AI algorithms are sets of rules that help machines learn from data, make decisions and solve problems. AI algorithms power everything from voice assistants and self-driving cars to medical tools and fraud detection systems.
AI algorithms follow a simple process, they collect data, clean and organize it, spot patterns and make predictions or decisions. This process helps AI systems improve in accuracy and performance over time through continued use.
There are 4 main types of AI algorithms including supervised learning, unsupervised learning, semi supervised learning and reinforcement learning. Each AI algorithm processes data and applies it to different tasks such as classifying images or recommending products.
Popular AI techniques include machine learning, deep learning, natural language processing (NLP), computer vision and generative AI. AI techniques allow AI systems to understand speech, recognize faces, write text and much more.
AI algorithms are transforming industries, they help businesses make better decisions, improve customer experiences and automate complex tasks. Emerging technologies like quantum AI and advanced deep learning are pushing these capabilities, which makes AI faster, smarter and more reliable.
What are AI algorithms?
AI algorithms are step by step computational methods that enable machines to learn from data, make decisions and solve problems without explicit human instructions.
AI algorithms adapt, improve themselves through learning and process large volumes of data to handle tasks like automation, problem solving and decision making. These include decision trees, neural networks, support vector machines, k means clustering and reinforcement learning, which power systems such as search engines, image recognition and spam filters.
How do AI algorithms work?
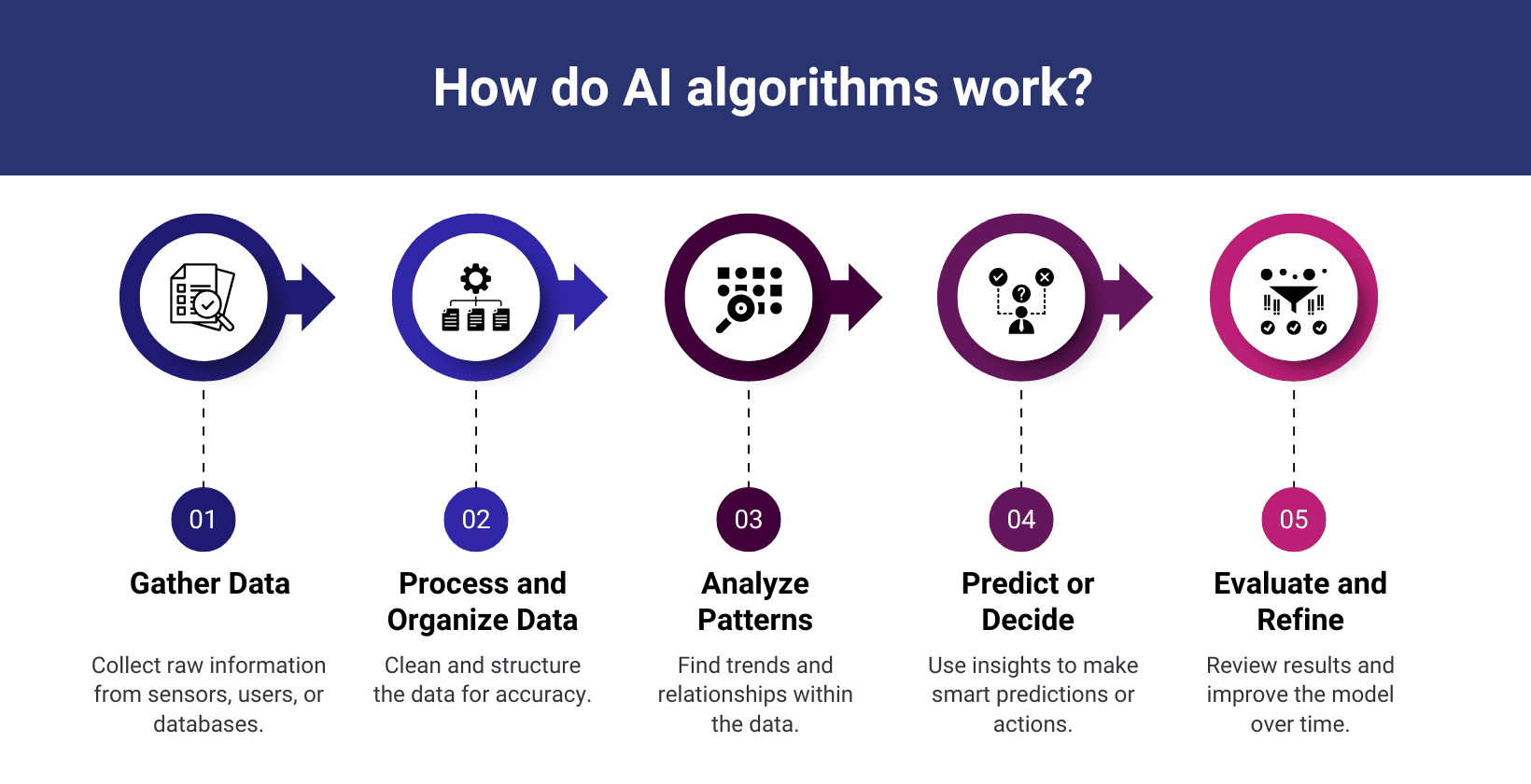
AI algorithms process data through 5 steps to identify patterns, recognize behaviors and make predictions.
5 steps of how AI algorithms work are explained below.
- Gather data: AI algorithms gather large volumes of raw data from different sources such as sensors, user inputs, or databases to define the problem space and prepare the foundation for intelligent decision making.
- Process and organize data: AI algorithms process and organize collected data. They remove inconsistencies, fill in missing values and structure the dataset to ensure accuracy and reliability during analysis.
- Analyze patterns: AI algorithms analyze the prepared data thoroughly to detect hidden patterns, identify meaningful trends and uncover relationships that help in understanding user behavior or system performance.
- Predict or decide: AI algorithms apply discovered patterns and knowledge to make accurate predictions or choose the most appropriate actions that solve specific tasks.
- Evaluate and refine: AI algorithms evaluate the outcomes of their decisions against expected results, identify errors and refine their internal models continuously to improve performance in future operations.
The working process of AI algorithms is visualized below.
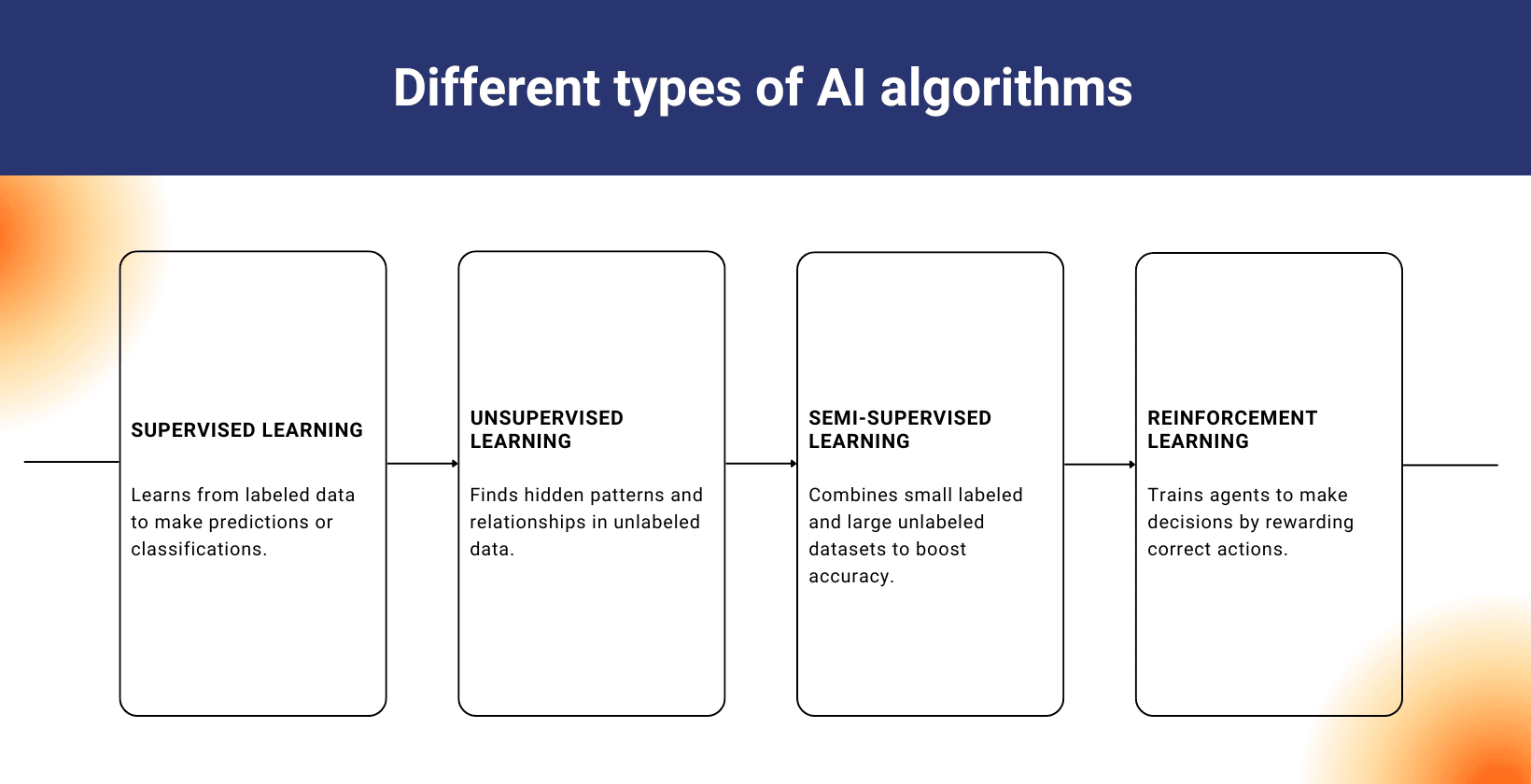
What are the different types of AI algorithms?
There are 3 main types of AI algorithms including supervised learning, unsupervised learning and reinforcement learning, with semi-supervised learning and transformer-based models also being major categories.
Top 5 types of AI algorithms are given below.
1. Supervised learning
Supervised learning algorithms use labeled data to train a model to make predictions or classify inputs based on learned patterns. Supervised learning algorithms are used in tasks like image classification, fraud detection and recommendation systems. Supervised learning algorithms perform two main types of tasks including classification (categorizing data) and regression (predicting continuous values).
The 6 types of supervised learning algorithms are listed below.
- Logistic regression
- Linear regression
- Decision trees
- Random forests
- Neural networks
- Support vector machines (SVM)
2. Unsupervised learning
Unsupervised learning algorithms analyze unlabeled data and find patterns or relationships without prior guidance. Unsupervised learning algorithms hide structures, group data points and reduce data dimensions for better understanding.
The common types of unsupervised learning include.
- Cluster algorithms (K means clustering, gaussian mixture model)
- Anomaly detection
- Association rule learning (Apriori algorithm)
- Dimensionality reduction (principal component analysis, PCA)
3. Semi supervised learning
Semi supervised learning algorithms use a small set of labeled data and a large set of unlabeled data to boost learning accuracy. Semi supervised learning algorithms first train on the labeled data, then refine the model with the unlabeled data to find patterns and improve predictions. This method connects supervised and unsupervised learning, cuts labeling costs and increases performance. Semi supervised learning is useful in areas like image classification and speech recognition, where labeled data remains limited but unlabeled data is available.
4. Reinforcement learning
Reinforcement learning algorithms train an agent to make decisions and take actions in a situation to earn maximum rewards. The agent learns through trial and error, receives rewards or penalties as feedback and improves its decision policy over time. The main types of reinforcement learning algorithms include model based, policy based and value based methods. Developers use these algorithms in robotics, games, autonomous vehicles and resource management in any situation.
5. Transformer-based models
Transformers are now core AI algorithms that power breakthroughs in natural language processing, computer vision, and multimodal systems. AI models such as BERT, GPT and Vision Transformers (ViTs) use self-attention mechanisms to process vast amounts of text, images or video data efficiently which makes them central to modern AI applications.
Transformer-based AI models and their applications are visualized below.
What are the techniques used in AI algorithms?
The techniques used in AI algorithms include neural network modeling, diffusion-based methods such as Stable Diffusion and Imagen, as well as general diffusion models. They also encompass decision tree induction, Bayesian inference, reinforcement learning frameworks, genetic algorithm search, and natural language parsing. Additional approaches include probabilistic graphical modeling, knowledge graph construction, and clustering analysis for identifying patterns and relationships in complex datasets.
The techniques used in AI algorithms are explained below.
- Neural network modeling: AI algorithm models neural networks with layered artificial neurons to detect complex patterns in image classification and speech recognition.
- Stable diffusion: A text-to-image diffusion AI model generating high-quality artwork from prompts, balancing creativity, realism and efficient open-source accessibility.
- Imagen (Google): Google’s diffusion-based text-to-image AI model emphasizing photorealism, detail and natural language understanding for highly accurate image generation.
- General diffusion models: Probabilistic generative AI models that iteratively refine noise into structured data, enabling realistic image, video and multimodal content creation.
- Decision tree induction: AI algorithm induces decision trees to divide datasets into hierarchical branches for clear, rule based predictions.
- Bayesian inference: AI algorithm uses bayesian inference to update probabilistic beliefs and make informed decisions under uncertainty.
- Reinforcement learning frameworks: AI algorithm drive reinforcement learning through rewards that guide agents to optimal behaviors in dynamic environments.
- Genetic algorithm search: AI algorithm conducts genetic search by evolving solutions with selection, mutation and crossover for optimization tasks.
- Natural language parsing: AI algorithm parses natural language to analyze sentence structure and enhance understanding in chatbots and translation tools.
- Probabilistic graphical modeling: AI algorithm constructs probabilistic graphical models to map variable dependencies and support structured inference.
- Knowledge graph construction: AI algorithm creates knowledge graphs to represent entities and relationships for semantic search and intelligent queries.
- Clustering analysis: AI algorithm performs clustering analysis to group unlabeled data and identify hidden patterns for anomaly detection.
What are the uses of AI algorithms?
The uses of AI algorithms enable machines to perform tasks that require intelligence such as data analysis, pattern recognition, prediction and automated decision making across various domains.
The applications of AI algorithms are given below.
- AI algorithms analyze data and detect patterns in complex datasets.
- AI algorithms make decisions and build predictive models for accurate forecasts.
- AI algorithms identify objects and interpret human speech in real time.
- AI algorithms understand language and respond through chatbots and assistants.
- AI algorithms detect fraud and protect systems against cyber threats.
- AI algorithms suggest products and content on e-commerce platforms.
- AI algorithms drive vehicles and control robots in dynamic environments.
- AI algorithms diagnose illnesses and discover new drugs in healthcare.
- AI algorithms target audiences and improve results in marketing campaigns.
- AI algorithms manage inventory and optimize routes in supply chains.
How do emerging AI algorithms shape future applications?
Emerging AI algorithms shape future applications as they automate tasks, personalize experiences and optimize processes across industries. Advanced deep learning models, machine learning techniques, generative AI and quantum AI lead this transformation. Emerging AI algorithms deliver accurate predictions, improve user experiences and create innovative solutions in healthcare, transportation, cybersecurity and creative sectors. It also increases efficiency, supports scalability and promotes sustainability.
Are AI algorithms used to detect cyber attacks?
Yes, AI algorithms are used to detect cyber attacks by analyzing large volumes of network, user and system data to identify patterns and anomalies that indicate threats. AI algorithms use machine learning and deep learning to spot unusual behavior, automate threat detection and respond to incidents in real time. It reduces response times and outperforms traditional methods. This proactive and adaptive approach helps organizations predict, prevent and stop cyber attacks as threats change.
How do AI algorithms enhance virtual reality?
AI algorithms enhance virtual reality based on user movements and behavior. AI algorithms recognize objects, power avatars with AI, predict motion, apply cognitive computing and interpret emotions. These techniques create intelligent NPCs and deliver personalized experiences that respond fast, which improves design, simulation and interaction within VR worlds.
What is a hybrid approach in AI algorithms?
A hybrid approach in AI algorithms is a combination of machine learning, symbolic AI and rule based systems to use the strengths of each for more robust and adaptable solutions. It integrates data driven models with logical reasons to improve accuracy, flexibility and explainability.
Examples of hybrid approaches include semi supervised learning, model based reinforcement learning and systems like Google’s search engine that combine deep learning with symbolic knowledge graphs.
In 2025, hybrid AI systems increasingly combine neural networks with symbolic reasoning (neuro-symbolic AI) and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG). These approaches improve explainability, allow grounding in external knowledge bases and make AI outputs more reliable and context aware.
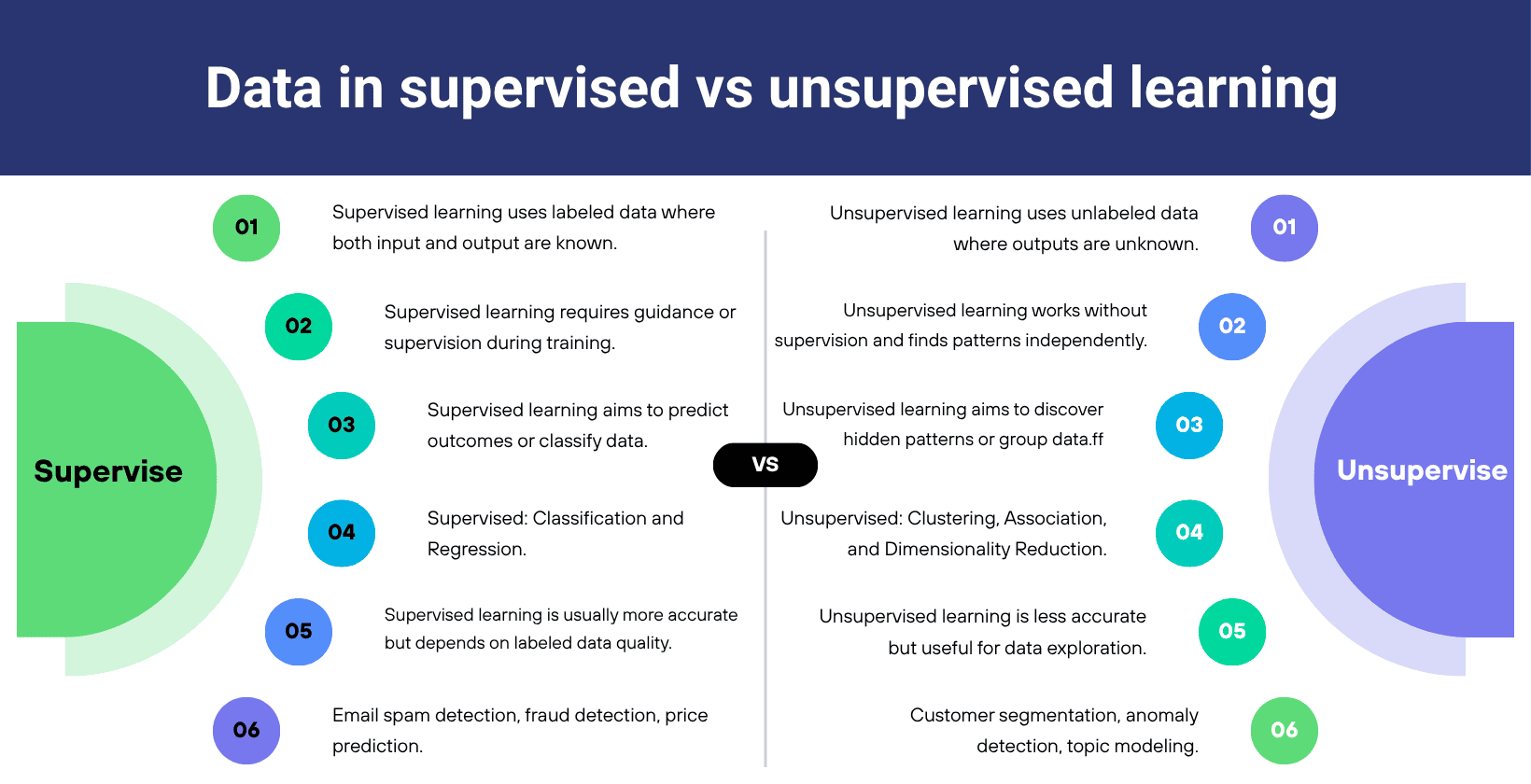
What is the difference between supervised and unsupervised learning?
Supervised learning uses labeled data to make predictions or classifications and unsupervised learning analyzes unlabeled data to find patterns or groupings. Supervised learning requires human supervision and solves tasks like regression and classification. Unsupervised learning works without labels and handles clustering, association and dimensionality reduction. Supervised methods deliver higher accuracy but depend on labeled data, whereas unsupervised methods explore raw data and support discovery.
The difference between supervised and unsupervised learning is visualized below.
What is a minimax algorithm in AI?
The minimax algorithm in AI is a decision making method that selects the best move in a two player game. It maximizes the AI's gain and minimizes the opponent's advantage.
The minimax algorithm constructs a game tree and recursively evaluates all possible moves. At "max" nodes and select the move that gives the highest score to the AI. At "min" nodes, the minimax algorithm assumes the opponent chooses the move that gives the lowest score to the AI. The minimax algorithm ultimately chooses the move that leads to the best possible outcome for the AI.
Can we make AI algorithms explainable?
Yes, we can make AI algorithms explainable through explainable AI (XAI), which develops techniques to clarify the AI decision making process and connect complex algorithms and human comprehension. XAI provides methods to make AI models transparent and interpretable. It allows users to understand how and why decisions are made, which is important for trust, accountability and improves AI systems in specific applications.
What is the difference between AI and algorithms?
The difference between AI and algorithms is that an algorithm is a fixed set of instructions designed to solve a specific problem and produce the same output for given inputs. AI refers to systems that use algorithms to learn from data, adapt and make decisions that mimic human intelligence. AI modifies its behavior based on new data and handles complex, unstructured tasks, whereas algorithms follow predefined rules and do not learn or adapt. AI involves multiple algorithms working together to achieve intelligent behavior.
Can AI create algorithms?
Yes, AI can create algorithms because machine learning techniques allow AI systems to generate and optimize algorithms for specific tasks and discover patterns in data without detailed human programming. AI improves and adapts algorithms on its own through repeated cycles, enhances performance and solves complex problems with greater efficiency.
What are the challenges in AI algorithm implementation?
The challenges in AI algorithm implementation include poor data quality, algorithmic bias, ethical concerns, high costs and integration into systems. Poor quality or limited data lead to inaccurate or biased results. Algorithmic bias and ethical concerns raise the need for fairness and transparency. AI developers struggle to integrate new systems with existing infrastructure and the costs for the right infrastructure and skilled experts is high. Navigating these challenges is key to using AI effectively and responsibly.
Are genetic algorithms a form of AI?
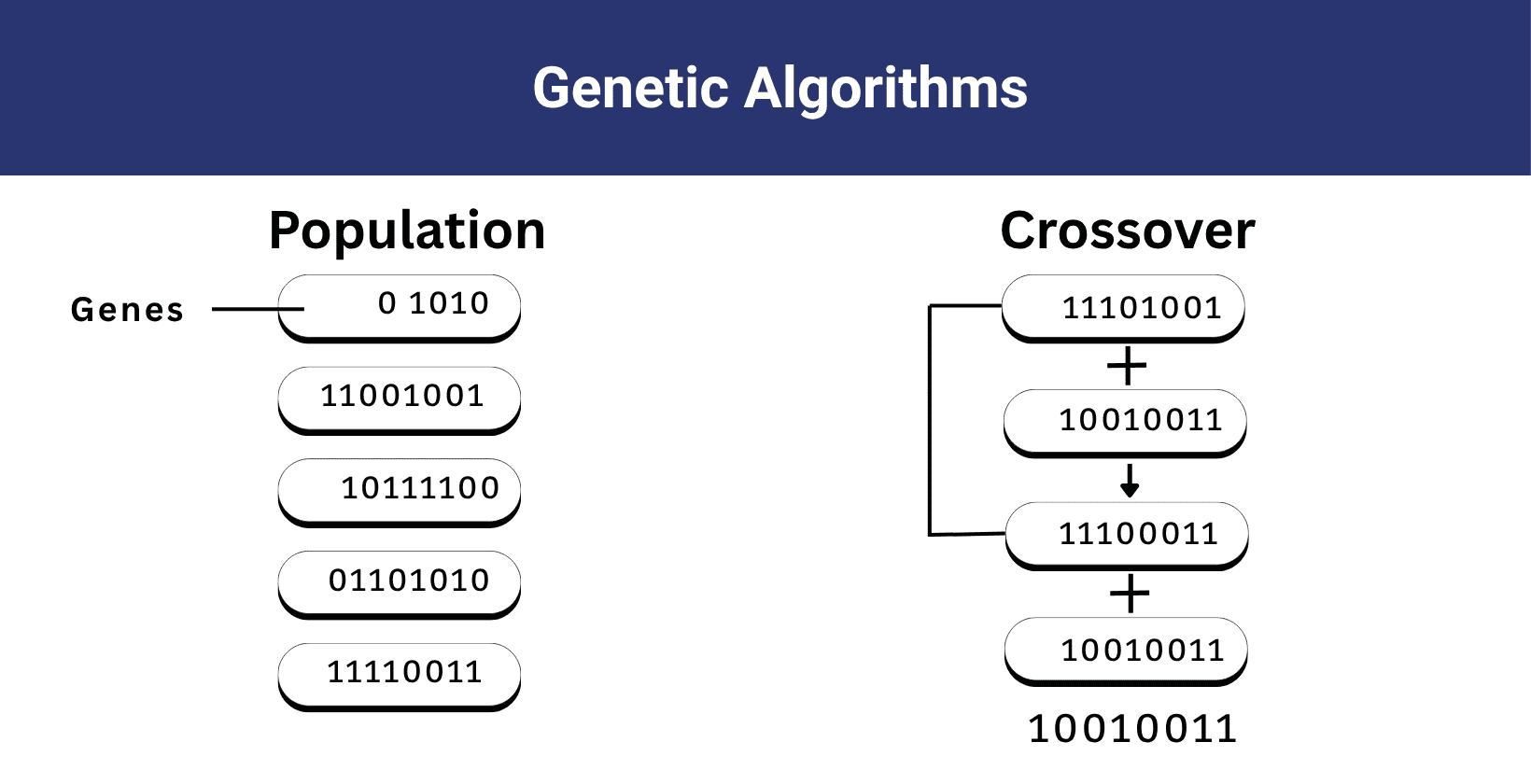
Yes, genetic algorithms are a form of AI because they mimic biological evolution and use selection, crossover and mutation to generate and improve solutions to difficult problems like traveling salesman problem or timetabling problems. Genetic algorithms belong to artificial intelligence and machine learning and they solve problems by applying principles of natural selection to find optimal or near optimal solutions.
The working principle of genetic algorithms in AI is visualized below.