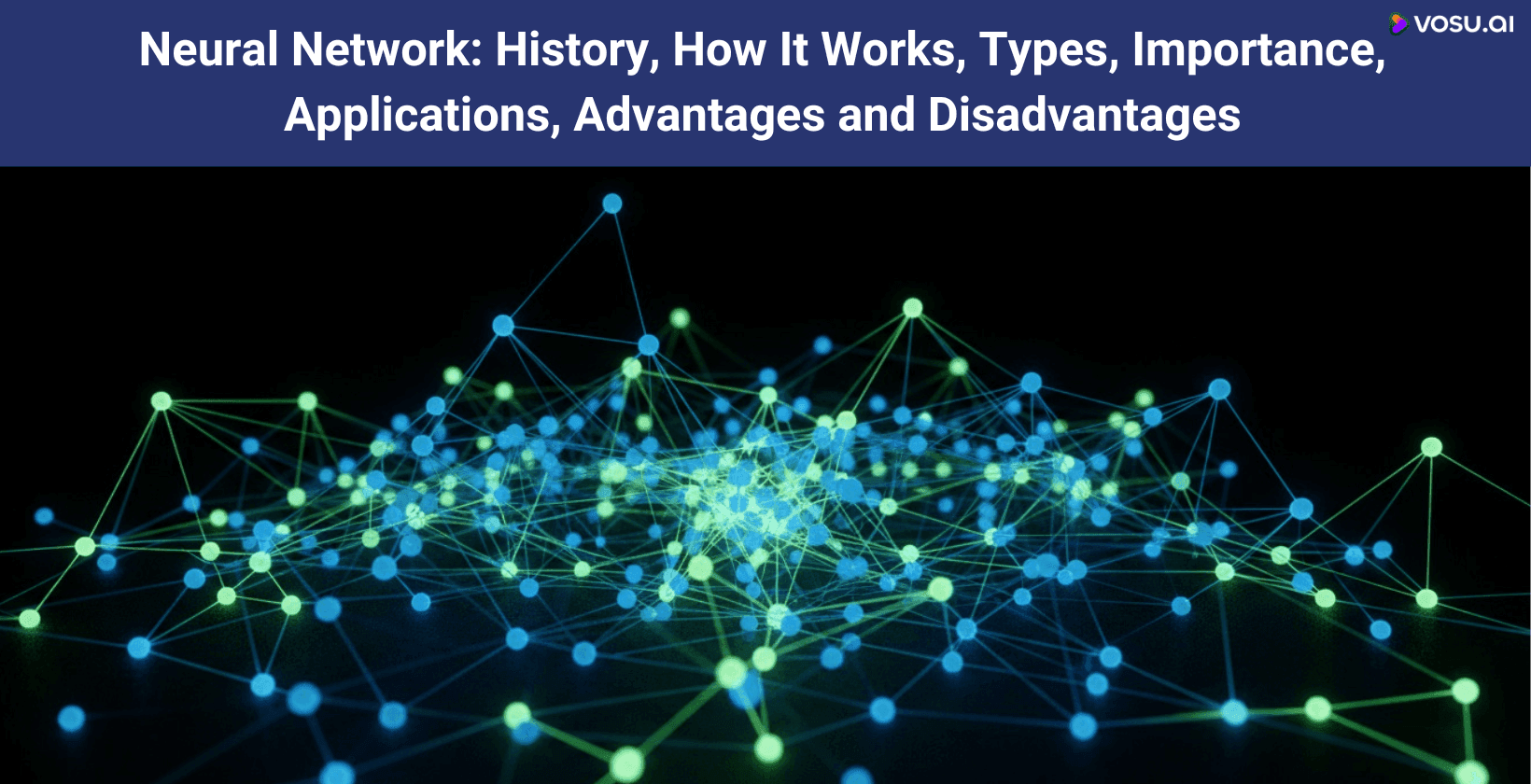
A neural network is an AI system that processes data through layers of interconnected nodes, similar to brain neurons. It recognizes patterns, adjusts weights during training and learns from labeled inputs to make accurate predictions.
Neural network history began in 1943 with McCulloch and Pitts’ model, followed by Hebbian learning in 1949 and Rosenblatt’s perceptron in 1958. The AI Winter happened in the 1970s to 80s, then progress resumed with backpropagation in 1986 and CNNs in 1989. Deep belief networks appeared in 2006, followed by AlexNet in 2012. Diffusion models emerged in 2022, alongside GPT-4 in 2023 and multimodal transformers like vosu.ai in 2024 to 25.
Neural networks process data through layered neurons using weighted sums and activation functions. They train with backpropagation, iteratively updating weights to minimize errors and improve accuracy in various tasks. They include convolutional neural networks (CNNs), recurrent neural networks (RNNs), generative adversarial networks (GANs), diffusion models and transformer networks that solve complex tasks through layered processing.
Neural nets are important because they solve nonlinear problems, adapt to changing data, and extract features automatically that allow scalable automation. Their applications extend across image and speech recognition, NLP, generative AI, cybersecurity, finance, healthcare, marketing and autonomous vehicles. Neural network training involves defining architecture, preparing data, initializing weights, forward propagation, calculating loss, backpropagation, updating parameters, evaluating performance and tuning hyperparameters for optimal results.
Neural networks also offer advantages such as nonlinear modeling, adaptability, parallel processing, automation and generalization. They also face disadvantages like high data requirements, computational costs, interpretability issues, overfitting, complexity and ethical risks.
What is a neural network?
A neural network, also known as artificial neural network (ANN) or neural net, is a computational model inspired by the structure and function of biological neural networks in the human brain. It is a fundamental concept in machine learning, designed to recognize patterns, make decisions and solve complex problems by mimicking the way neurons interact. It consists of interconnected layers of artificial neurons (or nodes) that process input data, perform computations and produce outputs.
Neural networks learn from data by adjusting the weights of connections between neurons, which improves their accuracy over time through training. Neural network application examples include medical imaging for detecting diseases like skin cancer or analyzing MRIs and self-driving cars, which process sensor data to make driving decisions. It is used in fraud detection in financial transactions, traffic accident prediction and agricultural tasks such as irrigation control and pest management.
What is the history of neural networks?
The history of neural networks began in 1943 when Warren McCulloch and Walter Pitts created a model of artificial neurons. Their model showed that networks of artificial neurons perform logical neural operations. Donald Hebb introduced a learning theory in 1949, known as Hebbian learning, where neural connections strengthen through repetition.
The perceptron, an early neural network, was developed by Rosenblatt in 1958. Minsky and Papert published Perceptrons in 1969, which highlighted limitations and led to the AI Winter in the 1970s to 1980s. Backpropagation revived interest in 1986 and the history of the convolutional neural network advanced in 1989 with LeCun’s CNN for handwriting recognition. Deep learning experienced a revival in 2006 with Geoffrey Hinton's deep belief networks, followed by the breakthrough of AlexNet in 2012.
Neural networks evolved into diffusion models such as Stable Diffusion, released in 2022 by researchers at Ludwig Maximilian University and Stability AI and Imagen, introduced by Google between 2022 and 2024. Around 2024 to 2025, multimodal transformer-based systems like vosu.ai began driving image, video and audio generation. Large language models such as GPT-4, released in 2023, share this evolutionary lineage.
How do neural networks work?
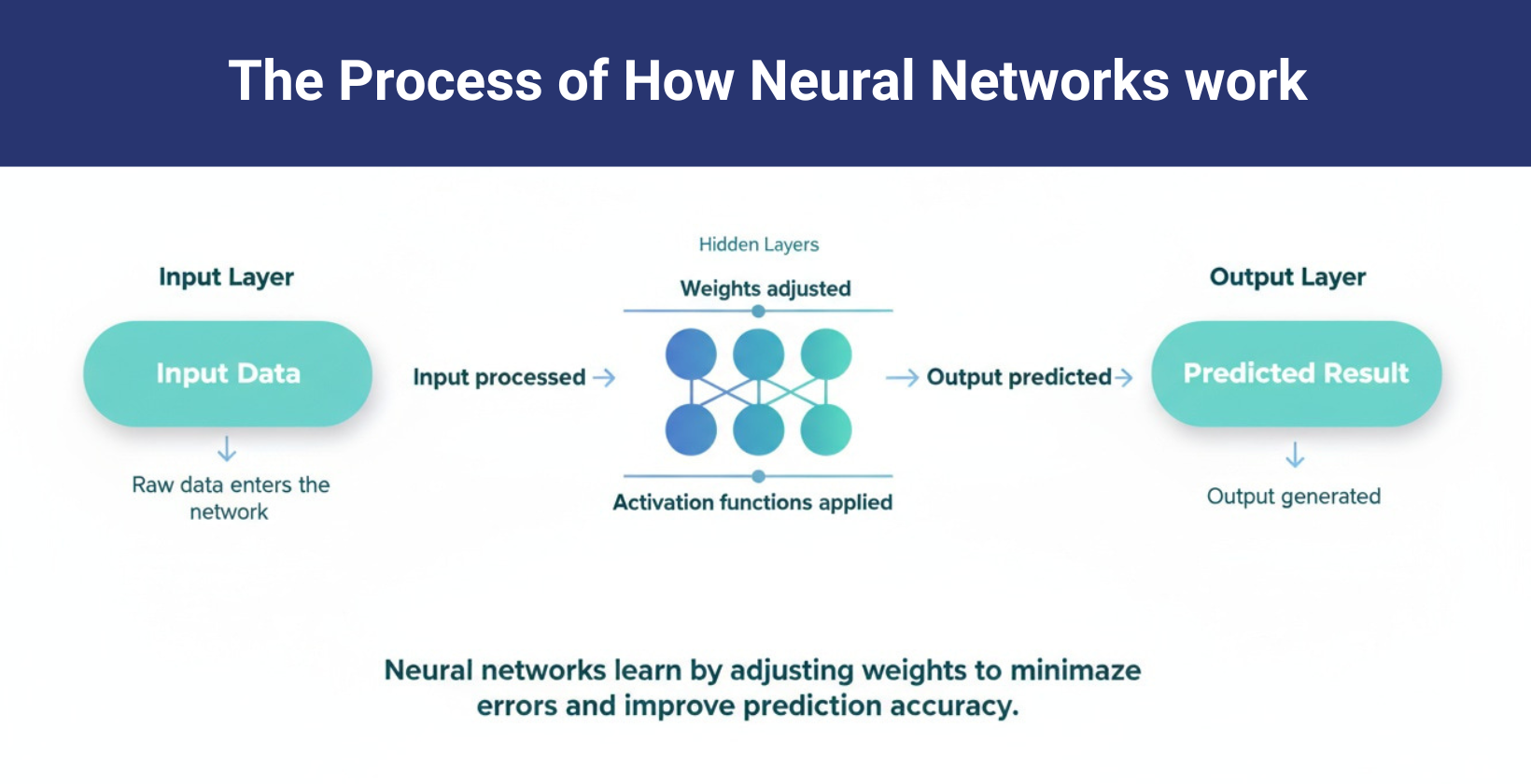
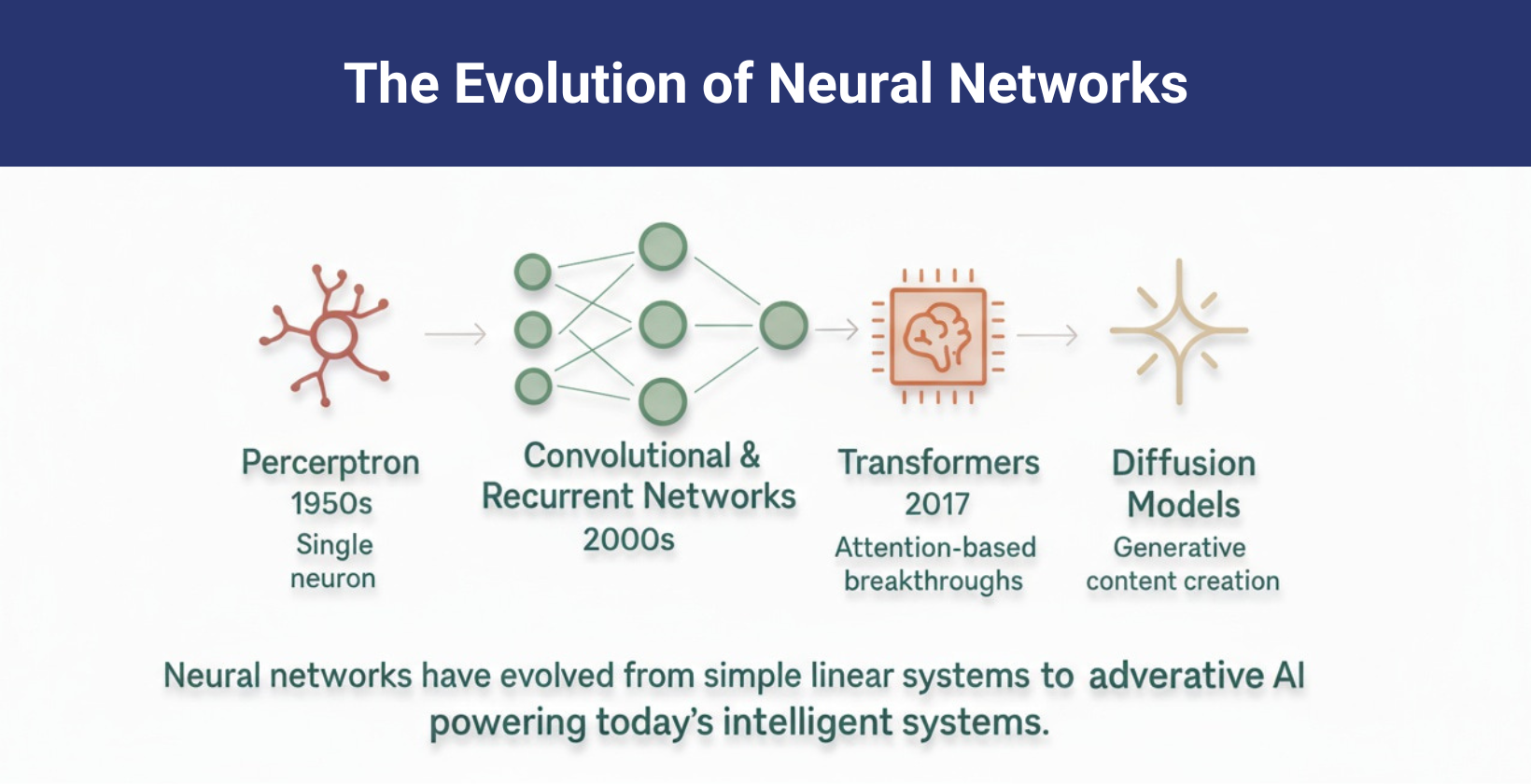
Neural networks work by processing information through interconnected artificial neurons arranged in layers. They use the input layer to receive raw data, apply weighted transformations in hidden layers, and generate predictions in the output layer. They connect each neuron with weights that regulate the strength of the signals.
The neural network combines input values as weighted sums z = ∑wᵢxᵢ + b during the feedforward phase and passes these sums through activation functions like ReLU or Sigmoid to add non-linearity. This non-linearity allows it to model complex patterns. It trains using backpropagation, where it computes the gradient of the loss function ∂L/∂w and updates weights with wₙₑw = wₒₗd − η⋅∇L, where η is the learning rate. It computes the neuron's output as a = f(z), with f representing the activation function. It iteratively updates weights to minimize prediction errors and improve accuracy in classification, regression and pattern recognition tasks.
The visual representation of the layers is shown below.
What are the types of neural networks?
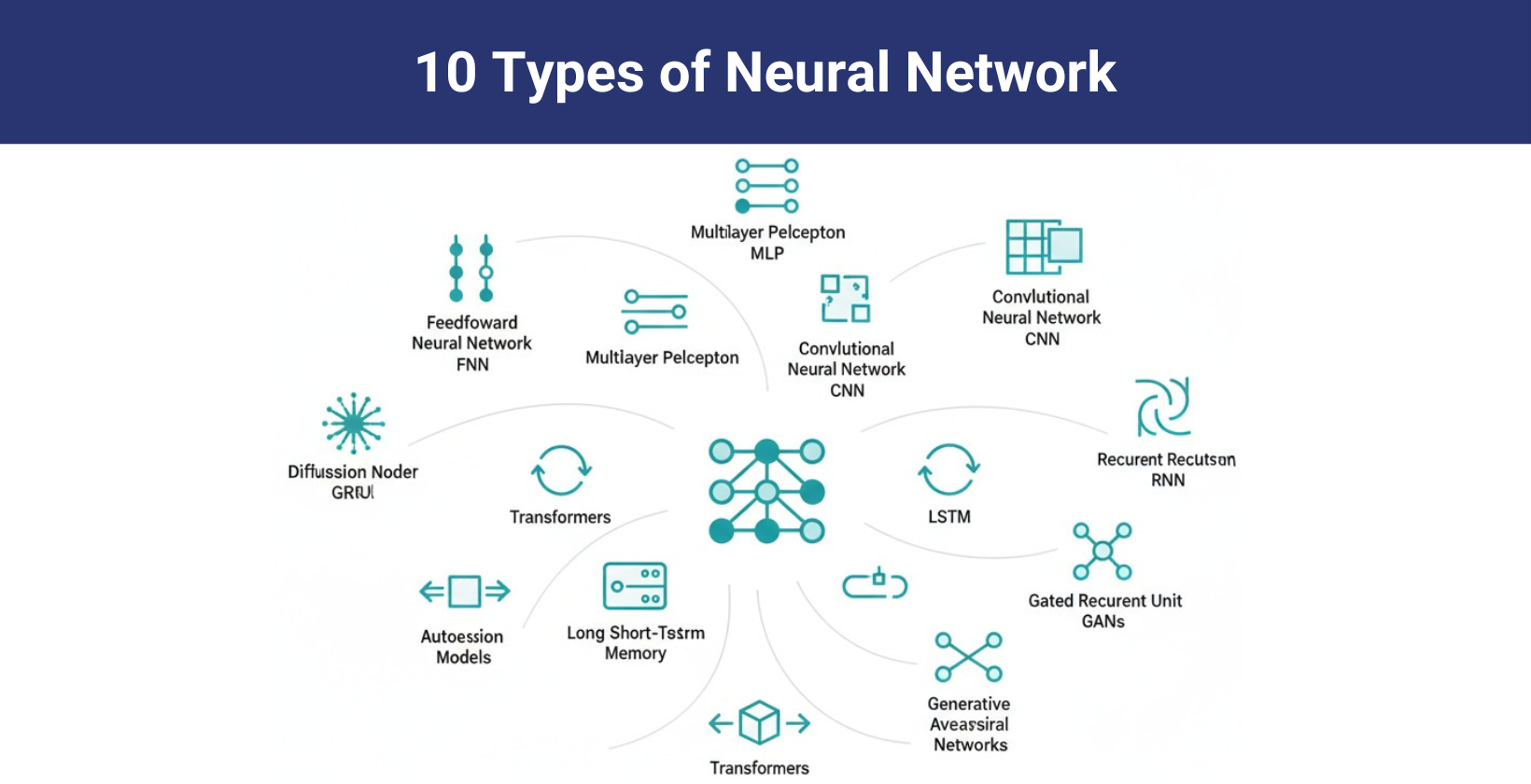
The types of neural networks include convolutional neural networks (CNNs), recurrent neural networks (RNNs), generative adversarial networks (GANs), diffusion models and transformer networks that solve complex tasks through layered processing. These systems mimic brain-like functions to recognize patterns, learn from data and generate accurate outputs for a wide range of applications.
10 main types of neural networks are given below.
- Convolutional neural networks (CNNs): CNNs process visual data through specialized layers that detect spatial patterns. These networks excel in image recognition, medical imaging and object detection by learning hierarchical features directly from pixel data.
- Recurrent neural networks (RNNs): RNNs handle sequential data by maintaining memory of previous inputs. This architecture powers applications like speech recognition, language translation and time series forecasting through its temporal processing capabilities.
- Long short term memory (LSTM): LSTMs are advanced RNNs that overcome vanishing gradient problems using specialized memory cells. They are particularly effective for tasks requiring long term dependencies like speech synthesis and predictive text.
- Feedforward neural networks (FNNs): FNNs transmit data in one direction from input to output nodes. These networks perform fundamental tasks like classification and regression, commonly used in credit scoring and customer behavior prediction.
- Single layer perceptron: Single layer perceptron is the simplest neural network with one layer of weighted input-output connections, effective for linearly separable problems and binary classification.
- Multilayer perceptrons (MLPs): MLPs feature multiple hidden layers with nonlinear activation functions. This architecture learn complex patterns and is widely used in applications like speech recognition and fraud detection.
- Radial basis function (RBF) networks: RBF networks use distance based activation functions for pattern recognition. They are useful for function approximation tasks and time-series forecasting.
- Generative adversarial networks (GANs): GANs consist of two competing networks, which are a generator and a discriminator that work together to produce realistic synthetic data. This powerful architecture helps applications like image generation and data augmentation.
- Diffusion models: Diffusion models are generative neural networks that create data by iteratively denoising random noise, widely used for realistic image synthesis and related generative tasks like image generation or audio synthesis.
- Transformer networks: Transformer networks are neural network architectures that use self attention to process entire input sequences in parallel. They excel in language tasks and are widely used in multimodal applications like text, images and audio.
What is the importance of neural networks?
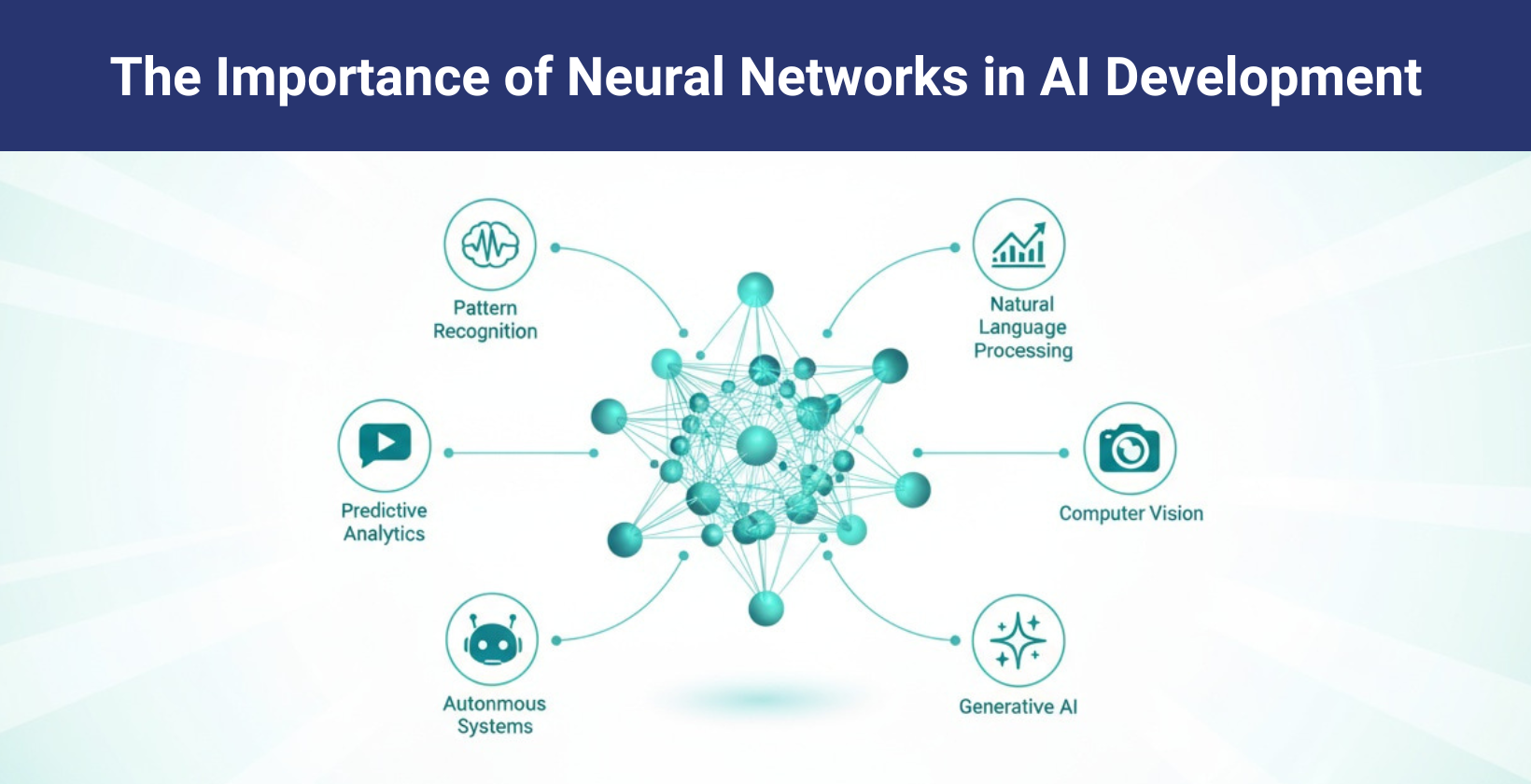
The importance of neural networks lies in their ability to solve complex, non linear problems that traditional algorithms fail to address. Neural networks automate image recognition, speech processing and predictive analytics with high precision by learning directly from data patterns.
Neural networks improve medical diagnostics, financial forecasting and autonomous control by extracting latent features without manual intervention. Neural networks adapt continuously through training that requires no explicit reprogramming in changing environments.
Neural networks process images, text and audio with human level precision, which allows real time translation, fraud detection, virtual assistants and autonomous vehicles. Neural networks form the backbone of modern AI, driving efficiency, scalability and intelligent automation across sectors.
What are the applications of neural networks?
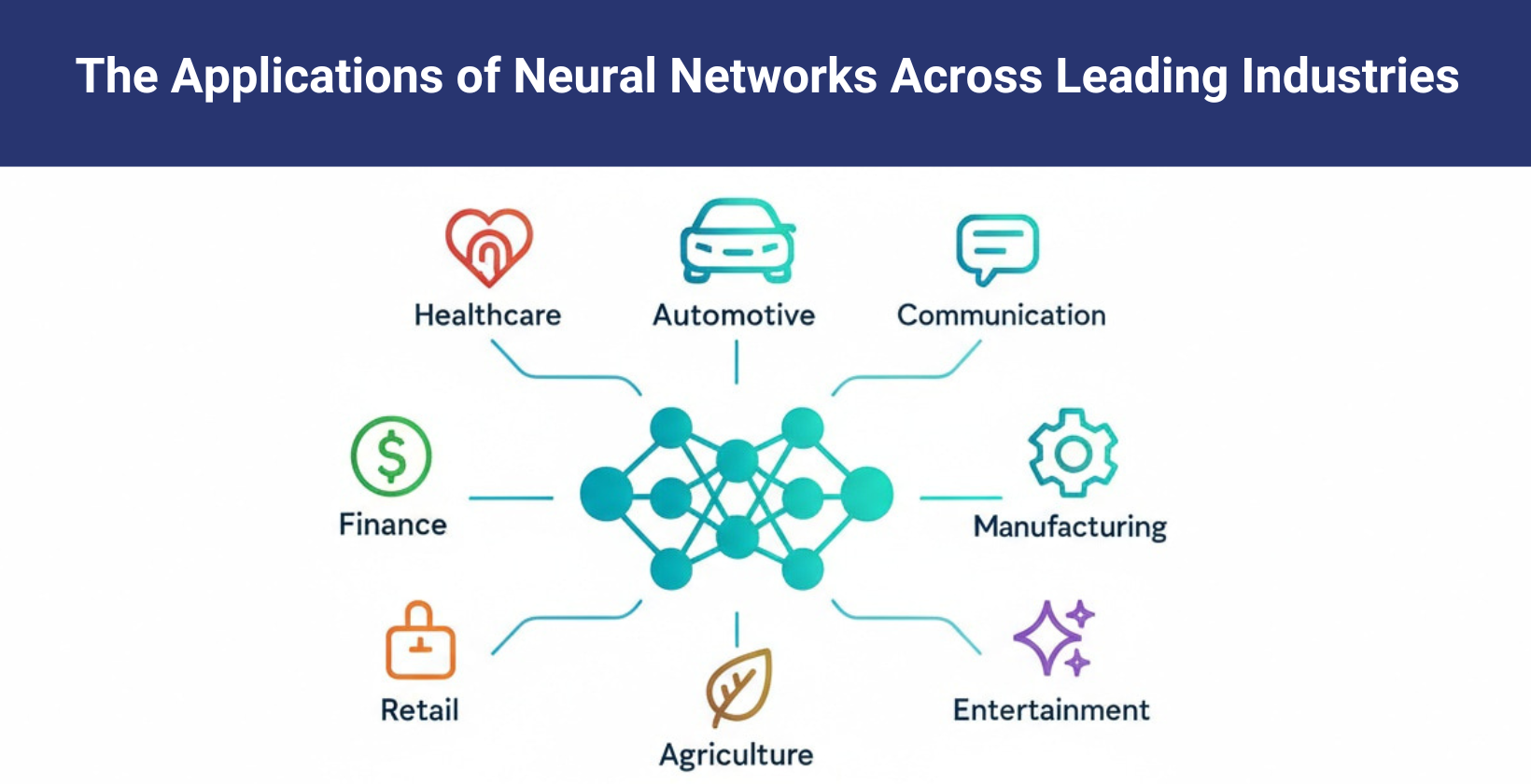
The applications of neural networks include image and speech recognition, natural language processing, generative AI, healthcare and automotive, which offer transformative solutions in technology, business and everyday life.
The use cases of neural networks are given below.
- Image and Speech Recognition: Neural networks power facial recognition systems, medical image analysis, and voice assistants like Siri. CNNs excel at identifying patterns in visual data, while RNNs process speech with human-like accuracy.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Neural networks power chatbots like ChatGPT or Google Gemini, machine translation, sentiment analysis and text summarization, which allows machines to understand, process and generate human language effectively at scale.
- Generative AI: Neural networks create realistic images, videos, music and text that help applications like vosu.ai in digital content creation, artwork, gaming, simulation and personalized media experiences.
- Cybersecurity: Neural networks detect anomalies, prevent intrusions, identify malware and provide adaptive defenses by recognizing suspicious behavior patterns and strengthening digital system security.
- Financial Modeling and Forecasting: Neural networks analyze stock market trends, detect fraudulent transactions, assess credit risks and provide predictive models for portfolio optimization and economic forecasting.
- Business and Marketing: Neural networks drive personalized recommendations on platforms like Amazon and Netflix. They analyze customer behavior to optimize pricing, ad targeting and sales forecasting.
- Healthcare: Neural networks assist in medical image analysis, disease diagnosis, personalized medicine, and drug discovery, which improves accuracy, efficiency and early detection in clinical decision making.
- Automotive: Neural networks drive autonomous vehicles, detect obstacles, recognize traffic signs and improve driver assistance systems that support safety and innovation in smart transportation.
How to train a neural network?
To train a neural network, define its architecture, prepare data, initialize weights, propagate inputs, calculate loss, backpropagate errors, update parameters, iterate learning, evaluate results and tune hyperparameters to achieve optimal performance and generalization.
10 steps to train neural networks are given below.
- Define the network: Specify architecture, layers, activation functions,and connections. This step sets the foundation for how the neural net training process learns patterns from input data effectively.
- Data preparation: Collect, preprocess,and split data into training, validation and testing sets. Proper preprocessing like normalization and augmentation, ensures the neural network training process handles variability effectively.
- Weight initialization: Assign small random weights to network connections. Appropriate initialization prevents vanishing gradients and accelerates convergence, which makes training neural networks more stable during optimization.
- Forward propagation: Pass input data through layers that apply weights and activation functions. The output represents predictions, central to understanding how neural net training models map inputs to outcomes.
- Loss calculation: Compute error between predicted and actual outputs using a loss function. This measure guides training neural networks by quantifying model performance.
- Backward propagation: Distribute error gradients back through the network. This step adjusts weights by calculating partial derivatives, a key mechanism in neural network training optimization.
- Parameter update: Adjust weights and biases using optimization algorithms like SGD or Adam. Continuous weight updates refine predictions throughout training neural networks for better accuracy.
- Iteration: Repeat forward and backward passes across data for multiple epochs. Iterative learning helps neural net training minimize loss while improving generalization.
- Evaluation: Test the trained network on validation or test data. Performance metrics like accuracy, precision and recall reveal effectiveness in training neural networks.
- Hyperparameter tuning: Adjust learning rate, batch size, layer count and regularization methods. Fine-tuning hyperparameters optimizes the neural net training process for better performance and reduced overfitting.
What are the advantages of neural networks?
The advantages of neural networks are their ability to model complex problems, capture non-linear relationships, learn from large datasets and allow smart automation and decision making across various fields like healthcare or finance.
The key advantages of neural networks are given below.
- Non-linear modeling: Neural networks model complex and non-linear relationships that offer solutions for challenges where linear models or simple equations are insufficient.
- Learning from data: Neural networks excel at learning from large datasets, which uncover hidden patterns and insights that traditional methods miss and continuously improve through exposure to new data.
- Adaptability: Neural networks adapt to changes in data or environments by adjusting their parameters, which makes them robust in dynamic situations such as evolving business or medical scenarios.
- Feature extraction: Neural networks automatically extract useful features from raw input data that reduce manual preprocessing and elevate the accuracy of downstream tasks like image or speech recognition.
- Parallel processing: Neural networks support parallel processing, which allows faster computations and efficient handling of extensive data and model training across multiple cores or machines.
- Fault tolerance: Neural networks still produce reasonable outputs even with noisy data or partial system failures, which makes them robust in real-world conditions.
- Automation: Neural networks drive automation by performing repetitive, complex tasks such as image classification or anomaly detection without direct human oversight. This rises productivity in various sectors like automotive, healthcare and finance.
- Generalization: Neural networks generalize learned knowledge to new, unseen data that provide strong prediction capabilities and reduce overfitting when trained correctly.
- Multimodal capabilities: Neural networks integrate multiple input modalities such as text, image and sound, which allow advanced applications like cross-domain search, multimodal translation and smart virtual assistants like Siri, Google Assistant and ChatGPT.
What are the disadvantages of neural networks?
The disadvantages of neural networks include high requirements for training data, substantial computational cost, black box interpretability, risk of overfitting, model complexity, difficulty in explaining results and ethical risks related to synthetic media and misuse.
The disadvantages of neural networks are given below.
- Data requirements: Neural networks require massive amounts of high quality training data to perform effectively, which is unavailable or expensive to acquire for certain applications.
- Computational cost: Neural networks require high processing power, memory and energy, which causes long training times and high costs like small projects cost $5,000 to $50,000 and advanced AI systems $60,000 to $150,000.
- Interpretability: Neural networks work as a black box that makes their predictions hard to understand or justify for important decisions or regulated settings.
- Overfitting: Networks memorize training data patterns rather than learning generalizable features that perform poorly on new, unseen data without proper regularization techniques.
- Complexity and tuning: Neural networks involve complex structures and hyperparameter tuning that demand expert knowledge and ongoing adjustments to avoid suboptimal performance.
- Difficulty in explaining results: Neural networks make outcomes hard to interpret for accountability or legal reasons, which challenges transparency efforts.
- Ethical risks: Neural networks help create realistic synthetic media, which increases deepfake, copyright and misuse concerns. Platforms like Vosu.ai use safety filters and responsible use policies to address these issues.
What is the difference between a neural network and deep learning?
The difference between a neural network and deep learning is that neural networks have a few layers for basic tasks, whereas deep learning uses many layers to solve complex problems and handle large data. Neural networks are simpler and need less computation. Deep learning networks learn features automatically with more data and power.
The differences between a neural network and deep learning are given in the table below.
| Aspect | Neural network | Deep learning |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Consists of an input, hidden and output layer | Contains multiple hidden layers, often more than three |
| Complexity | Less complex, fewer layers | Highly complex with many layers and architectures like CNNs and RNNs |
| Applications | Suitable for simpler tasks | Used for advanced AI tasks like image recognition, natural language processing |
| Training time | Requires less training time | Needs significant training time and powerful hardware |
| Hardware needs | Less demanding | Requires ample power, GPUs and large RAM |
What is the difference between a neural network and a deep neural network?
The difference between a neural network and a deep neural network is that a neural network has a single hidden layer, while a deep neural network contains multiple hidden layers, which makes it deeper and capable of learning more complex patterns.
The difference between a neural network and a deep neural network is given in the table below.
| Aspect | Neural network | Deep neural network |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Usually, one hidden layer | Simpler, fewer layers |
| Complexity | Simpler, fewer layers | More complex, many layers |
| Learning capability | Limited to simpler patterns | Learns complex representations |
| Data processing | Requires manual feature selection | Learns features automatically |
| Application examples | Basic classifications | Image recognition, speech processing |
What is a deep neural network?
A Deep Neural Network (DNN) is an artificial neural network with three or more hidden layers. Its depth allows learning of complex, hierarchical data by transforming features through successive layers. A deep neural network, known as an advanced artificial neural network, is applied in image recognition, natural language processing and speech analysis. It captures intricate patterns in large datasets that confirm accurate predictions and effective decision making across diverse tasks.
What is the difference between a convolutional neural network and a deep neural network?
The difference between a convolutional neural network and a deep neural network is defined by their architecture and use cases. A convolutional neural network (CNN) employs convolutional layers to capture spatial patterns that make it effective for image classification and object detection like facial recognition. A deep neural network (DNN) relies on fully connected layers, suited for general predictive tasks such as natural language processing or credit risk assessment, which show flexibility beyond visual data.
What is the difference between a neural network and a convolutional neural network?
The difference between a neural network and a convolutional neural network is in data processing. A regular neural network, known as a feedforward neural network, connects every neuron in one layer to every neuron in the next layer that handles structured or tabular data. A convolutional neural network (CNN), on the other hand, uses convolutional layers to process grid-like or image data, excels at extracting spatial features and is mainly applied in image classification and computer vision tasks.
Where are convolutional neural networks used in real life?
The practical applications where convolutional neural networks (CNNs) are used in real life are given below.
- Facial recognition: CNNs in facial recognition analyze unique facial features for authentication. These systems power smartphone unlocking (Face ID) and security surveillance with high accuracy.
- Medical imaging: CNNs in medical diagnostics detect tumors in X-rays and MRIs. They assist radiologists by identifying abnormalities faster than traditional methods.
- Autonomous vehicles: CNNs in self-driving cars process camera feeds to identify objects. These systems recognize pedestrians, traffic signs and road conditions in real-time.
- Retail and e-commerce: CNNs in retail allow visual product searches and inventory tracking. They analyze shelf images to automate stock management and recommendations.
- Agriculture: Convolutional neural networks in farming analyze drone captured field images. These systems monitor crop health, detect pests and optimize irrigation schedules.
- Industrial automation: CNNs perform visual inspection, defect detection and predictive maintenance that improve product quality and operational uptime.
- Natural language processing (NLP): CNNs in text processing analyze words as 1D patterns. These models perform sentiment analysis, spam detection and document classification.
- Art and entertainment: CNNs in creative apps transform photos into artistic styles. They apply filters mimicking famous painters like Van Gogh or Picasso.
Are GANs still used today?
Yes, Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) are still used today, though their dominance has waned with the rise of diffusion models. Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) are popular for specific applications like image generation, data augmentation and style transfer due to their ability to produce highly realistic synthetic data, but newer architectures like Stable Diffusion offer better stability and control.
Is ChatGPT a neural network?
Yes, ChatGPT is a neural network because it is built as a large language model based on the transformer neural network architecture. It uses deep learning techniques to process vast amounts of text data, which allows it to generate coherent, context aware responses across diverse topics.