AI analytics is the use of artificial intelligence technologies to analyze and interpret complex data, which represents a major shift from traditional data analysis. AI powered and AI driven analytics automate and improve the process of generating insights from vast and varied datasets. This allows people to make faster and smarter decisions in industries such as healthcare, finance, retail, manufacturing, transportation, energy and education.
Artificial intelligence analytics combines elements such as machine learning, deep learning, natural language processing (NLP) and automation tools. These components work together to identify patterns, make predictions and deliver actionable insights with minimal human intervention. AI analytics involves core steps such as data input and processing, machine learning algorithms, pattern recognition and prediction, decision making and analysis and action execution.
There are various types of AI analytics, including machine learning, deep learning, NLP, computer vision and generative AI. The applications of AI analytics include automated reporting, anomaly detection, big data analysis, customer personalization, diagnostic analytics and extracting insights from unstructured data like text, images and videos.
The benefits of AI analytics include improved speed and accuracy, real time analysis, deep insights and improved decision making processes. AI analytics faces challenges like issues with data quality, bias present in training data, lack of explainability and ethical concerns, despite having advantages.
What is AI analytics?
AI analytics is the integration of artificial intelligence technologies such as machine learning (ML), natural language processing (NLP) and deep learning networks into the data analysis process. It analyzes structured and unstructured data to identify patterns, trends and actionable information faster and more accurately than traditional manual methods.
The examples of AI analytics include predictive analytics, image and video analysis, AI driven insights and natural language processing for sentiment analysis.
AI analytics extracts insights from large and complex datasets, predicts outcomes and optimizes business operations. AI analytics reveals hidden patterns and correlations by automating data analysis for more proactive decisions and streamlined operations. It democratizes advanced analytics, reduces reliance on data specialists and supports businesses for faster responses to market, customer and operational changes.
What is the relationship between AI and analytics?
The relation between artificial intelligence and analytics is that analytics extracts insights from data and artificial intelligence uses those insights to predict outcomes, automate decisions and optimize actions. Analytics focuses on collecting, processing and interpreting data to extract insights and artificial intelligence brings advanced capabilities like pattern recognition, prediction and automation to the analytical process.
AI analytics is improved with routine automation such as data preparation, cleansing and modeling, which increases processing speed and reduces manual effort. Machine learning in AI analytics finds hidden patterns, predicts outcomes and delivers real time insights beyond the reach of conventional methods. Natural language processing (NLP) allows analytics to analyze unstructured data, such as customer feedback and social media posts, which gives contextual understanding and richer insights.
AI supports analytics with predictive and prescriptive decision making that shifts organizations from reactive to proactive strategies by predicting trends, prescribing optimal actions and continuously learning from new data. Artificial intelligence in data analytics supports faster, more accurate and evidence based business decisions. The examples of AI augmenting analytics are optimizing supply chains, personalizing customer experiences and identifying fraudulent transactions.
What is the history of AI analytics?
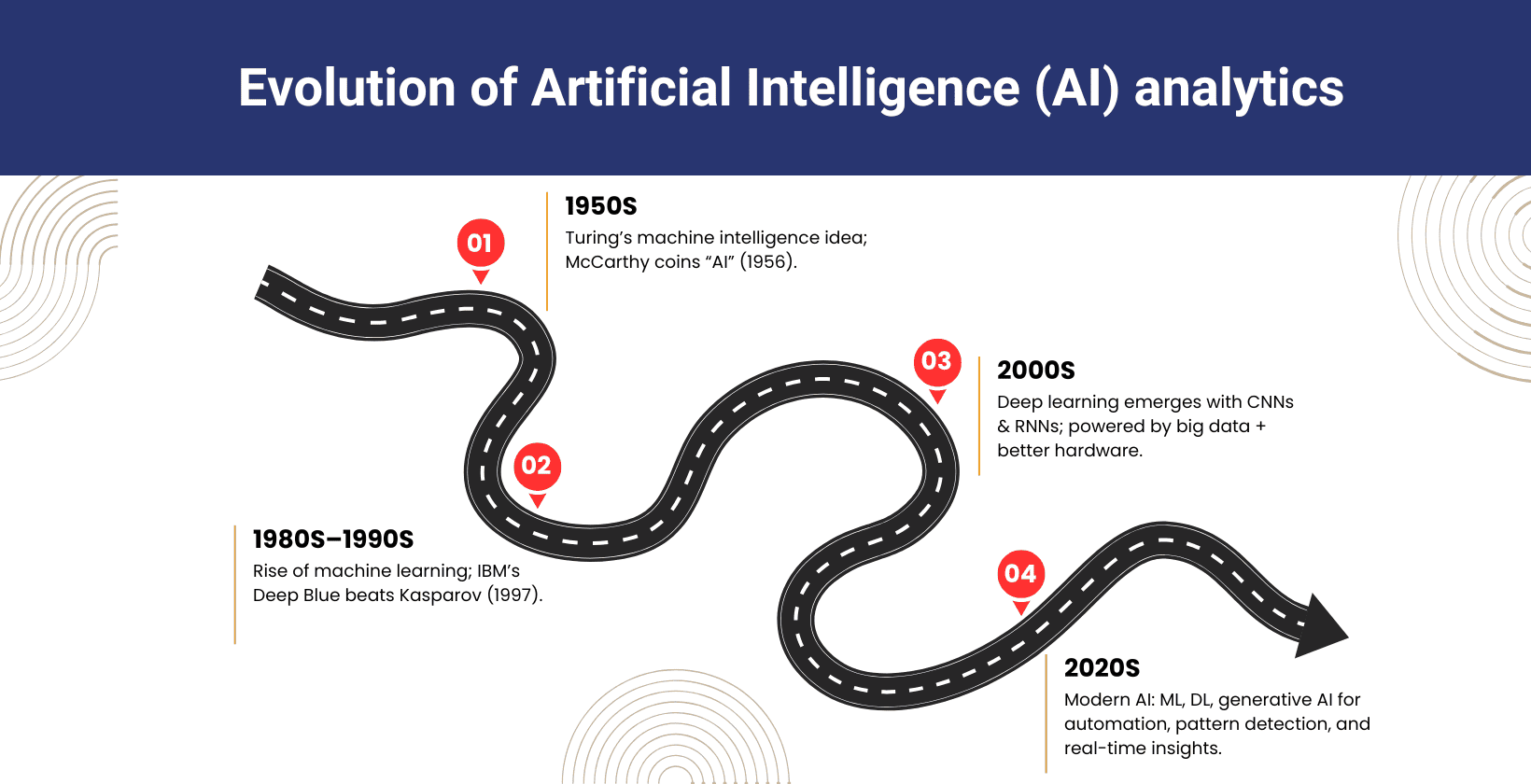
The history of AI analytics began in the 1950s when Alan Turing conceptualized machine intelligence and John McCarthy introduced the term “artificial intelligence” at the 1956 Dartmouth Conference. AI research focused on symbolic reasoning, expert systems and basic neural networks that faced limitations due to insufficient data and low computational power. The 1980s and 1990s introduced machine learning algorithms that led to practical applications, such as IBM’s Deep Blue, which defeated the world chess champion in 1997.
AI analytics adoption increased when organizations used it to improve process efficiency, customize client interaction and support large scale decisions based on factual data. AI analytics drives business intelligence by converting raw datasets into structured insights that guide strategic planning and influence organizational decisions globally.
Modern AI analytics uses machine learning, deep learning and generative AI to automate data preparation, detect patterns, generate synthetic data and provide real time insights across industries such as healthcare, finance and marketing. Deep learning emerged in the 2000s as computational resources increased, which allowed neural network models like convolutional networks and recurrent networks. It processes unstructured data such as images and texts with high accuracy, which transforms analytics in healthcare, finance, marketing and other sectors.
The development timeline of AI analytics is visualized below.
What are the elements of AI Analytics?
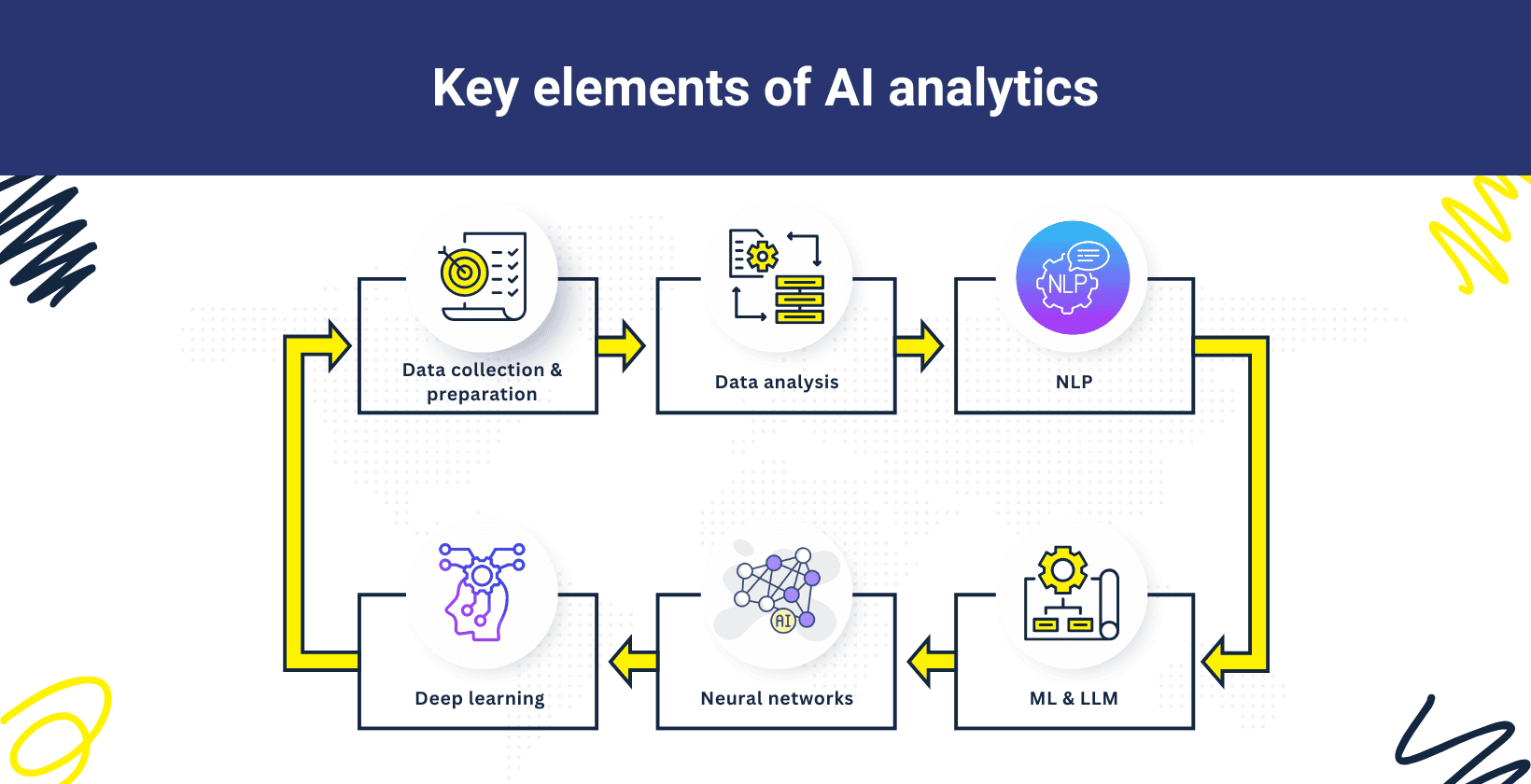
The elements of AI analytics are data collection and preparation, data analysis, natural language processing (NLP), machine learning (ML), large language models (LLMs), neural networks and deep learning.
The elements of AI Analytics are given below.
- Data collection and preparation: AI analytics collects, cleans and organizes data from multiple sources like websites, apps, sensors and social media platforms to assure quality and accuracy for analysis and model training.
- Data analysis: AI analytics applies statistical and computational techniques to explore, interpret and extract insights from data and support evidence based decisions.
- Natural language processing (NLP): AI analytics uses NLP to allow machines to understand, interpret and generate human language, which facilitates the analysis of text and speech data such as reviews or social content.
- Machine learning (ML): AI analytics uses machine learning to recognize patterns, predict outcomes and automate decisions based on data without explicit programming.
- Large language models (LLMs): AI analytics utilizes LLMs, which are trained on vast text datasets to understand, generate and analyze human language in business tasks.
- Neural networks: AI analytics uses neural networks modeled on human brain architecture to process data, learn complex patterns and improve prediction accuracy.
- Deep learning: AI analytics applies deep learning, a subset of ML using multi-layered neural networks, to learn from large datasets and perform tasks like image, speech and text analysis.
The core elements of AI analytics are visualized below.
How does AI analytics work?
AI analytics uses advanced algorithms and machine learning to convert raw data into actionable insights and automated decisions. The process includes key steps such as data input and processing, machine learning model training, real time analysis and execution of intelligent decisions.
The 5 steps on how AI analytics works are listed below.
- Data input and processing: AI analytics begins with collecting data from multiple sources, cleaning, integrating and transforming it into a consistent format suitable for analysis, maintaining quality and reliability for subsequent steps.
- Machine learning algorithms: AI analytics applies machine learning algorithms to the processed data, training models to learn patterns, relationships and trends, improving accuracy and predictive power over time.
- Pattern recognition and prediction: AI analytics identifies hidden patterns, trends and anomalies in data, then predicts future outcomes or behaviors based on learned relationships to support proactive business strategies.
- Decision making and analysis: AI analytics generates actionable insights and recommendations that allow users to analyze scenarios, evaluate options and make informed decisions based on data at scale.
- Action execution: AI analytics automates or supports the execution of recommended actions, integrating with business systems to implement decisions and continuously monitor results for improvement.
The diagram below shows how AI analytics works.
1. Descriptive analytics
Descriptive analytics applies statistical measures such as mean, median and variance, with data visualization techniques like charts and dashboards, to analyze and summarize historical or current data, describing past or present events and answering "what happened?”.
Descriptive data examples include sales reports, website traffic summaries, KPI dashboards, customer satisfaction surveys and financial statements. The features of descriptive analytics include data aggregation, historical analysis, the use of statistical measures such as mean, median and variance and clear data visualization through charts, dashboards and tables.
Descriptive analytics provides a clear snapshot of business performance, allows organizations to identify trends and patterns, supports decision making based on data and establishes the basis for advanced analytics like predictive and prescriptive analysis.
2. Diagnostic analytics
Diagnostic analytics is an advanced form of data analysis that identifies the causes of trends, patterns, or anomalies in historical data, answering the question “Why did it happen?”. Diagnostic analytics examples include the analysis of why sales dropped in a quarter, identifying the causes of increased customer churn, or why a marketing campaign underperformed.
Data analytics helps organizations identify problems, refine strategies and make informed decisions by uncovering the factors driving outcomes. The key features of diagnostic analytics include data drill down, correlation, regression and anomaly detection, which support root cause analysis and connect patterns to results.
Diagnostic analytics works by the collection and preparation of relevant data, followed by the application of techniques such as hypothesis testing, statistical analysis and data visualization to uncover relationships and causal factors. Common techniques of diagnostic analytics include correlation analysis for identifying relationships between variables, regression analysis for understanding how factors impact outcomes, root cause analysis for finding the origin of issues and data drilling for exploring data at deeper levels.
The use cases of data analytics span industries, such as healthcare for identifying disease patterns, finance for analyzing fraud triggers, retail for understanding customer behavior and IT for pinpointing system bottlenecks. Diagnostic analytics benefits organizations to address the true causes of problems, optimize operations, minimize risks and make objectives and support decision making for continuous improvement.
3. Predictive analytics
Predictive analytics is the practice of using historical and current data, statistical algorithms and machine learning techniques to estimate future outcomes and answer the question, "What might happen?”.
Predictive analytics works to collect and prepare relevant data, whereas AI improves analytics through a data automation process, increased efficiency and supports real time, scalable analysis of datasets. It excels at recognizing patterns, uncovering deep insights and generating accurate predictions.
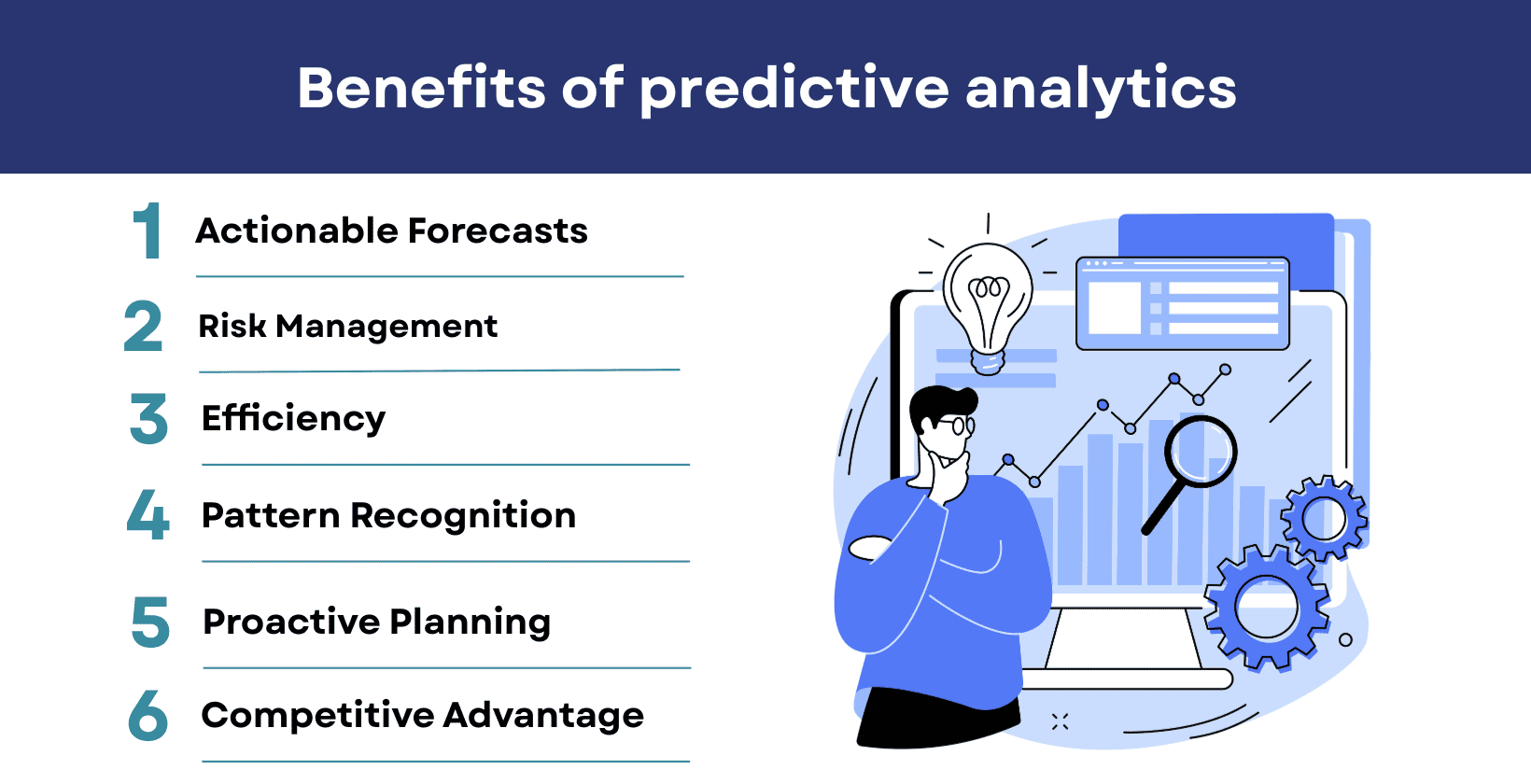
The benefits of predictive analytics include improved decision making through actionable forecasts, improved risk management through early identification of potential issues and increased efficiency through proactive strategies and optimized resource allocation. Organizations move from reactive to proactive planning and gain a competitive edge in their industries by using AI and predictive analytics.
The predictive analytics process and benefits are visualized below.
4. Prescriptive analytics
Prescriptive analytics is an advanced form of data analytics that uses historical data, advanced algorithms and machine learning to recommend optimal actions or strategies, directly answering the question, “What should we do?”. It suggests specific actions to achieve goals or avoid negative outcomes.
The examples of prescriptive analytics include recommendations that personalize treatment plans in healthcare, optimize investment portfolios in finance, improve inventory management in retail and improve route planning in logistics.
Prescriptive analytics integrates data collection, predictive modeling and decision optimization. It combines structured and unstructured data, uses predictive models to forecast scenarios and applies optimization algorithms like linear programming, simulation and decision trees to evaluate actions and their trade offs.
The benefits of prescriptive analytics allow informed decision execution, improve operational efficiency, reduce costs, improve risk management, personalize services and help organizations achieve their goals in changing business conditions.
What are the applications of AI in analytics?
The applications of AI analytics in analytics are listed below.
- Machine learning: AI analytics algorithms learn from historical data to identify patterns, classify information and make predictions for improved business outcomes.
- Deep learning: AI analytics uses neural networks with multiple layers to automatically extract complex features, recognize patterns and improve predictive analytics, especially for unstructured data.
- Natural language processing (NLP): AI analytics allows machines to understand, process and analyze human language, which makes it possible to extract insights from text, speech and documents.
- Automating data management: AI analytics automates repetitive tasks like data cleaning, entry, integration and classification to improve data quality and free analysts for higher value work.
- Efficient big data analysis: AI analytics processes and analyzes massive, complex datasets quickly, uncovering trends, patterns and correlations not easily found manually.
- Diagnostic analytics: AI analytics identifies root causes and correlations within complex datasets, which allows more accurate and timely problem solving and root cause analysis.
- Anomaly detection: AI analytics automatically identifies data points or events that deviate from normal patterns and helps in fraud detection, system monitoring and quality control.
- Data visualization: AI analytics tools automate the creation of charts and dashboards, highlight trends and make large data sets more accessible and actionable.
- Generating insights and explanations: AI analytics extracts actionable insights from data and explains findings in human language, supporting better, faster decision making.
How to use AI in data analytics?
The steps to use AI in data analytics are given below.
- Define the analytics goals: Clearly state what you want to achieve with AI analytics, such as automating tasks, uncovering patterns, or making predictions.
- Choose the right AI tools and platform: Select an AI analytics platform that matches your data type, business needs and technical capabilities for optimal results.
- Collect and prepare data: Gather data from various sources, then clean, organize and preprocess it to guarantee quality and readiness for AI analysis.
- Use AI to explore and explain data: Leverage AI analytics to automate data exploration, identify underlying patterns and generate explanations for relationships within your data.
- Develop, train and validate AI models: Build AI models, train them on prepared data and validate their performance to guarantee accurate AI analytics and reliable predictions.
- Analyze, visualize and automate reporting: Use AI analytics to create visualizations, generate automated reports and present insights in accessible formats for stakeholders.
- Make data driven decisions: Apply AI analytics and AI generated insights to inform strategies, optimize operations and support business decisions with evidence based recommendations.
- Continuously monitor and improve: Regularly track model performance, update data and refine AI analytics systems to maintain accuracy and adapt to changing needs.
How to use AI for business analytics?
The steps to use AI for business analytics are given below.
- Focus on strategic alignment: Align AI analytics initiatives with the overall business strategy to secure AI analytics projects directly support organizational goals and measurable outcomes.
- Develop AI literacy: Invest in training to build AI analytics and data literacy that allow employees to understand, trust and effectively use AI analytics driven insights.
- Collaborate with stakeholders: Engage business leaders, IT and end users to define requirements, resolve issues and encourage adoption of AI analytics solutions.
- Identify AI friendly tasks: Pinpoint repetitive, data heavy, or predictive tasks where AI analytics automate processes, improve accuracy and deliver measurable business value.
- Choose the right AI tools: Select AI analytics tools that fit your needs, integrate with existing systems and offer scalability, usability and strong support.
- Automate data preparation and reporting: Use AI analytics to clean, organize and process data and to generate automated, real time reports and dashboards for faster, more accurate decision making.
- Allow self service analytics: Deploy AI analytics powered platforms that let non technical users independently explore data, extract findings and build data visual representations.
- Improve customer experience with personalization: Use AI analytics to analyze customer data and deliver personalized recommendations and interactions to increase retention.
- Optimize operations and risk management: Apply AI analytics for predictive analytics, anomaly detection and process optimization to reduce costs, manage risks and improve efficiency.
- Continuously improve through machine learning: Retrain AI analytics models such as classification, regression and clustering with new data, monitor performance and refine processes to maintain accuracy and adapt to changing business needs.
- Anticipate future trends and demand: Use AI analytics forecasting and trend analysis to predict market shifts, customer needs and resource requirements, which allows proactive business planning.
What are the benefits of using AI in analytics?
The benefits of using AI in analytics are given below.
- Improved speed, scalability and efficiency: AI analytics automates data processing and analysis, handling datasets and scaling effortlessly as data grows, which increases productivity.
- Superior accuracy and reduced human error: AI analytics reduces errors in data analysis and reporting by minimizing manual intervention, which guarantees more reliable, precise and consistent results.
- Deep insight and pattern discovery: AI analytics uncovers complex patterns, correlations and trends within large, diverse datasets, revealing business opportunities and risks that traditional analytics might miss.
- Advanced predictive analytics and forecasting: AI analytics uses advanced models to anticipate future trends, customer behaviors and market shifts that allow proactive planning and more accurate business forecasting.
- Real time analysis and adaptability: AI analytics processes and analyzes data in real time, allowing organizations to respond quickly to changes and make agile, informed decisions.
- Comprehensive data integration and quality: AI analytics integrates and cleanses data from multiple sources, which improves data quality and provides a unified, comprehensive view for better analytics.
- Authorized decision making and communication: AI analytics gives actionable insights, democratizes access to analytics and supports better communication of findings that allow faster, more confident decision making across the organization.
What are the challenges of AI in analytics?
The challenges of AI analytics are data quality and integration, bias in training data, resource intensive computing, lack of explainability, ethical concerns, legal and privacy issues and scalability issues.
The challenges of AI analytics are listed below.
- Data quality and integration: AI analytics models depend on clean, consistent and real time data and poor quality, fragmented, or delayed data leads to unreliable insights and failed AI analytics initiatives.
- Bias in training data: If training data is incomplete, unbalanced, or biased, AI analytics models amplify these biases, resulting in unfair or inaccurate AI analytics predictions and decisions.
- Resource intensive computing: AI analytics requires substantial computational power and storage, making AI analytics costly and challenging for organizations without the budget to support it.
- Interpretability and lack of explainability: AI analytics models, deep learning, are “black boxes,” making it difficult for users to understand or trust their AI analytics recommendations and decisions.
- Ethical concerns and bias: AI analytics systems inadvertently perpetuate discrimination, privacy violations, or unethical outcomes, if not monitored for fairness, transparency and responsible use of AI analytics.
- Legal and privacy issues: Handling sensitive data in AI analytics raises compliance risks with data protection laws, requiring strict governance, security and audit trails to avoid legal penalties from AI analytics operations.
- Scalability issues: Managing and processing ever growing, complex datasets at scale leads to performance bottlenecks, integration failures and increased operational complexity for AI analytics platforms.
Is AI a threat to data analytics?
No, AI is not a threat to data analytics, because it transforms and improves the field as it automates routine tasks, processes datasets quickly, improves the accuracy of predictions and delivers insights in real time. It introduces several challenges, such as potential job displacement in roles, bias and fairness issues that distort outcomes, security vulnerabilities that require mitigation, a lack of explainability that reduces transparency and privacy concerns that demand responsible management.
Can AI replace a data analyst?
No, AI cannot replace data analysts, but it transforms their roles. AI performs routine tasks and accelerates data processing, but it does not replicate human insight, critical thinking, accountability, or the capacity to interpret complex business contexts. Data analysts provide context to results, assure ethical oversight, resolve issues and develop evolving skill sets that align with business needs and technological advances.
How does Gen AI affect data analytics?
Generative AI reshapes data analytics through complex tasks automation, improved predictive accuracy and makes insights more accessible to a broader audience. Generative AI automates data preparation and cleaning, reducing manual effort and improving data quality. Generative AI delivers real time, scalable insights through the datasets, democratizes analytics via natural language interfaces accessible to non technical users and improves innovation.
Should Generative AI be used for data analysis?
Yes, generative AI should be used for data analysis because it offers major advantages like automated data preparation and cleaning, generating synthetic data for robust modeling, improving predictive analytics and repetitive tasks. Gen AI permits faster insights, improves data quality, supports anomaly detection and code generation and motivates users with advanced data visualization and real time, actionable recommendations for better decision making.
Are there any differences between AI and traditional analytics?
Yes, there are differences between AI and Traditional analytics. AI powered analytics automates data processing, handles large and unstructured datasets, gives real time and predictive insights and adapts to new information, whereas traditional analytics relies on manual processes, structured data and retrospective analysis. AI excels in scalability, automation and forecasting, while traditional analytics offers simpler, more interpretable models and focuses on historical trends.
What are the artificial intelligence (AI) analytics tools?
The artificial intelligence (AI) analytics tools are listed below.
- Power drill AI
- Tableau
- Microsoft Power BI
- Polymer
- Julius AI
- Simple Analytics
- Akkio
- MonkeyLearn
- Sisense
- Kanaries
- Qlik Sense
- Domo
- IBM Cognos Analytics
- Google Looker
- TIBCO Spotfire
- Databricks Unified Data Analytics Platform
- KNIME Analytics Platform
- RapidMiner
- AgencyAnalytics
- Google Cloud AI Platform
- IBM Watson Analytics
- AnswerRocke
Can AI analytics tools be used in video analysis?
Yes, AI analytics tools can be used in video analysis. These tools automatically process video streams to detect objects, recognize actions and identify events in real time, transforming surveillance, safety and business intelligence. AI video analytics allows instant alerts, operational efficiency, improved security, customer behavior analysis and rapid investigation, making video data actionable across industries like retail, transportation, healthcare and smart cities.
How does AI enhance analytics?
AI enhances analytics through automation of data processing, increasing efficiency and real time, scalable analysis of datasets. It excels at pattern recognition, uncovering deep insights and generating accurate predictions. AI powered analytics improves decision making through timely delivery, actionable recommendations and continuous learning from new data, which refines its models and insights for ongoing accuracy and business value.