Generative AI is a form of artificial intelligence that uses machine learning models to generate new content such as text, images, audio, or videos, based on the data it has been trained on. There are 7 types of generative AI, each with a distinct method to create new text, images, sounds or data. These types of generative artificial intelligence focus on how models build, refine and produce new content. Each method has unique strengths for handling text, images, 3D scenes or sequences.
7 main types of generative AI are given below.
- Generative adversarial networks (GANs): GANs use two networks, one creates fake data and the other checks if it is real. They improve through back and forth training. GANs create images, videos, art and deepfakes.
- Variational autoencoders (VAEs): VAEs compress data into simpler forms, then rebuild it. They spot important patterns and use them to make new or cleaned up content. VAEs work well for noise removal, pattern discovery and data generation.
- Diffusion models: Diffusion models add noise to real data and learn how to remove it step by step. They use this skill to create high quality images from random noise. They are popular in image tools and visual design.
- Autoregressive models: Autoregressive models predict the next item in a sequence by using earlier ones. They create content like sentences, audio or code line by line. They follow a clear logic, but slow down with longer data.
- Neural radiance fields (NeRFs): NeRFs build 3D scenes from 2D photos and map how light behaves at every point in space to create lifelike images. NeRFs help in 3D modeling, object scans and digital worlds.
- Large language models (LLMs): LLMs understand and write text by learning from books, websites and documents. They answer questions, write content, translate and help in research.
- Flow models: Flow models turn simple data into complex forms using step by step changes. They also reverse the process to trace data back to its source. They are accurate, fully reversible and useful in scientific work and analysis.
1. Generative adversarial networks (GANs)
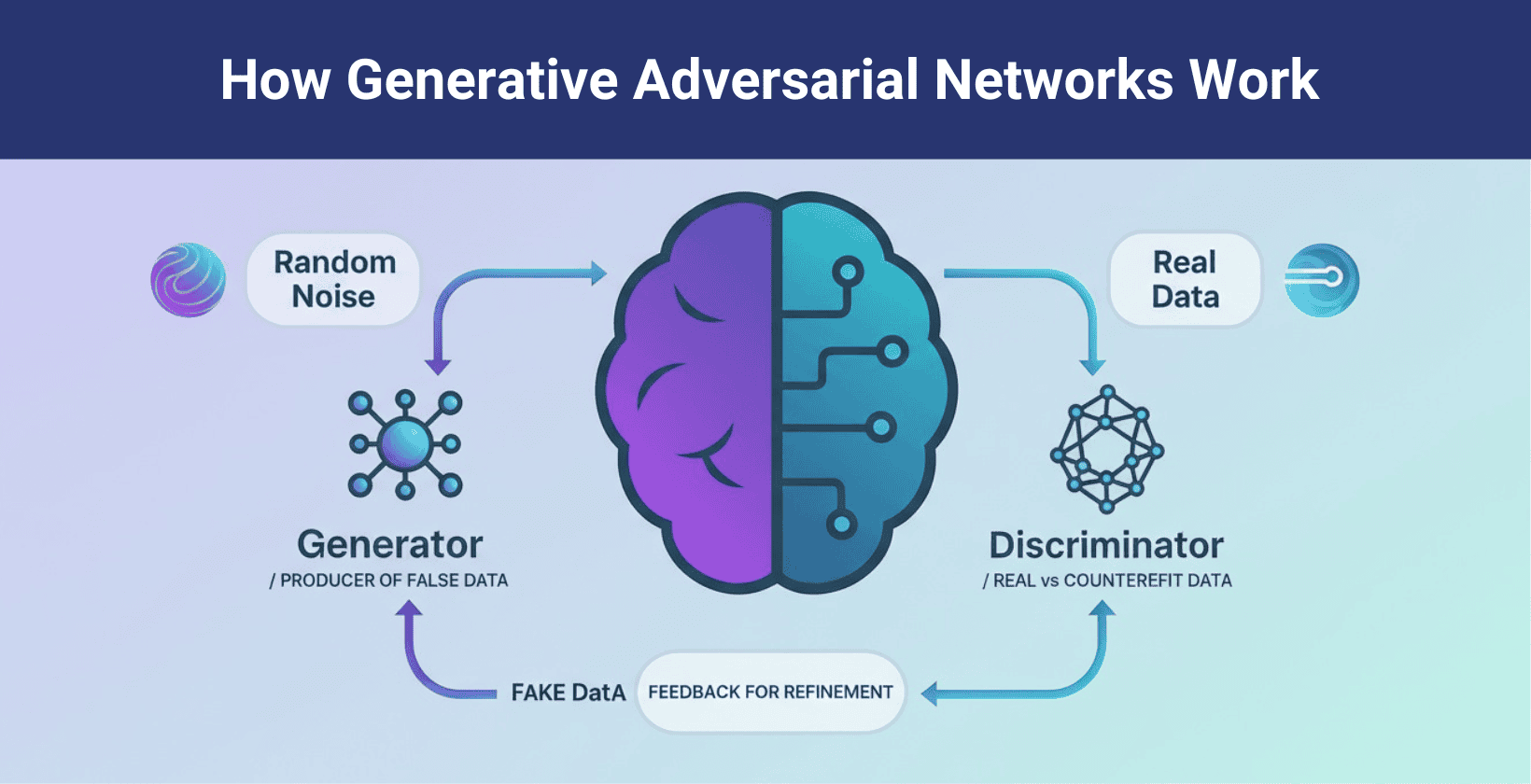
Generative adversarial networks (GANs) are deep learning models that use two neural networks. They were introduced by Ian Goodfellow in 2014 and marked a major breakthrough in generating realistic images, audio and other data. The generator creates synthetic data and the discriminator evaluates its realism. GANs operate as the generator creates data, such as images and the discriminator checks if each sample is real or fake**.** Both networks improve through competition until the generated data matches real examples.
Generative adversarial networks (GANs) learn from unlabeled datasets, create realistic samples and refine results through adversarial training. This competitive process enables applications in image synthesis, super resolution and artistic content generation. It supports video prediction, medical data augmentation and the creation of new digital assets for games and films.
Generative adversarial networks (GANs) face challenges such as unstable training, mode collapse and high computational requirements. They pose ethical risks like the creation of deepfakes and other misleading visual content. Responsible implementation requires careful network design, strong evaluation metrics and safeguards against misuse.
2. Variational autoencoders (VAEs)
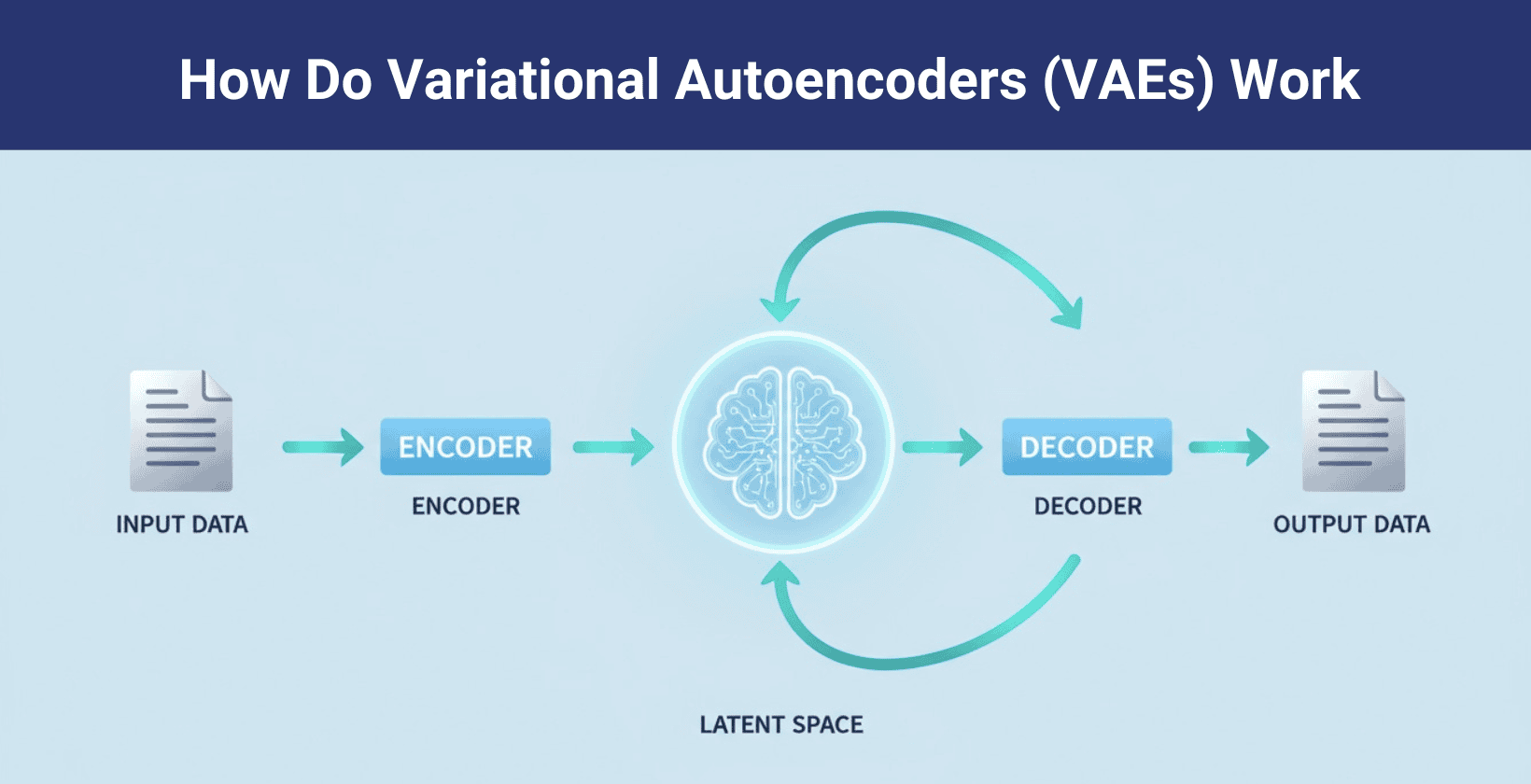
Variational autoencoders are artificial neural networks that simplify complex data into smaller, useful patterns. They were created in 2013 as a generative model for producing new data that turns input data into a compact format called a latent space. This helps the model understand and recreate important features of the original data.
VAEs use two parts, an encoder and a decoder. The encoder studies the input and turns it into two values. These values describe a pattern, not a fixed point. The decoder then uses this pattern to rebuild the original input or make something new.
VAEs compress and recreate data using probability based models. They learn key patterns and represent inputs as statistical values which allows them to rebuild or create new samples. This method improves variety in output and helps the model handle unseen data more effectively.
VAEs generate images and text, detect unusual patterns and remove noise from corrupted inputs. They produce more flexible and diverse results than standard autoencoders. This advantage makes VAEs useful for creative tasks and data analysis.
3. Diffusion models
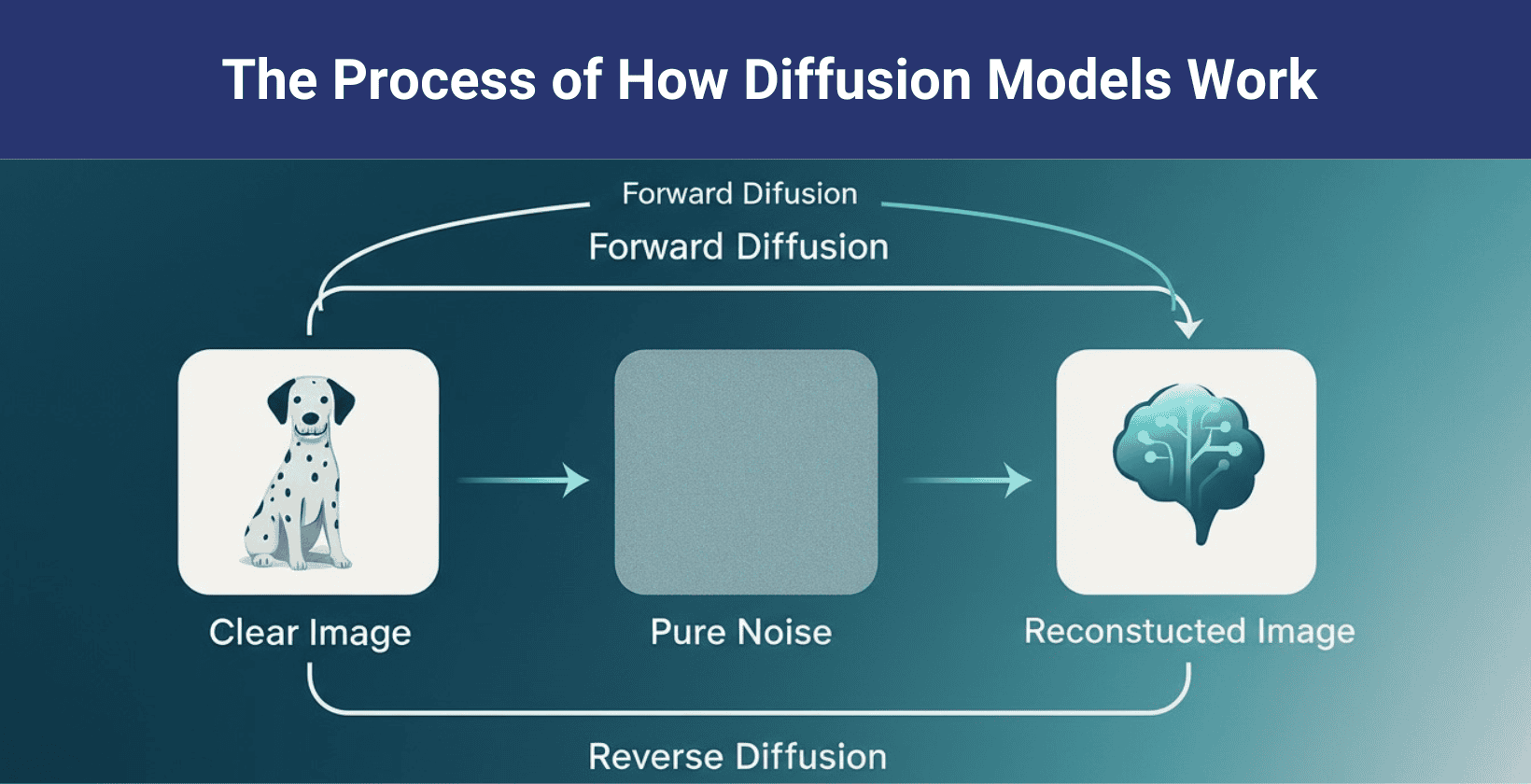
A diffusion model is a generative model that creates new data by reversing a process that gradually adds random noise to training data. They were introduced in 2015 and powered breakthroughs like DALL-E 2, Stable Diffusion, Midjourney and Google’s Imagen by 2020 to generate data by iteratively adding and removing noise, and the process starts by adding noise to real data following a fixed, step by step procedure, which hides the original details. This part is the forward diffusion process. The reverse diffusion process starts with noise and removes it step by step to recover or create an image. The model handles each step as a Markov chain, so each step depends only on the one before it.
Diffusion models include latent variable models that reveal hidden patterns in data.
They use denoising methods to remove noise and restore the original structure.
Diffusion models support tasks such as image generation, audio synthesis and computer vision. The process creates high quality images and restores damaged ones, which makes diffusion models valuable for creative and repair tasks.
4. Autoregressive models
An autoregressive model is a type of predictive model that forecasts the next element in a sequence by using the values of previous elements. Generative AI history involves key developments across decades and it started with early neural networks in the 1950s and 1960s and advanced through recurrent and long short-term memory networks in the 1980s and 1990s. Each prediction uses a rule based on conditional probability and depends on previously seen values. Autoregressive models include examples of AR (Autoregressive) models and ARIMA (Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average).
Autoregressive models work by breaking down sequential data into small steps. The model uses previous values to decide each next value. This setup allows accurate sequential prediction when previous elements give strong clues about what comes next.
Autoregressive models perform well with sequential data and provide clear prediction logic. They slow down when fast predictions are needed, since each step depends on the last. They also allow errors to build up over long sequences.
5. Neural radiance fields (NeRFs)
A neural radiance field (NeRF) is a neural network based model that generates photorealistic 3D scenes by learning to represent volume density and color from multiple 2D images. They were first introduced by Mildenhall et al. in 2020, and it is a relatively young field in generative AI. Since then, the technology has rapidly advanced, with over 620 papers published and more than 250 related repositories on GitHub by December 2023. The model learns a radiance field that maps color and transparency to every point in space. Volumetric rendering allows the model to produce images from any angle by simulating light passing through the 3D scene.
Neural radiance fields encode spatial and view directions to create patterns the network understands. Hierarchical volume sampling directs the model to key scene areas and preserves critical detail. The neural network processes each camera ray and calculates the color and density along the ray’s path in the scene.
Neural radiance fields work with a fully connected network. The network takes in a 3D position and a 2D view direction, which produces output that describes how much light appears at that spot from a given angle. Applications create 3D environments, reconstruct objects, improve medical scans and generate computer graphics scenes.
6. Large language models (LLMs)
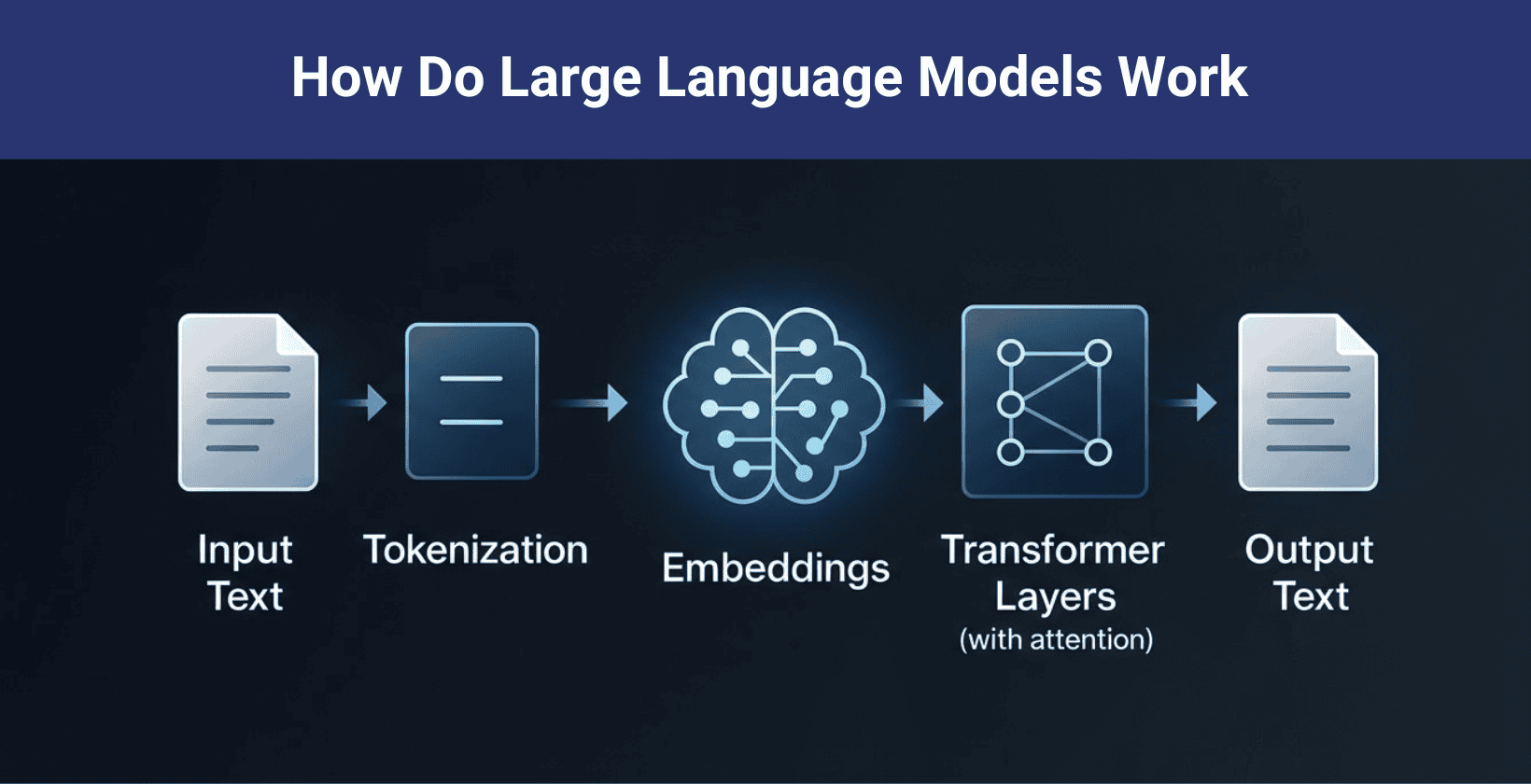
Large language models (LLMs) are generative AI that learn from huge collections of written text to produce clear and natural language. Examples include GPT 3, ChatGPT and BERT. These models handle questions, summarize articles, translate between languages and power chatbots for digital assistants.
Large language models (LLMs) in generative AI evolved from early natural language processing research beginning in the 1950s, with major breakthroughs occurring in the 2010s through the integration of neural networks and transformer architectures. A key milestone was Google's BERT model in 2019, followed by OpenAI’s GPT-2 in 2019, GPT-3 in 2020 and GPT-4 with around one trillion parameters.
LLMs train on vast books, articles and internet texts so that they recognize patterns, grammar and context. Capabilities cover conversation, text creation, code suggestion, translation and document review. LLMs make chatbots smarter, help teams create content, improve virtual support and speed up research, though challenges like bias and accuracy persist.
7. Proprietary diffusion models
Proprietary diffusion models are generative AI systems developed and controlled by a private company or group, with restricted access to their architecture, weights and training data. They use deep neural networks to add noise to data and then systematically remove it, which generates new high quality content.
Proprietary diffusion model examples include Flux, Veo, Imagen, OpenAI’s DALL-E and Midjourney. Proprietary diffusion models key characteristics include high quality data generation, noise adding and removal processes, neural network based architecture, stable training, scalability and controlled access. They are used in image generation, art creation, video synthesis, medical imaging, drug discovery, synthetic data production and autonomous system design.
What is a generative AI model?
A generative AI model is an artificial intelligence system that creates new content by learning patterns and structures from existing training data. Examples include GPT 3 for text, DALL E for images and diffusion models for image and video creation. These AI models go beyond traditional machine learning by content creation, handling different formats like text, images, videos or code rather than just making predictions or classifications, according to MIT Sloan experts.
Generative AI models absorb massive training collections to find hidden relationships. They use those patterns to generate new and realistic outputs in language or visuals. These models boost creativity, automate tasks and quickly produce quality results in content, art and research. Flow models, as a type of generative AI, offer exact data mapping, transparent steps and simple control over the creation process.
According to MIT Sloan experts, generative AI goes beyond traditional machine learning by generating novel content such as text, images, or videos rather than just making predictions or classifications.
Is ChatGPT a generative AI model?
Yes, ChatGPT is a generative AI model that uses a large language model (LLM) to create human like text based on user prompts. ChatGPT is built upon OpenAI's generative pre-trained transformer (GPT) architecture, pre-trained on massive text data and fine-tuned with reinforcement learning, enabling it to generate coherent, natural language responses, according to Coursera, thus confirming it is generative AI.
What is one of the most widely used generative AI models?
One of the most widely used generative AI models is GPT, which comes from OpenAI , according to OpenAI's official statistics. GPT supports text generation, conversational AI and programming help. Many people use GPT in chatbots, content creation and virtual assistants because it produces detailed, human like responses and adapts well to many topics. Its popularity grows as more services use GPT for realistic conversation and smart automation.
What are the common applications of generative AI?
The common applications of generative AI are given below.
- Content creation: Generative AI enables text-to-image, image-to-image, image effects, text-to-video, image-to-video, consistent characters, product URL-to-video, video-to-lip-sync and video effects on platforms like Vosu.ai with top AI models (Luma, Recraft, Minimax, Haiper, Hunyuan, Flux, Ideogram, Kling, DeepMind, PixVerse, Runway, Vidu).
- AI avatars creation: Generative AI is used on platforms like Vosu.ai to create AI twins, influencers and talking realistic and dynamic AI avatars for virtual environments, gaming and online interactions.
- AI Voice cloning & music generation: Generative AI models can synthesize natural sounding voice clones for voiceovers and music generation on platforms like Vosu.ai.
- 3D and NeRF powered environment: Generative AI helps produce immersive 3D environments and Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) powered visuals for virtual reality, gaming and training simulations. This enables the creation of realistic, interactive worlds that adapt dynamically.
- Marketing and advertising: Generative AI is widely used in marketing to produce personalized content such as text, images and videos tailored to target audiences.
- Automated tasks: Generative AI speeds up automated task processes in finance and healthcare, which cuts manual work and errors.
- Enhance existing processes: Generative AI improves decision making and analysis by providing accurate data insights and predictions.
What are the limitations of Gen AI?
The limitations of generative AI are given below.
- Lack of understanding and reasoning: Generative AI does not truly understand information and cannot perform deep human like reasoning.
- Biases and inaccuracies: Generative AI produces biased, hallucinated or incorrect information based on its training data.
- Context and complexity: Generative AI handling complex or nuanced situations often leads to mistakes or oversimplified answers.
- Potential for misuse: Generative AI creates misleading content or is used unethically.
- Copyright Lawsuits: Generative AI faces a growing wave of copyright infringement lawsuits globally.
- Security Risks: Generative AI introduces new security risks, including prompt injection attacks where malicious users exploit model input mechanisms to manipulate outputs or evade controls.
- High computational costs: Generative AI requires large computing power resources and energy costs for training and running these models.
- Ethical implications: Generative AI raises concerns around privacy, fairness and maintaining ethical principles.
What is bias in generative AI?
Bias in generative AI means unfair or skewed outputs caused by data or design. It affects the accuracy and fairness of results. Types of bias include training data bias, algorithmic design bias and user interaction bias. They each influence AI behavior differently. Understanding bias helps improve AI fairness and reliability.
Is genAI unethical?
No, generative AI is not unethical by itself, its ethical impact depends on design decisions and user application. Generative AI raises concerns related to bias, privacy and misuse. Ethical use requires transparent development, strict oversight and well defined guidelines. Gen AI ethics, according to Denis Potemkin (a technology analyst), are compared to factory farming, which he calls 'a priori unethical' because it relies on mass scraping of data and content without user consent, similar to how factory farmed meat involves suffering and ethical compromises.
What is the future of generative AI?
The future of generative AI transforms work by automating tasks and boosting productivity. It will revolutionize creativity in art, writing and design. Technology advances improve accuracy and integration with tools. Generative AI faces challenges like bias and ethics, requiring responsible use to ensure trust and fair outcomes.
The future of generative AI in 2025 is characterized by several key trends, including the rise of multimodal models, increasing enterprise adoption, growing regulatory frameworks and the integration of generative AI into creative platforms. Multimodality leads innovation, with platforms like Vosu.ai integrating text, images, video, audio and avatars into unified creative workflows. Community driven growth accelerates adoption, demonstrated by Vosu.ai’s large user base and active social engagement, fostering collaboration. Enterprise adoption has evolved from trial phases to embedding AI deeply within marketing, production, customer service and content creation processes. Meanwhile, regulatory frameworks such as the EU AI Act and U.S. AI Safety Institute efforts, alongside ongoing copyright litigation, are establishing ethical, transparent and intellectual property focused guidelines for responsible AI use.
The global generative AI market is projected to reach approximately USD 37.89 billion in 2025 and is expected to grow to around USD 1,005.07 billion by 2034, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 44.20% from 2025 to 2034, according to Precedence Research.

