Image processing transforms images into digital data, improving visual clarity, reducing errors and extracting useful information for faster decision making. It enables automation, enhances image based applications and supports better outcomes in medicine and security.
Image processing comes in two main types, analog image processing and digital image processing. Image processing relies on interconnected components such as image sensors, processing hardware, computers, software, mass storage, hard copy devices and networks to capture, manipulate, store and share images seamlessly.
Image processing phases are image acquisition, pre-processing, enhancement, restoration, color processing, morphological processing, segmentation, representation, object recognition and compression. Image acquisition captures and stores images, while pre-processing removes noise, corrects defects and enhancement adjusts image attributes. Restoration recovers lost data, color processing balances visual details and morphological methods analyze pixel structures for accuracy. Segmentation separates regions, representation encodes them, object recognition identifies patterns and compression reduces image size for efficient storage.
Image processing applications cover medical imaging, remote sensing, computer vision and multimedia. Its benefits include increasing accuracy by detecting details, which lowers costs through early defect detection, providing real time updates for quick response, improving customer experience via better tracking, enhancing image quality for clearer visuals and automating repetitive tasks to boost workflow efficiency.
What is image processing?
Image processing is the conversion and manipulation of images into digital data using computer algorithms to enable analysis, enhancement, information extraction and overall improvement of visual quality. It started with digital image processing in the 1920s when newspapers sent pictures by submarine cable between London and New York. Image processing used a Bartlane cable picture transmission system to code and transmit images quickly. Digital image processing techniques grew in the 1960s with applications in medical imaging and satellite photos. Image analysis involves processing image data to extract important information. Online image processing uses the internet to manipulate images remotely. This technology shapes many fields by improving how images deliver information.
What are the types of image processing?
There are two types of image processing, including analog image processing and digital image processing. Analog handles continuous signals in photos or videos with basic adjustments, while digital uses pixel data and algorithms for segmentation, compression, enhancement and efficient storage.
2 types of image processing are given below.
- Analog image processing: Analog image processing processes analog signals using physical media like photographs or videos. It manages two dimensional signals mainly through electrical manipulation. Analog processing handles image intensity in continuous forms.
- Digital image processing: Digital image processing analyzes and modifies digital image signals composed of pixels. It supports complex tasks like segmentation and compression. Digital processing uses algorithms to enhance image quality and extract detailed information.
What are the components of image processing?
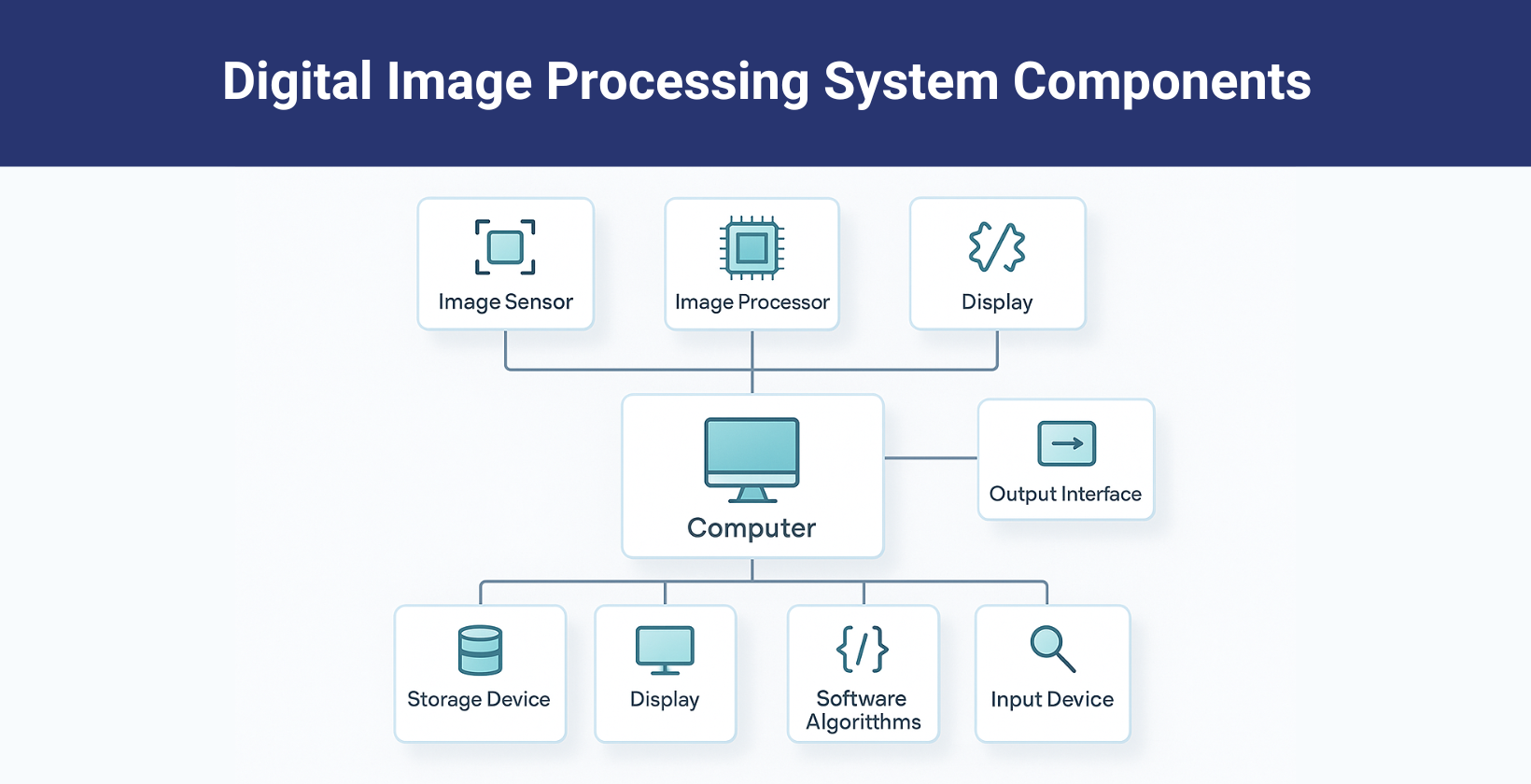
The components of image processing are image sensors, image processing hardware and a computer. These components enable efficient storage, retrieval and manipulation of images across different devices and platforms.
The components of image processing are given below.
- Image sensors: Image sensors detect light intensity and image details by converting photons into electrical signals using cameras and scanners as image acquisition devices.
- Image processing hardware: Image processing hardware uses specialized circuits to process data from sensors, delivers fast computation and outputs these results directly to computers.
- Computer: Computer runs general or specialized programs to analyze and manipulate images and accesses the knowledge database for further image processing.
- Image processing software: Image processing software contains algorithms and tools to modify and analyze images and users develop new functions directly within the software environment.
- Mass storage: Mass storage efficiently holds raw and processed image data temporarily or long term for retrieval.
- Hard copy devices: Hard copy devices convert digital data into physical images using printers and film recorders to create photographs, documents or graphics in tangible form.
- Network: Network connects all components for cloud communication and data transfer, enabling remote access and image sharing.
What are the phases of image processing?
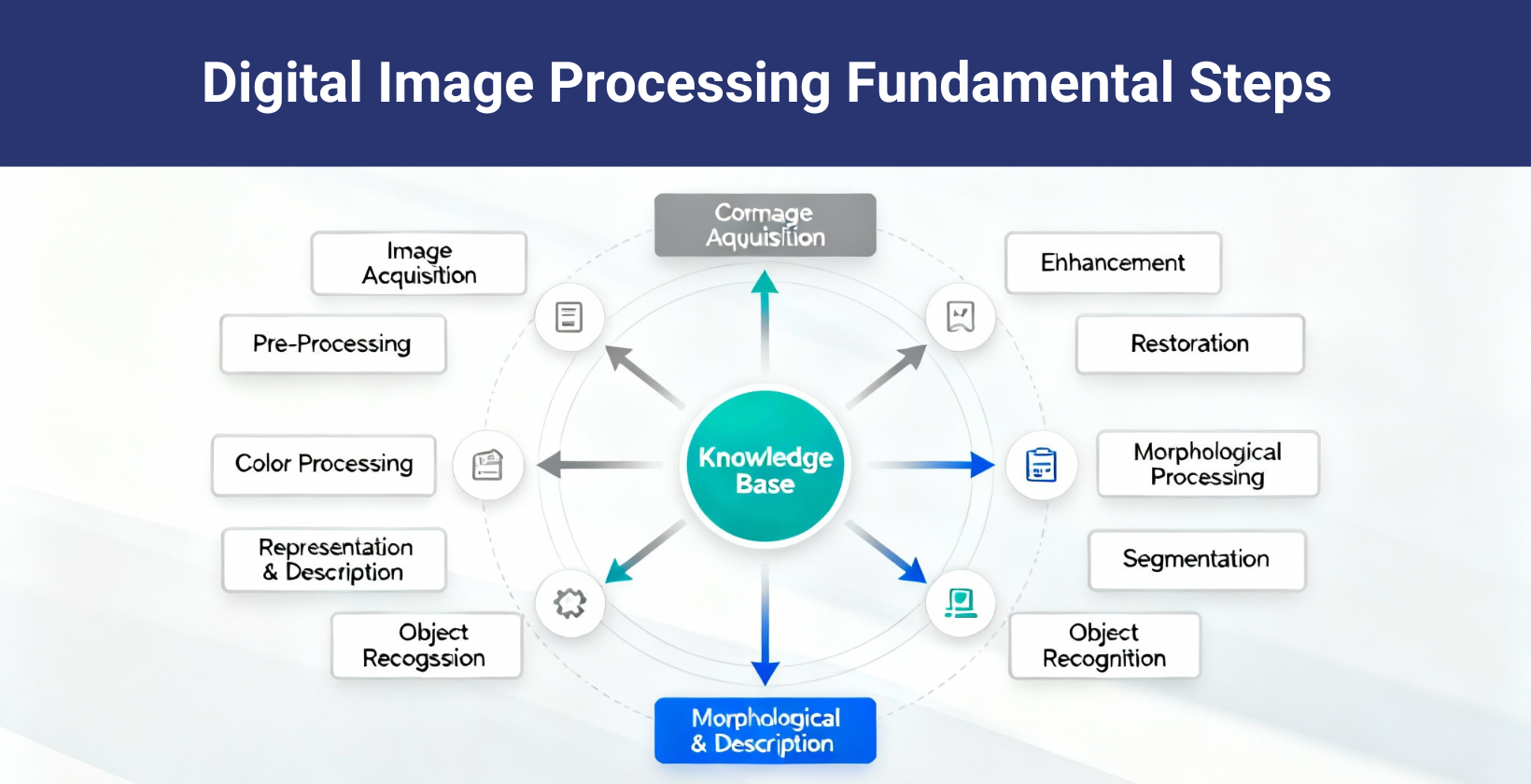
The phases of image processing are image acquisition, image pre-processing and image enhancement. These phases form a clear workflow that digital image processing algorithms use to manipulate and analyze pictures efficiently.
The 10 phases of image processing are given below.
- Image acquisition: Image acquisition captures digital pictures, transforms signals and stores them for future analysis, which forms the base of digital image processing.
- Image pre processing: Image pre processing removes noise or corrects distortions, which prepares each digital image for further steps in the computer image processing system.
- Image enhancement: Image enhancement improves clarity and highlights useful details by using algorithms to adjust features like contrast or color balance in an image processing workflow.
- Image restoration: Image restoration recovers lost or blurred data from digital pictures that fix errors caused by sensors, environment or transmission faults.
- Color image processing: Color image processing manipulates color channels to correct color balance and enhance visual information in digital image processing applications.
- Morphological image processing: Morphological image processing studies pixel structure for object identification in image processing algorithms, strengthening or removing particular shapes.
- Image segmentation: Image segmentation divides digital pictures into regions with similar properties, which allows focused analysis of smaller parts during image processing tasks.
- Representation and description: Representation and description convert segments into forms for knowledge base use, which enables systematic computer image processing workflows.
- Object recognition: Object recognition in image processing identifies meaningful patterns from processed segments, connecting digital image data to real world concepts or labels.
- Image compression: Image compression reduces data size for online image processing transmission, supporting storage, sharing and efficient use of resources in digital systems.
What are the applications of image processing?
The applications of image processing are medical imaging, remote sensing, computer vision and multimedia. Image processing plays a key role in improving diagnostic accuracy, enhancing environmental monitoring, enabling automated security systems and elevating multimedia content quality.
The applications of image processing are given below.
- Medical imaging: Medical imaging applies image processing to create clear medical visualization from scans like MRI and CT. It supports accurate diagnosis and surgical planning using advanced image software.
- Remote sensing: Remote sensing uses image processing to analyze data from image sensors on satellites and aircraft. It converts raw sensor data into detailed maps and reports for environmental monitoring and resource management.
- Computer vision: Computer vision employs image processing to interpret images and videos automatically. It facilitates object detection, facial recognition and scene analysis in security and surveillance systems.
- Multimedia and entertainment: Multimedia and entertainment integrate image processing for editing, enhancing and generating visual content. Image processing software improves film quality, special effects and interactive applications.
What are the benefits of image processing?
The benefits of image processing are increasing accuracy, cost savings and getting real time updates. It enhances customer experience and strengthens safety by improving defect detection, reducing waste, sharpening image quality and automating repetitive tasks.
The benefits of image processing are given below.
- Increased accuracy: Image processing improves the detection of details that human eyes might miss. This increased accuracy reduces errors in complex tasks like medical diagnosis and quality control, which provides reliable results.
- Cost savings: Image processing minimizes costs by detecting defects early in manufacturing. Early detection reduces waste, recalls and rework, which saves money and resources in production and service industries.
- Real time updates: Image processing delivers real time data in security and surveillance. Immediate updates enable quick reactions to incidents, which improves safety and operational efficiency in various fields.
- Improved customer experience: Image processing enhances customer experience by enabling faster, accurate inventory tracking and personalized services. Retailers use these capabilities to maintain product availability and support customer satisfaction.
- Enhanced image quality: Image processing sharpens image clarity for better visual analysis. Enhanced image quality supports critical applications in healthcare, remote sensing and multimedia production by providing clearer and more precise images.
- Automation: Image processing automates repetitive tasks such as inspection, categorization and monitoring. This automation increases workflow flexibility and frees human operators for higher level activities.
- Medical advancements: Image processing supports advanced medical imaging techniques. It improves visualization for diagnosis and treatment planning, enabling earlier disease detection and better patient outcomes.
- Safety applications: Image processing helps systems that monitor hazards and improve security. Technologies like autonomous vehicle sensors and surveillance cameras use these systems to enhance safety and prevent accidents.
What is the importance of the phases in image processing?
The importance of the phases in image processing lies in capturing structural and geometrical information, which is essential for visual perception and feature detection. It supports image registration with robustness to noise and distortions. Phase image guides feature detection and segmentation accurately. It prevents errors in reconstruction for clearer visual perception.
What is the main goal of image processing?
The main goal of image processing is to improve image quality for better human perception and enable processing systems to extract meaningful data. Human perception influences goals like noise reduction and image enhancement. Image processing systems enable machine understanding and image reconstruction for clearer results and better analysis. These goals allow processing systems to transform raw images into clearer, more useful forms for analysis or display.
Which language is used in image processing?
Python is used in image processing because Python supports fast prototyping and machine learning models with extensive libraries. MATLAB works well for mathematical models and image analysis. C++ handles low level hardware control and high speed applications. Java, R and Julia also appear frequently in image processing tasks because of their specialized libraries and strong community support.
What is ringing in image processing?
Ringing in image processing is the appearance of visible ripples near sharp edges, caused by the loss of high frequency components after low pass filtering. Truncation of frequency data creates oscillations, producing the ringing effect image. An example is JPEG compression, where ringing appears near text edges due to high frequency loss.
What is image pre-processing?
Image pre-processing is the stage of cleaning raw digital images by removing acquisition artifacts and correcting ringing effects. It improves image quality and standardizes them into a consistent format. Image pre-processing prepares data for subsequent machine learning algorithms, increasing accuracy and efficiency in image analysis. This step creates reliable and uniform inputs essential for advanced processing.
What is image post processing?
Image post processing is the process of changing raw photo data into a finished image by converting raw files into a usable format. Photographers adjust exposure, balance and contrast, color correction and sharpening. These adjustments enhance image quality and achieve a creative or technical goal. Post processing improves clarity and visual impact while correcting flaws. Image post processing converts raw photo files into finished images by adjusting exposure, balance, contrast, color and sharpness. This process improves image clarity and quality. Photographers use post processing for technical fixes and creative effects.
Is image processing a part of AI?
Yes, Image processing is a part of AI because it uses computer algorithms to analyze, enhance and manipulate digital images to extract useful information or improve visual quality. AI powered image processing improves accuracy in object recognition and enhancement tasks. AI in image processing expands capabilities beyond traditional methods, which makes processes faster and more precise. AI and image processing work together to advance visual data analysis and automation.
Does image processing require a GPU?
Yes, image processing requires a GPU because image processing involves computationally intensive tasks with large datasets. GPUs perform better with large datasets because they process multiple operations simultaneously. They deliver speed and efficiency for complex image transformations, while CPUs process tasks sequentially and slowly.
Can image processing be done on CPU only?
Yes, image processing can be done on CPU only because CPUs handle pixel level operations and sequential or limited parallel processing well. It manages complex transformations, but struggles with deep learning based image analysis. CPUs perform best on tasks with fewer parallel demands. Deep learning based image analysis benefits from specialized hardware beyond typical CPU limits.