcome is less time spent on research and more focus on innovation.
- Structured data extraction: AI converts unstructured documents into usable data points for operations. For example, an insurance provider uses AI to extract claim details from handwritten forms. The measurable outcome is faster approvals with fewer clerical mistakes.
- Risk monitoring in finance: AI actively scans transactions, market patterns, and compliance documents for hidden threats. For example, an investment firm uses AI to detect unusual trading activity before it escalates. The measurable outcome is lower financial exposure and quicker risk response.
- Healthcare and medical imaging: Hospitals apply AI for diagnosis, treatment predictions, and scan analysis. For example, AI identifies early‑stage lung abnormalities from CT (computerized tomography) images. The measurable outcome is earlier treatment planning that improves patient recovery chances.
- Manufacturing automation: Factories use AI robots and sensors for predictive maintenance and quality assurance. For example, AI predicts machine part failures in advance to schedule timely repairs. The measurable outcome is minimized downtime and consistent output quality.
- Customer service chatbots: AI chatbots handle routine queries and escalate complex cases to humans with context included. For example, a travel company’s AI bot instantly reschedules flights and updates customers. The measurable outcome is shorter wait times and higher customer satisfaction.
The key applications of artificial intelligence in 2025 are visualized below.
How do we use AI in our daily lives?
10 uses of artificial intelligence in daily life are outlined below.
- Smart AI home devices: Smart speakers, thermostats and lights use AI to automate routines, recognize voice commands and optimize comfort in homes.
- Digital assistant: AI voice activated digital assistants like Siri, Alexa and Google Assistant help schedule tasks, answer questions and manage reminders.
- Banking: AI detects fraudulent transactions, offers personalized financial advice and powers chatbots for instant customer support in banking apps.
- Self driving automobile: Advanced driver assistance systems and autonomous vehicles use AI to interpret sensor data, guide traffic navigation and allow safer driving.
- Communication: Email filters, autocorrect and real time language translation apps use AI for smarter communication and error free messaging.
- Social media: AI curates newsfeeds, suggests friends, filters content and detects harmful behavior on platforms like Facebook, Instagram and Twitter.
- Online shopping: AI recommends products, personalizes shopping experiences and powers chatbots in e-commerce platforms for customer assistance.
- Navigation apps: Maps and GPS navigation apps use AI to update traffic conditions, estimate arrival times and provide optimal routes in real time.
- Search engine: AI algorithms improve search accuracy, rank results and suggest relevant content when users browse the internet.
- Text editing: AI powered tools offer grammar correction, style suggestions and plagiarism checks which improve the quality of writing for emails, documents and posts.
How is AI being used in business?
7 uses of artificial intelligence in business are outlined below.
- Content generation: AI tools produce articles, marketing copy, product descriptions and even multimedia content which saves time and improves creative campaigns.
- Customer service: Chatbots and virtual assistants provide 24/7 support, answer questions and resolve issues instantly which improves customer engagement and satisfaction.
- Efficient workflow: AI automates repetitive tasks, manages documents and optimizes operations which increases productivity and reduces errors throughout the organization.
- Market research: AI analyzes large datasets to identify trends, forecast demand and deliver actionable insights which allows smarter, data driven business strategies.
- Security: Businesses use AI to detect cybersecurity threats, monitor systems and prevent fraud by quickly identifying unusual activities and potential risks.
- Decision making: AI systems support leadership with predictive analytics, scenario simulations and real time data analysis which aids faster and informed strategic decisions.
- Talent acquisition: AI helps HR teams screen applications, assess skills and match candidates which reduces bias and improves hiring processes for top talent.
Can AI be used for marketing?
Yes, artificial intelligence (AI) can be used for marketing because it streamlines task automation and improves data analysis to guide decisions. Marketers use AI in marketing to personalize campaigns, improve team efficiency, and optimize resources. AI-driven insights strengthen a marketing campaign by predicting trends while boosting customer experience. This assures brands connect better with audiences and drive measurable growth.
Can AI be used for content marketing?
Yes, artificial intelligence (AI) can be used for content marketing because it automates repetitive tasks, analyzes large volumes of data for actionable insights and optimizes marketing campaigns for better results. AI improves customer experience through personalized content, improves team efficiency by handling audience segmentation, predicts customer behavior and helps marketers create targeted and effective campaigns, all leading to smarter, data driven marketing decisions.
Should AI be used in healthcare?
Yes, AI should be used in healthcare because it improves the quality of care through faster and more accurate disease diagnosis. An AI system supports medical image interpretation which helps doctors detect conditions earlier. Usage of AI in healthcare also aids treatment selection, improves patient outcomes, and reduces errors which makes healthcare efficient, reliable, and responsive to individual needs.
What are the future uses of AI?
4 future uses of artificial intelligence are outlined below.
- Scientific discovery: AI accelerates scientific breakthroughs by analyzing massive datasets, modeling complex systems and helping discoveries in medicine, climate and physics.
- Robotics: AI powered robots perform advanced tasks like surgery, elderly care, manufacturing and space exploration which improves precision, safety and scalability.
- Communication: AI revolutionizes global communication through real time language translation, emotion aware virtual assistants and advanced human machine interfaces for seamless cross cultural interaction.
- Applications: AI transforms sectors using autonomous transport, personalized education, precision agriculture and intelligent cybersecurity which improves efficiency, sustainability and life quality.